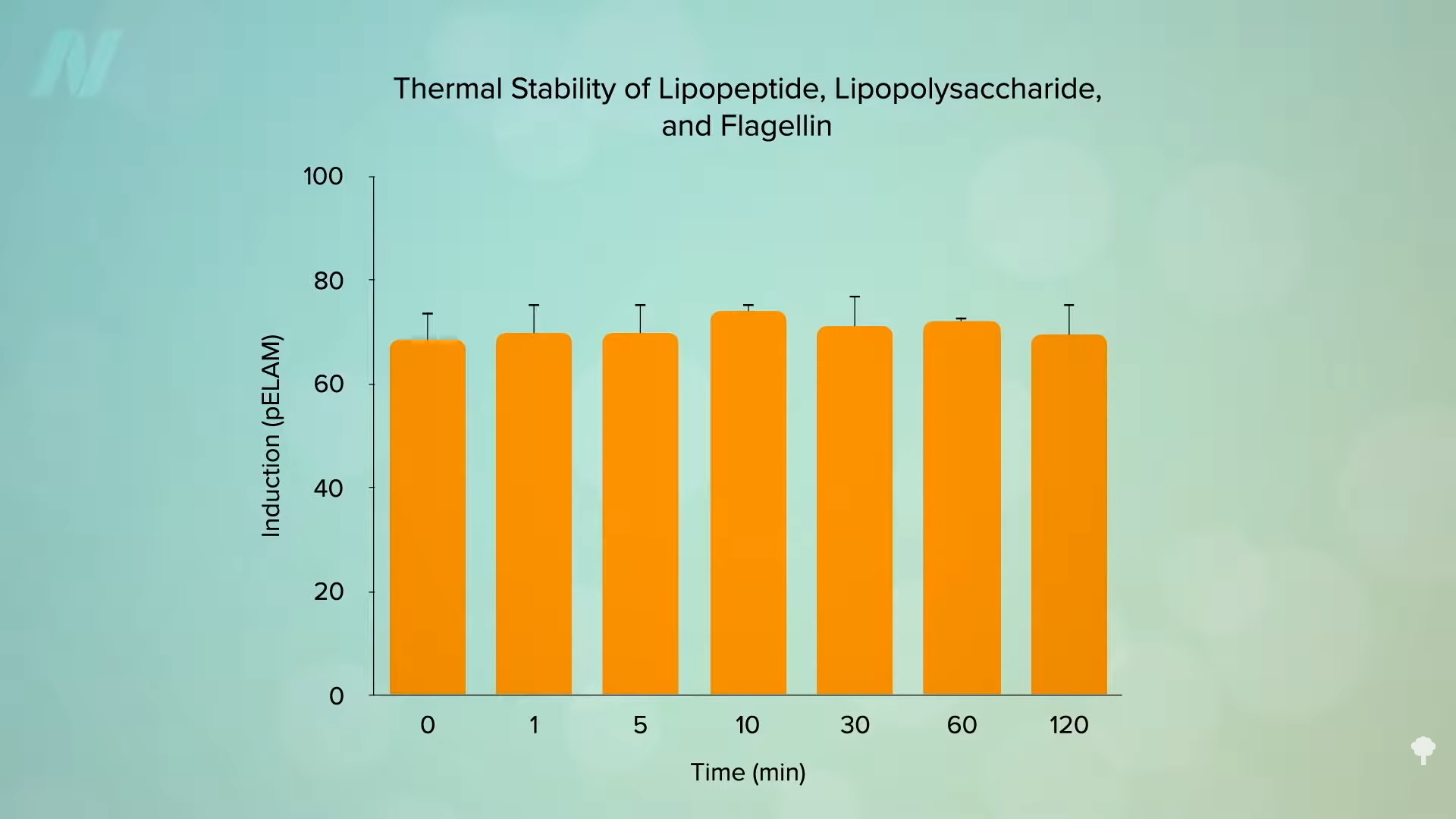
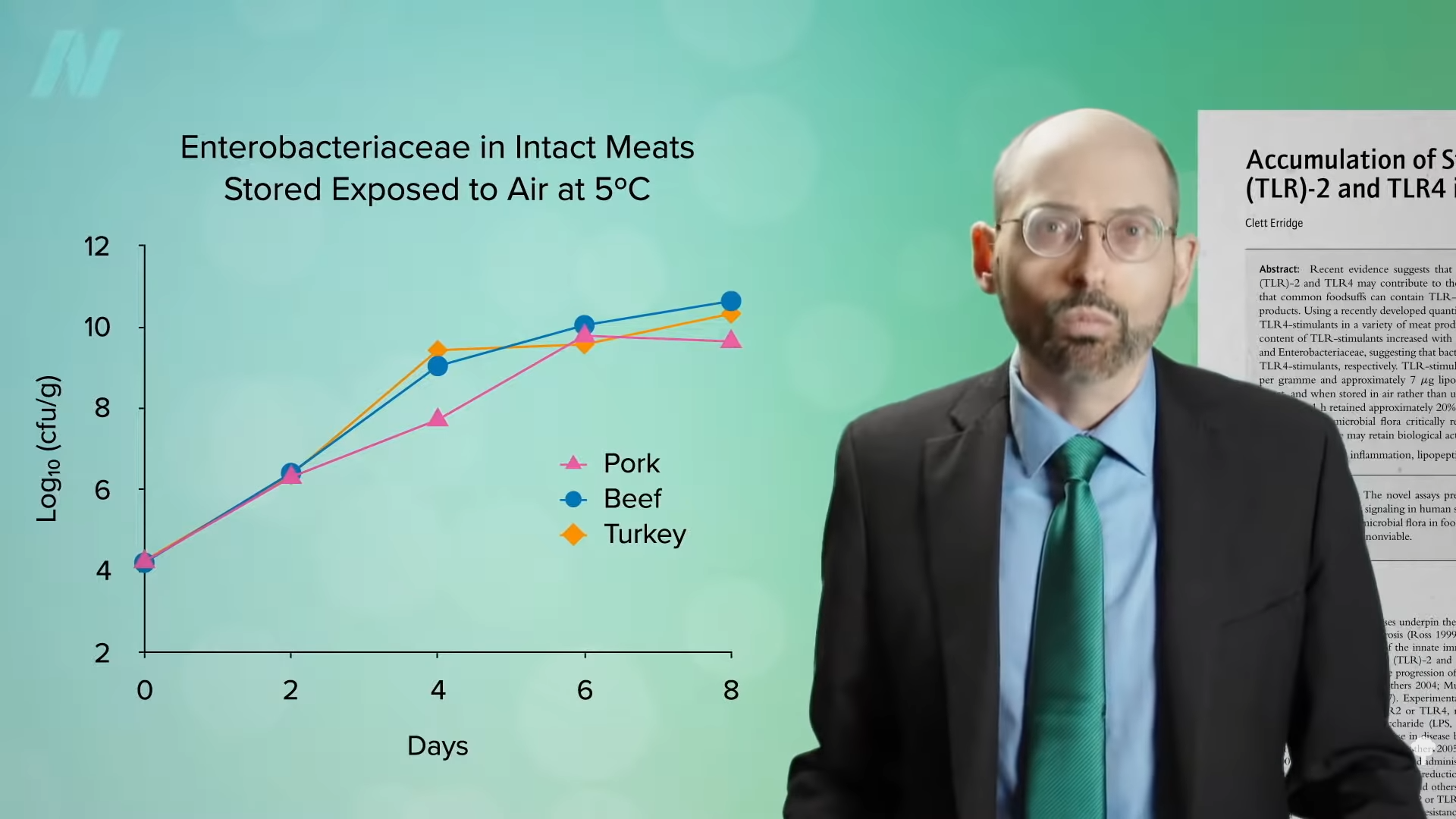
