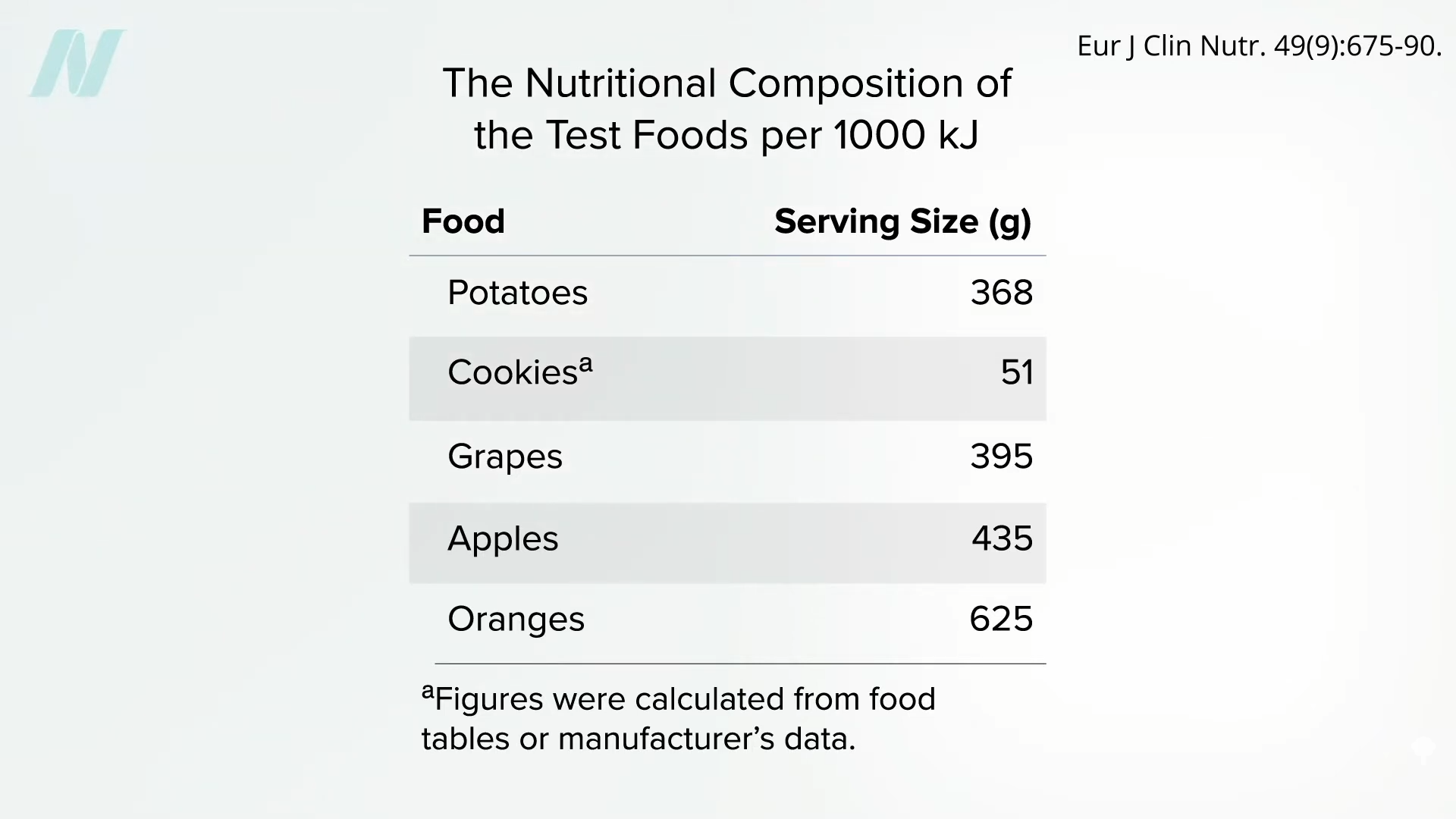
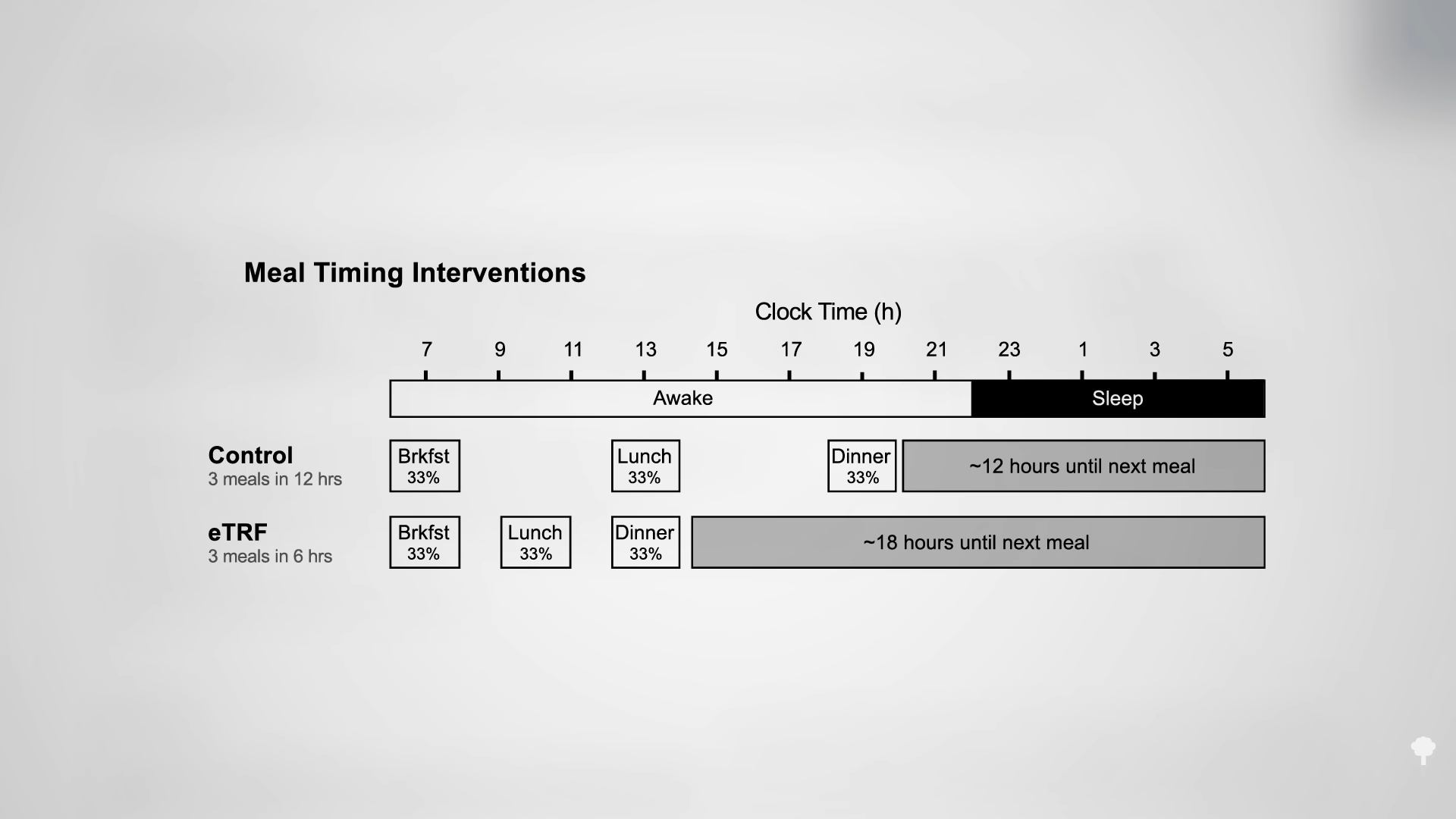
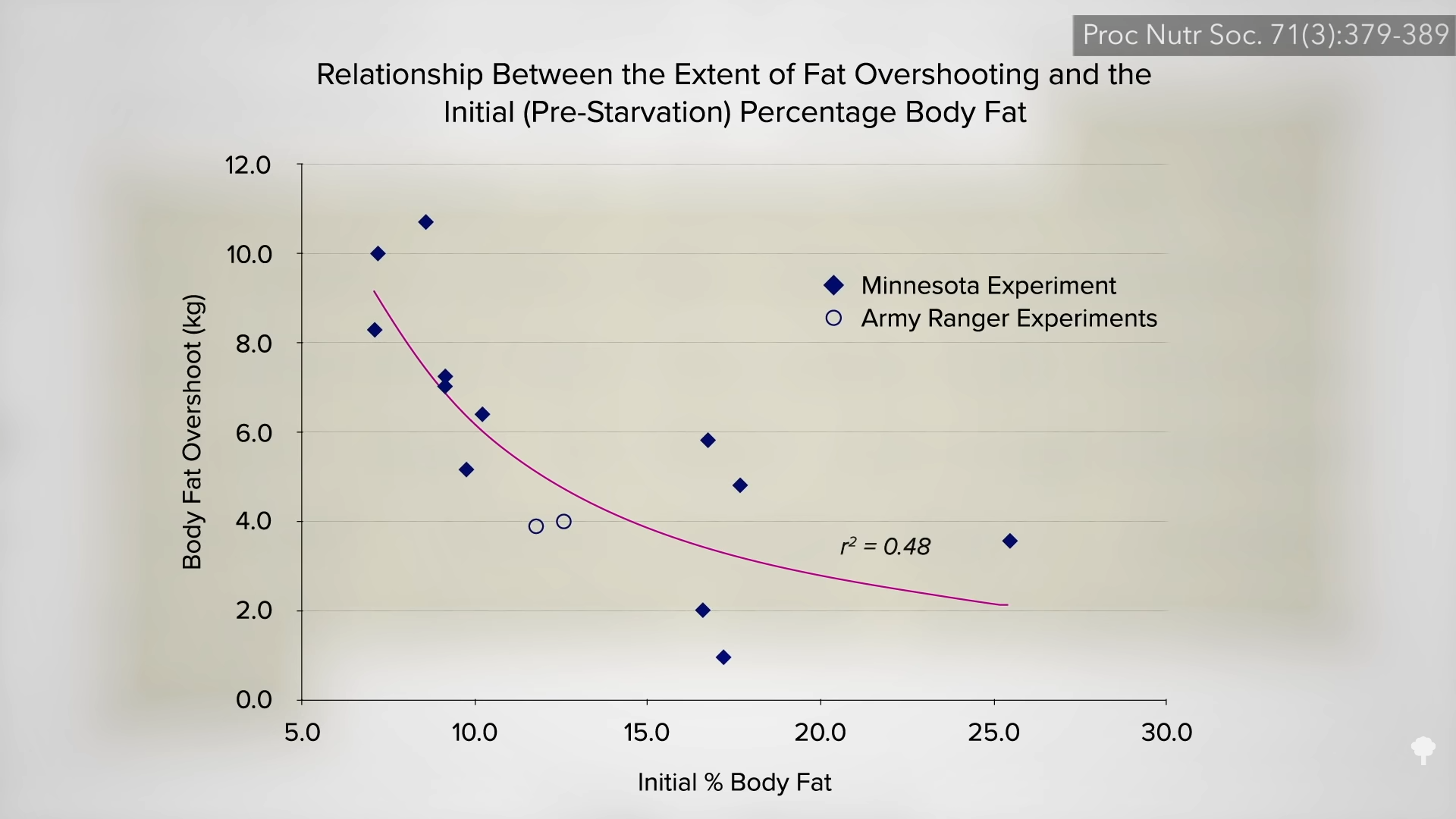
Like the keto diet, fasting for one or two weeks can actually slow the loss of body fat rather than accelerate it.
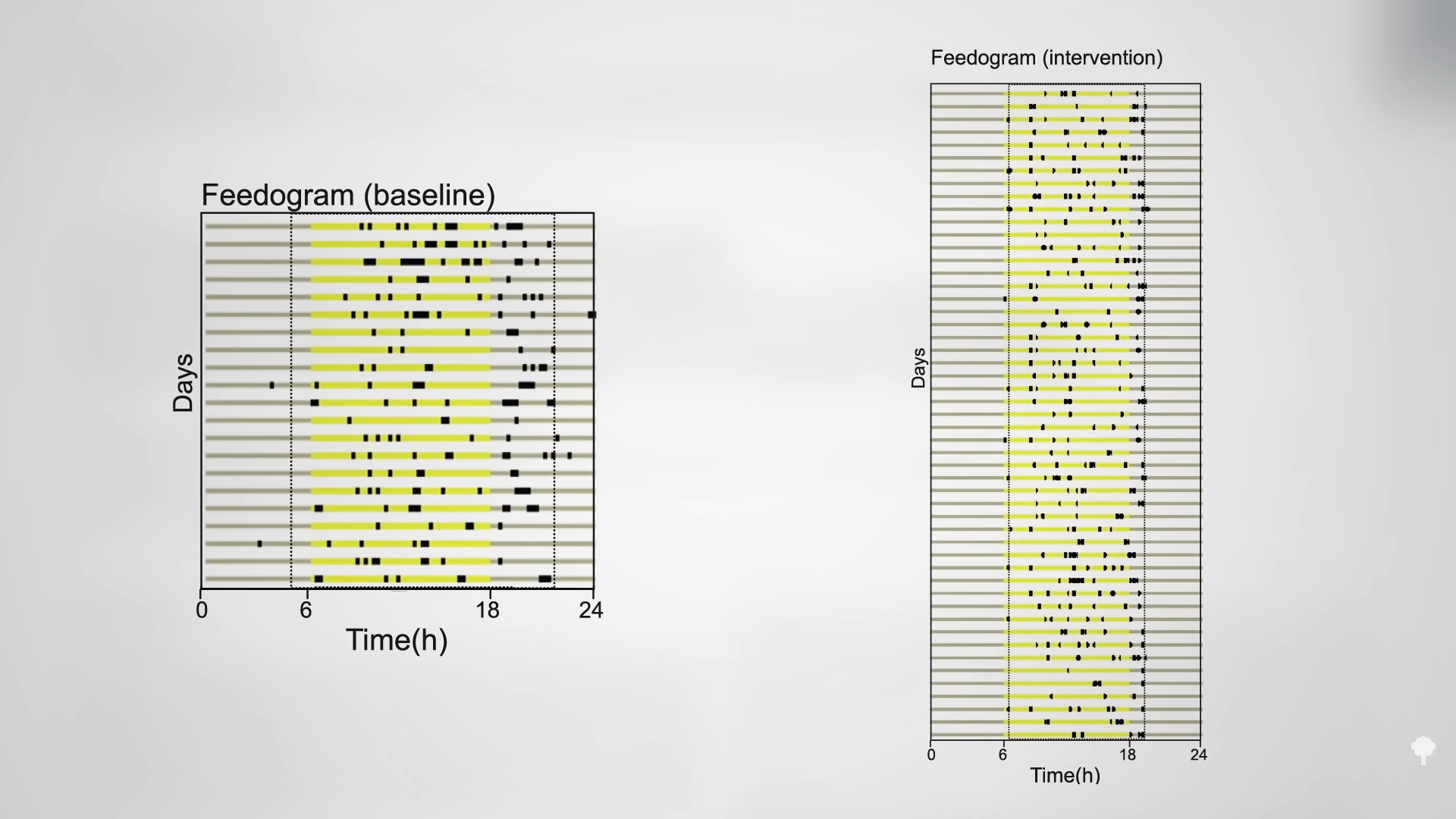