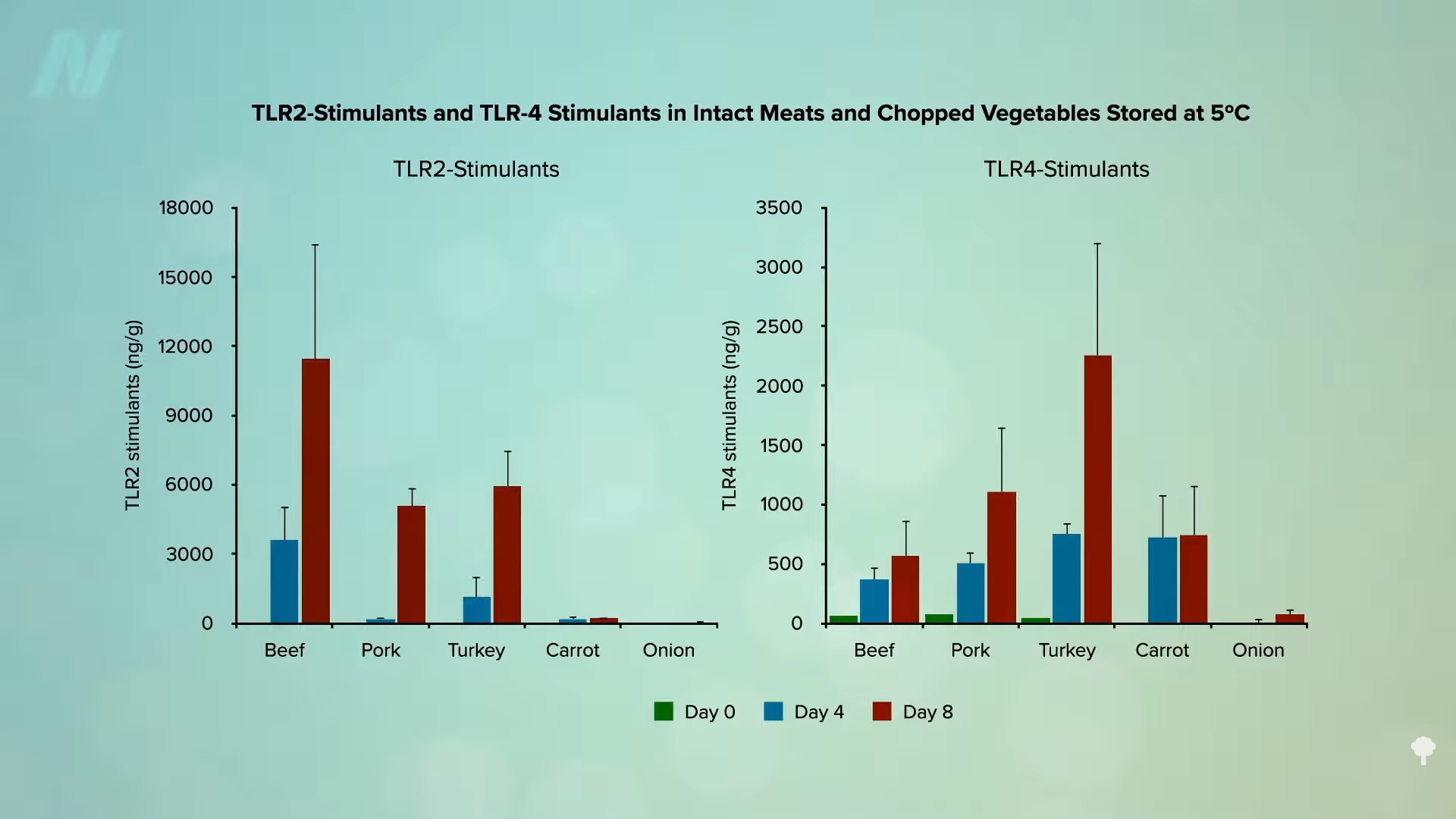
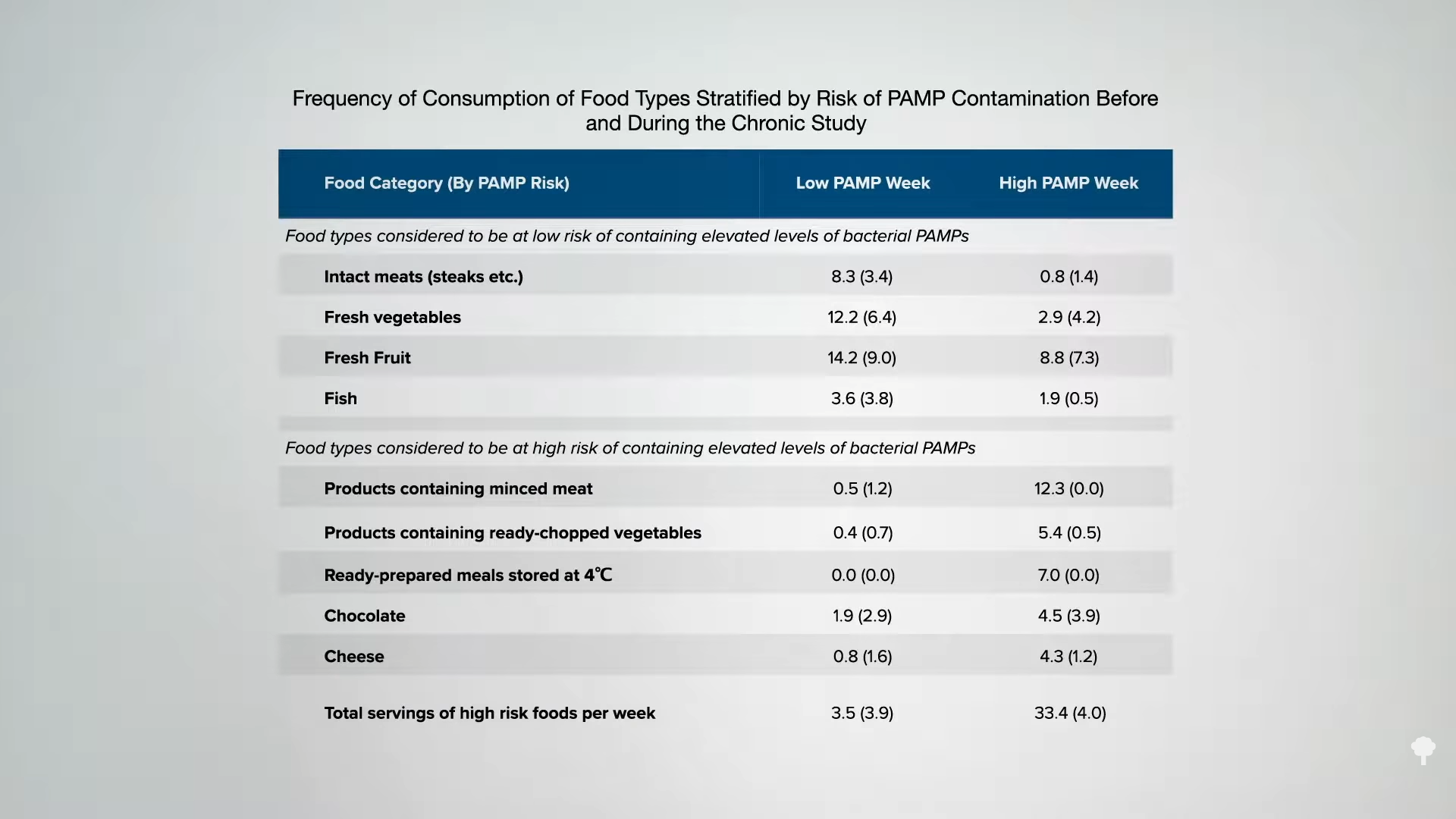
Medically important antibiotics are being squandered by animal agriculture to compensate for typical factory farming practices.
Cultivating muscle meat directly from cells instead of raising and slaughtering animals would reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses “due to fecal contamination during slaughtering and evisceration of carcasses” because there would be no feces, no slaughter, and no carcasses to eviscerate. In addition, cultivating meat would also reduce the threat from antibiotic resistance.
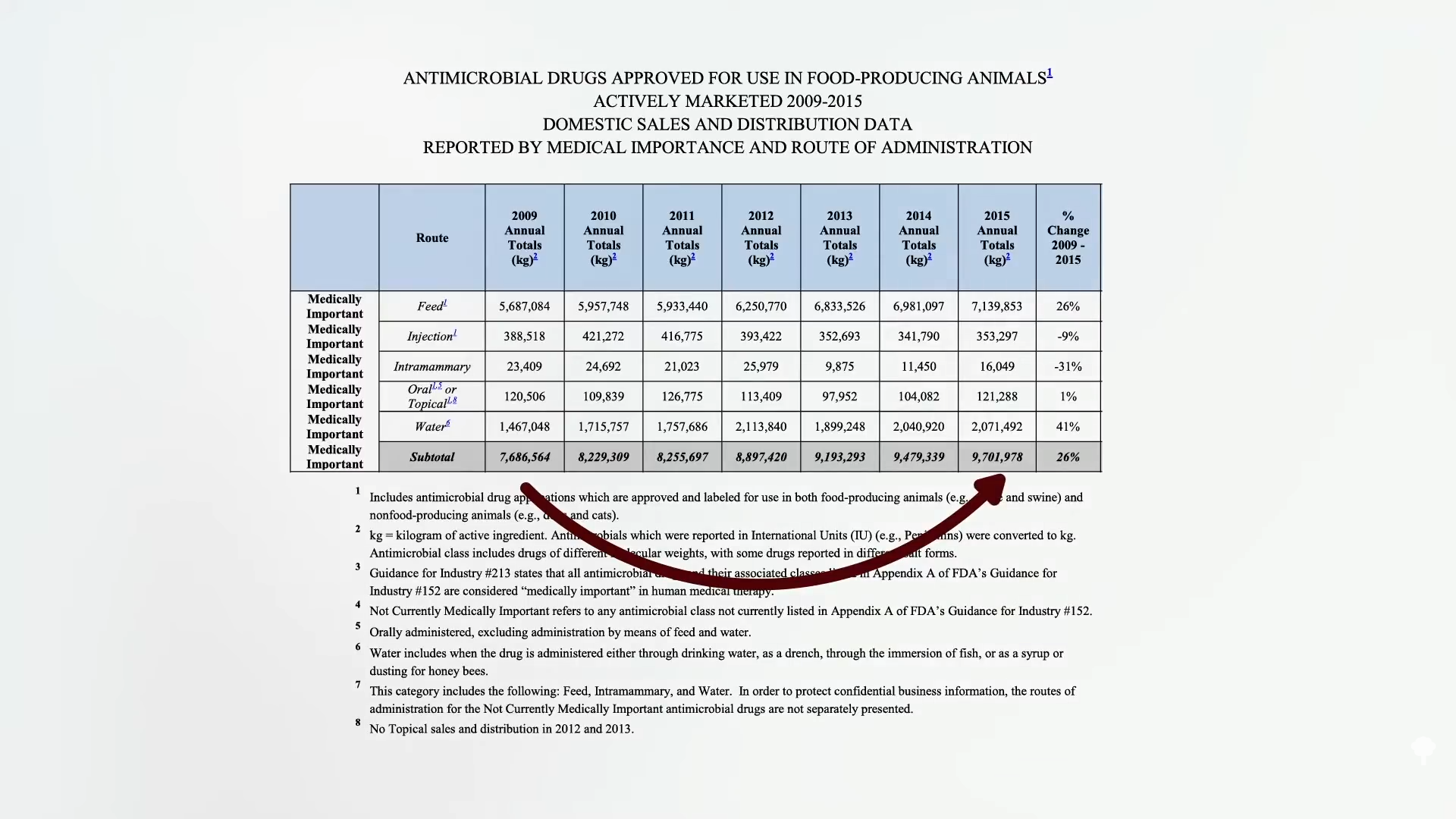
To compensate for overcrowded, stressful, and unhygienic conditions on factory farms, animals are typically dosed en masse with antibiotics. A lot of antibiotics. About 20 million pounds of medically important antibiotics a year, as you can see here and at 0:57 in my video, The Human Health Effects of Cultivated Meat: Antibiotic Resistance.
In the United States, for example, farm animals are given about 2 million pounds of penicillin drugs and 15 million pounds of tetracyclines annually. This is madness.