Fasting obviously causes consistent, dramatic weight loss, as shown in the graph below and at 0:09 in my video Is Fasting Beneficial for Weight Loss?, but how do fasted individuals do long-term? Some research groups reported “extremely disappointing long-term effects,” as you can see in the graph below and at 0:19 in my video.
Average subjects started at about 270 pounds and, in the six months before the fast, continued to gain weight as obese persons tend to do. After 24 days of “inpatient starvation,” they experienced a dramatic 27-pound weight loss. Then, what do you think happened? 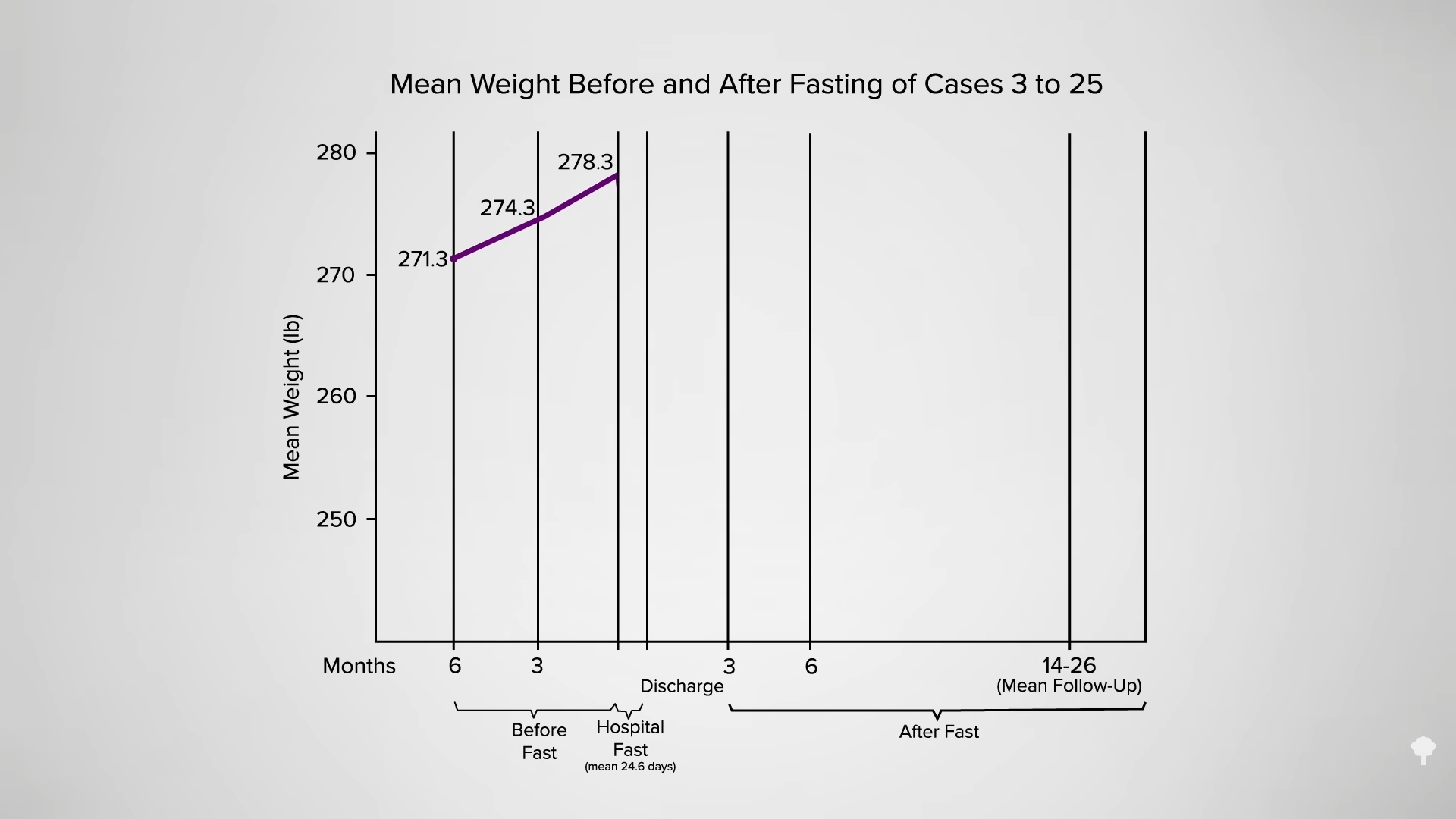
They gained it all back and more, though one could argue if they had not fasted, they might have weighed even more at that point, as seen in the graph below and at 0:45 in my video. 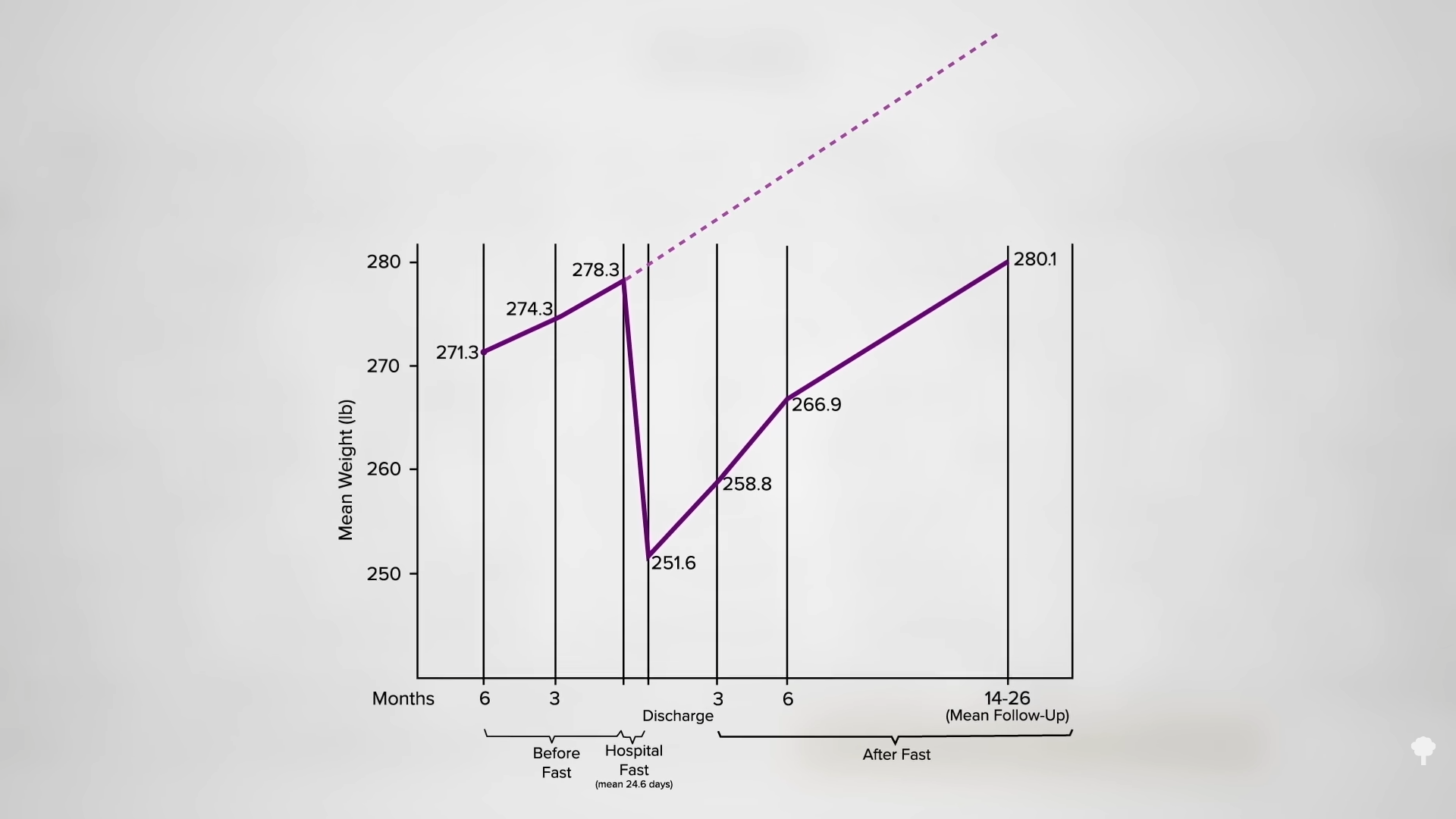
In another study with follow-ups ranging up to 50 months, only 4 out of 25 “superobese” patients achieved even partial sustained success. Based on these kinds of data, some investigators “concluded that complete starvation is of no value in the long-term treatment of obese patients.”