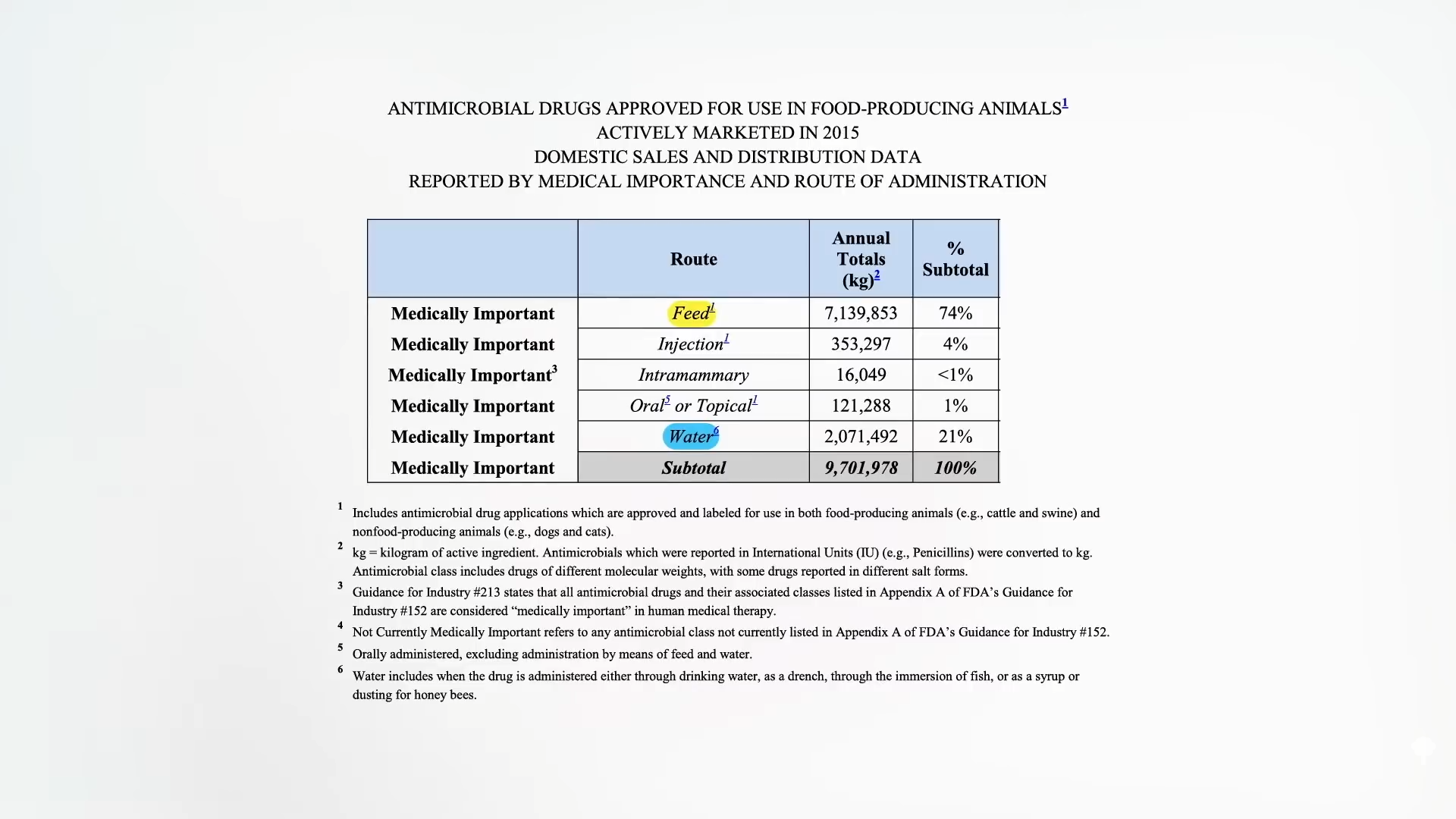
Antibiotic drugs important to human medicine go right into the feed and water of animals like cows, pigs, and chickens, by the ton and by the thousands of tons, as shown below and at 1:02 in my video. And that is all without a prescription.
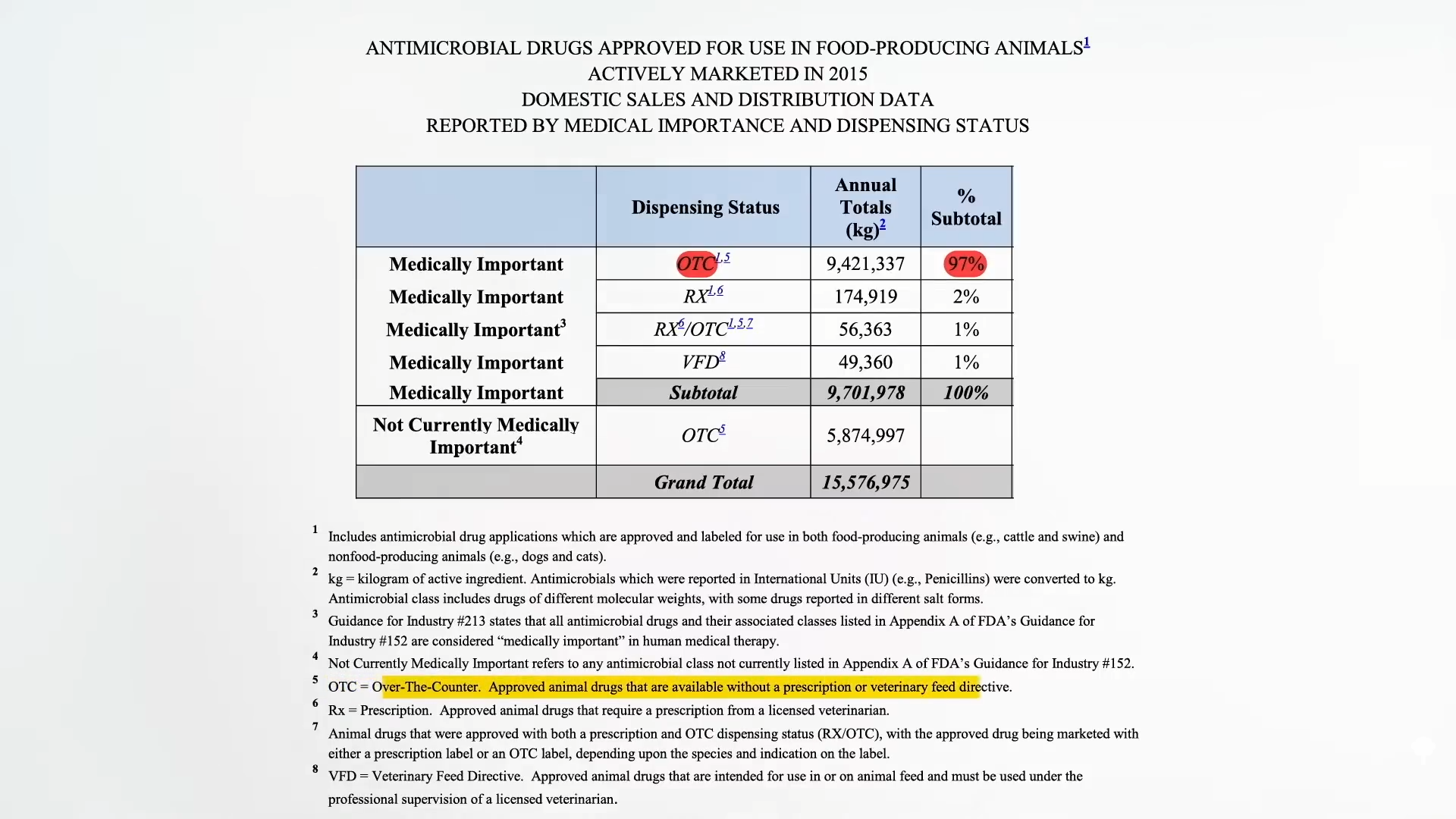
Ninety-seven percent of the tens of millions of pounds of antibiotics given to farm animals in the United States are bought over the counter—without a prescription or even an order from a veterinarian, as seen here and a 1:24. To get even a few milligrams of penicillin, we need a doctor’s prescription, because these are miracle wonder drugs that can’t be squandered. Meanwhile, farmers can just back their trucks up to the feedstore.
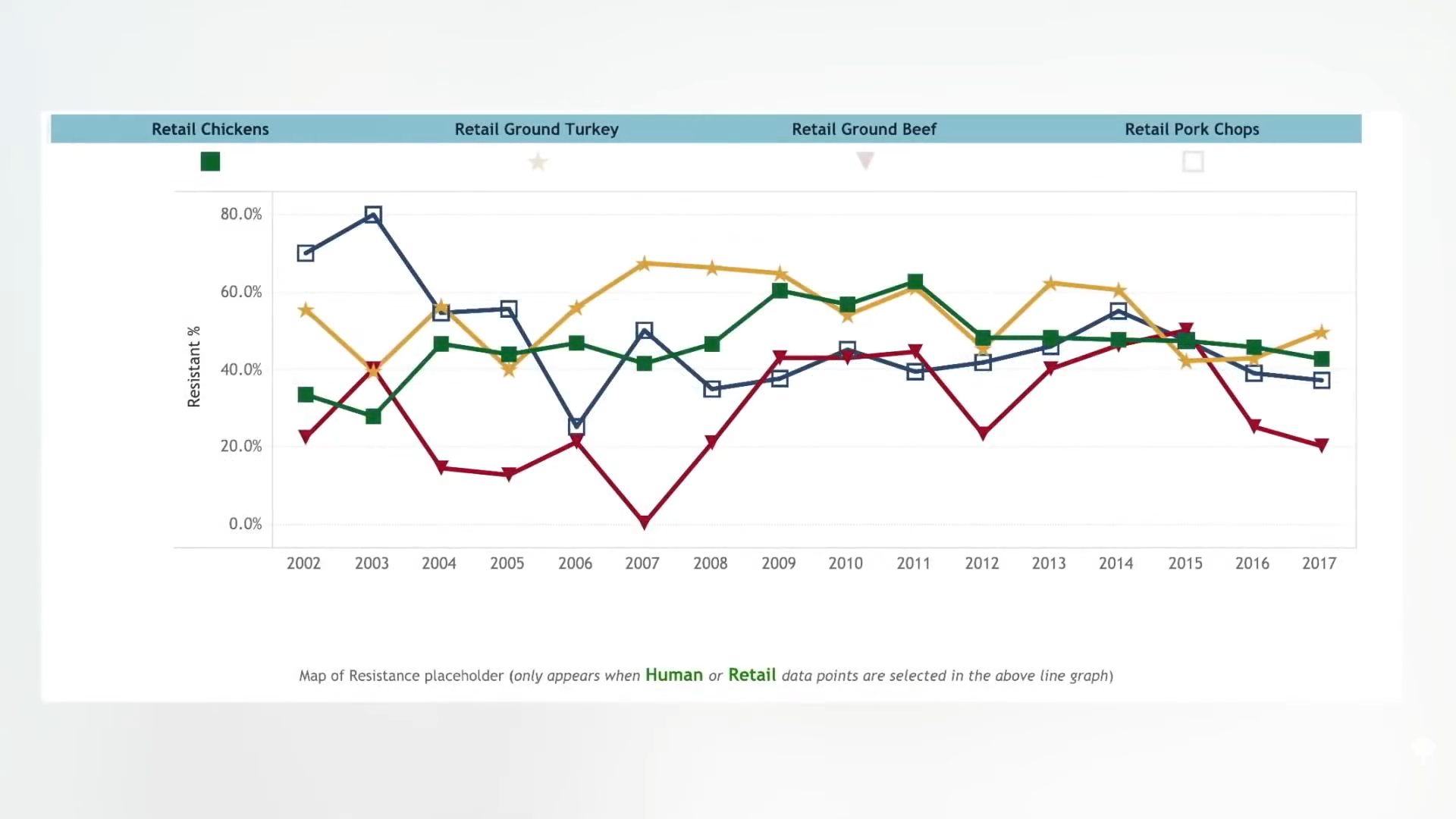
Now, half the Salmonella in retail meat—chicken, turkey, beef, and pork—is resistant to tetracycline, as shown below and at 1:50 in my video. About a quarter of the bugs are now resistant to three or more entire classes of antibiotics, including some resistant to “cephalosporins such as ceftriaxone [which] are critically important drugs we use to treat severe Salmonella infections, especially in children.”
Such agricultural applications for antimicrobials are now considered an “urgent threat to human health.” “The link between antibiotic use in animals and antibiotic resistance in humans is unequivocal.”
As shown here and at 2:20 in my video, it all starts with the poop.

Antibiotic-resistant bugs are selected for and then can spread via meat or produce contaminated by poop or they can spread through the wind, the air, or the water, or be carried by insects. There are many pathways by which resistant superbugs can escape. So, even if you don’t eat meat, you can be “put at risk by the pathogens released from stressed, immunocompromised, contaminant-filled livestock” dosed with antibiotics. That’s one of the reasons the American Public Health Association called for a moratorium on factory farms, due in part to all the pollution from concentrated animal feed operations (CAFOs) to the surrounding communities.