Other research teams reported better outcomes. One series with about 100 individuals found that 60 percent retained at least some weight loss at follow-up or even continued losing. The follow-up periods varied from 1 to 32 months with no breakdown as to who fasted and for how long, though, making the data hard to interpret. In another study, 62 patients were down an average of 16 pounds after fasting for 10 days. After one year, 40 percent of the group had retained at least 7 pounds of that weight loss.
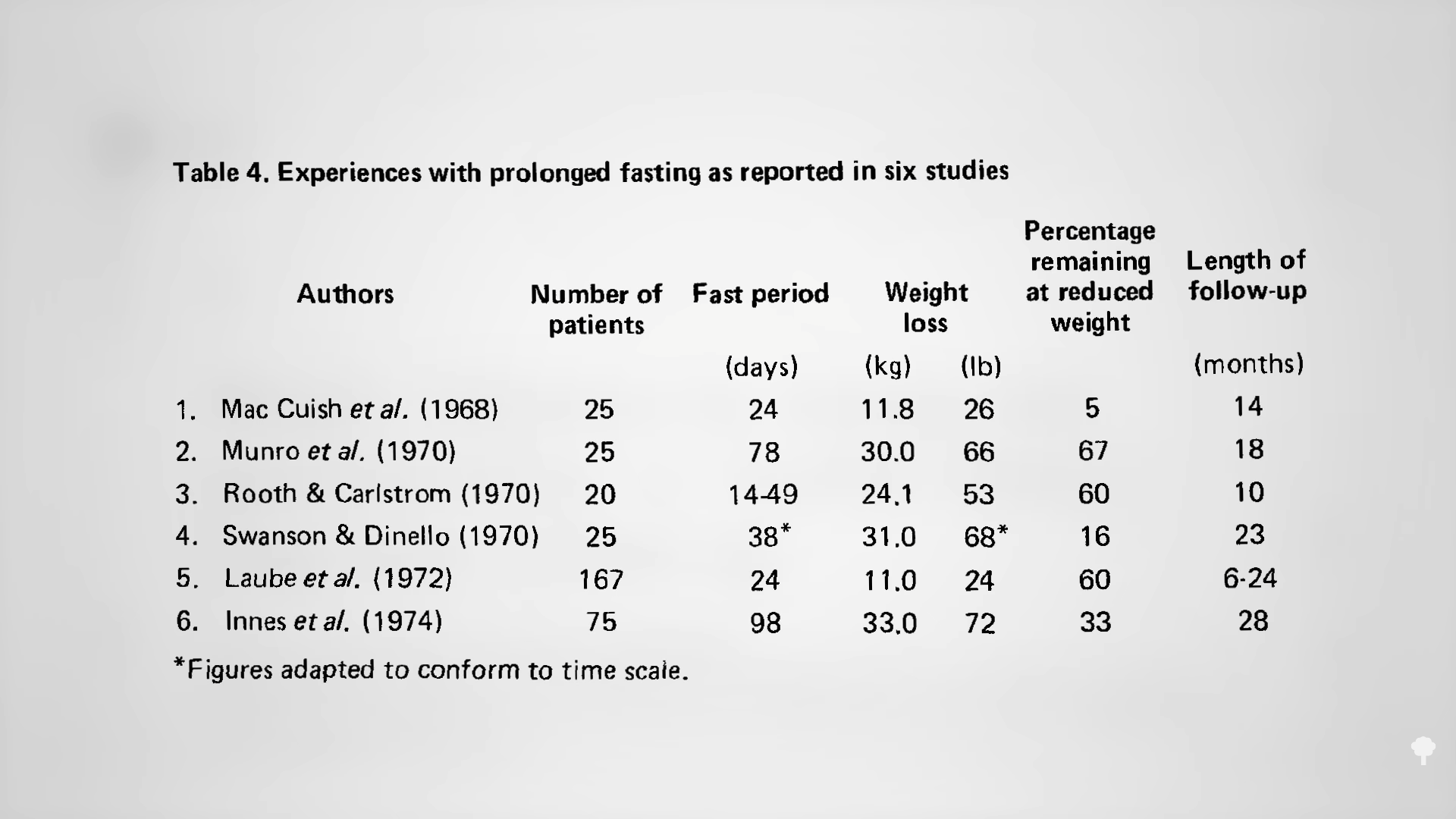
As you can see below and at 1:37 in my video, when you put together six such studies, hundreds of obese subjects fasted for an average of 44 days and lost an average of 52 pounds. And, around one or two years later, 40 percent retained at least some of that weight loss. So, most gained back all of the weight they had lost, but 40 percent is extraordinary for a weight-loss study.
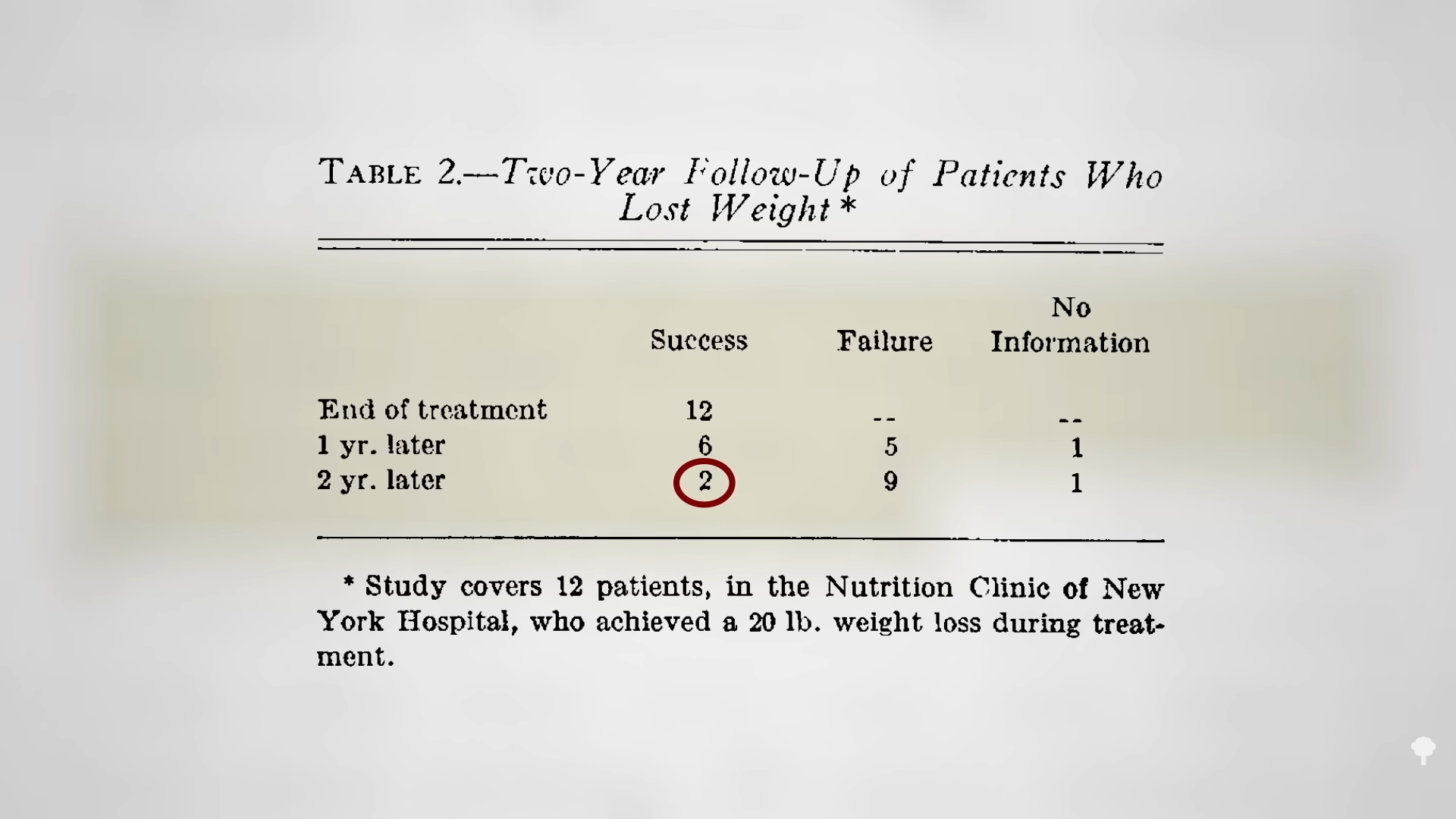
Following a hundred obese individuals getting treated at a weight-loss clinic with a standard low-calorie diet, researchers found that only one out of a hundred lost more than 40 pounds and only about one in ten lost even 20 pounds, with overall successful weight maintenance at only two patients over two years, as seen below and at 2:08 in my video. That’s why having a control group is so important. What may look like a general failure may actually be a relative success compared to more traditional weight-loss techniques.