Every year, more than five tons of animal manure are produced for every man, woman, and child in the United States. Again, it all starts with the poop. But cultivated meat means no guts, no poop, no fecal infections, and no antibiotics necessary. It also means no fecal or antibiotic residues left in “foodstuffs such as milk, egg, and meat” that can potentially cause a variety of side effects beyond just the transfer of antibiotic-resistant bacteria to humans.
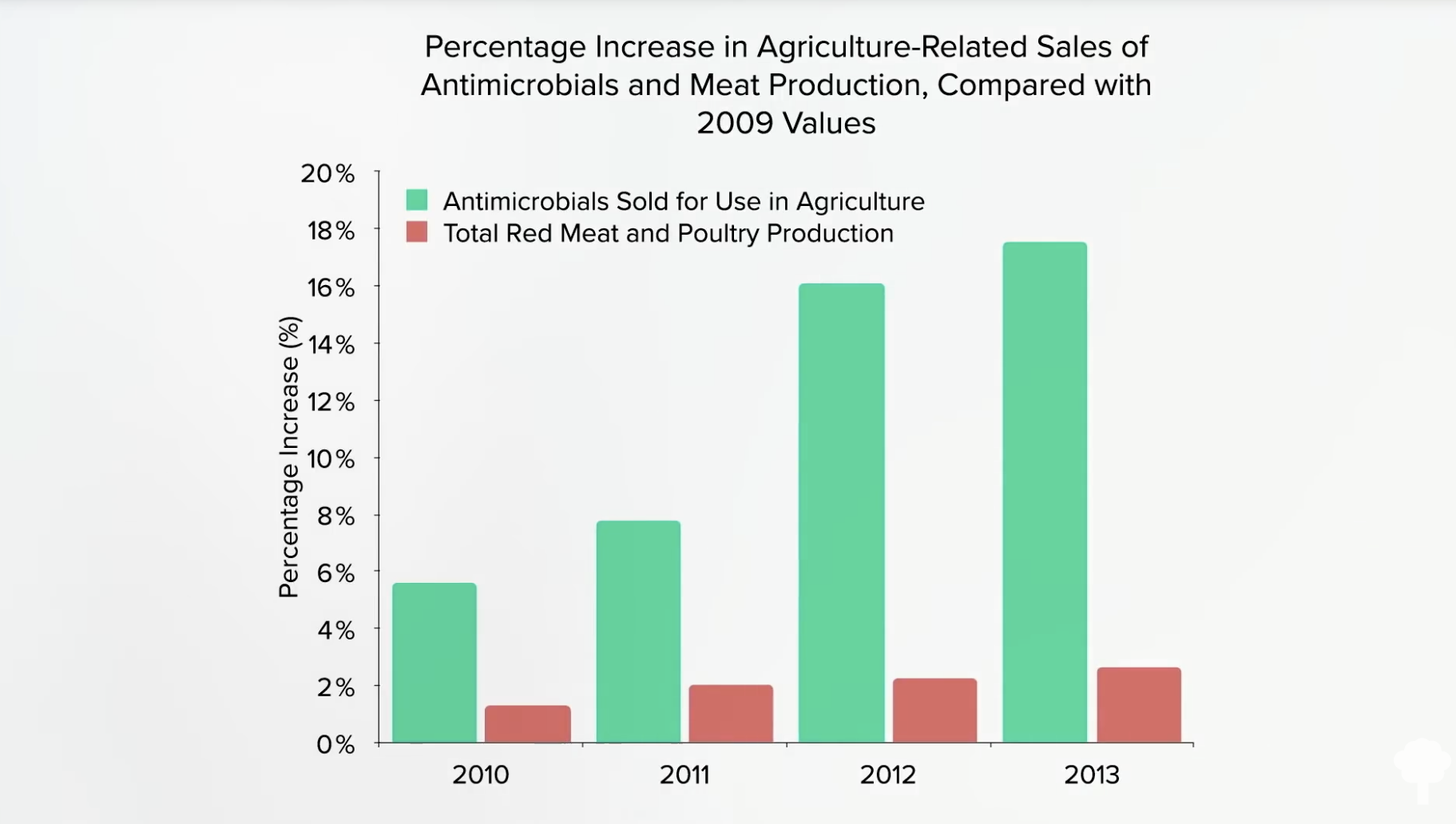
And, as you can see here and at 3:30 in my video, things are getting worse, not better. U.S. animal agriculture is using more antibiotics now than ever.
This isn’t only because more animals are being raised for food, either. Antibiotic sales in the United States are outpacing meat production. Yes, meat production is going up, but there is a serious rise in antibiotic sales for meat production, as shown below and at 3:46.
With the combined might of Big Ag and Big Pharma (who profit from selling all the drugs), it’s hard to imagine anything changing on the political side. The only hope may be a change in the production side.
“The unstoppable rise of super-resistant strains of bacteria is a serious worldwide problem, resulting in 700 000 deaths every year,” and the projections for global antibiotic use in the production of farm animals are “ominous,” estimated to exceed 100,000 tons of antibiotics pumped into animals raised for food by 2030. Quite simply, we may be “on the path to untreatable infections” by using even some of our “last resort antibiotics,” like carbapenems, just to shave a few cents off a pound of meat.
And it’s not just foodborne bacteria. Mad cow disease, swine flu, and bird flu have the potential to kill millions of people. Skeptical? I’ve got a book for you to read, whose author’s “superb storytelling ability makes every page of the book interesting and fascinating for both specialist and layperson.” (Thanks, Virology Journal, for the wonderful book review and calling my book “a must read.”)
Given the threat of the chickens coming home to roost, an editorial in the American Journal of Public Health thought that “it is curious, therefore, that changing the way humans treat animals—most basically, ceasing to eat them or, at the very least, radically limiting the quantity of them that are eaten—is largely off the radar as a significant preventative measure. Such a change, if sufficiently adopted or imposed, could still reduce the chances of the much-feared influenza epidemic…Yet humanity does not consider this option.”
That may be moot, though, because we could cultivate all the chicken we want, without guts or lungs.
It’s hard to stress the importance of that American Journal of Public Health editorial. As devastating as COVID-19 has been, it may just be a dress rehearsal for an even greater threat waiting in the wings—the wings of chickens.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the leading candidate for the next pandemic is a bird flu virus known as H7N9, which is a hundred times deadlier than COVID-19. Instead of 1 in 250 patients dying, H7N9 has killed 40 percent of the people it infects.
The last time a bird flu virus jumped directly to humans and caused a pandemic, it triggered the deadliest plague in human history—the 1918 pandemic that killed 50 million people. That had a 2 percent death rate. What if we had a pandemic infecting billions where death was closer to a flip of a coin?
The good news is that there is something we can do about it. Just as eliminating the exotic animal trade and live animal markets may go a long way toward preventing the next coronavirus pandemic, reforming the way we raise domestic animals for food may help forestall the next killer flu. The bottom line is that it’s not worth risking the lives of millions of people for the sake of cheaper chicken.
If you missed the previous video, see The Human Health Effects of Cultivated Meat: Food Safety. Up next is The Human Health Effects of Cultivated Meat: Chemical Safety.