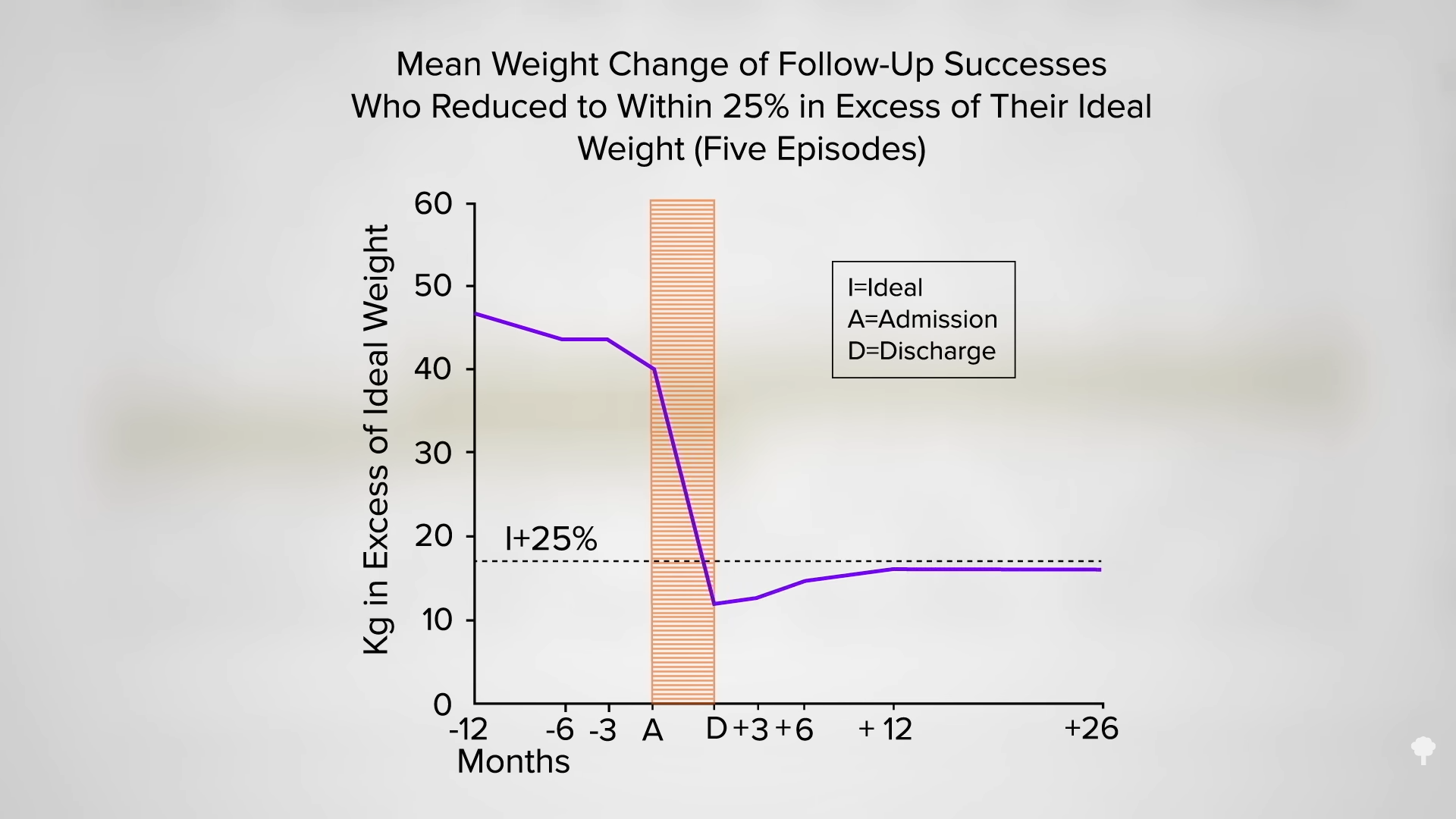
 Researchers new to the field may find it “clearly disappointing” that the “overall results of follow-up for 12 months or more” found that “two-thirds of the patients were ‘failures’ and more than one-third actually regained all the weight lost.” But, 12 percent were labeled successes, maintaining 59 pounds of weight loss two years later. As you can see in the graph below and at 2:42 in my video, the subjects lost massive amounts of excess weight and kept it off.
Researchers new to the field may find it “clearly disappointing” that the “overall results of follow-up for 12 months or more” found that “two-thirds of the patients were ‘failures’ and more than one-third actually regained all the weight lost.” But, 12 percent were labeled successes, maintaining 59 pounds of weight loss two years later. As you can see in the graph below and at 2:42 in my video, the subjects lost massive amounts of excess weight and kept it off.
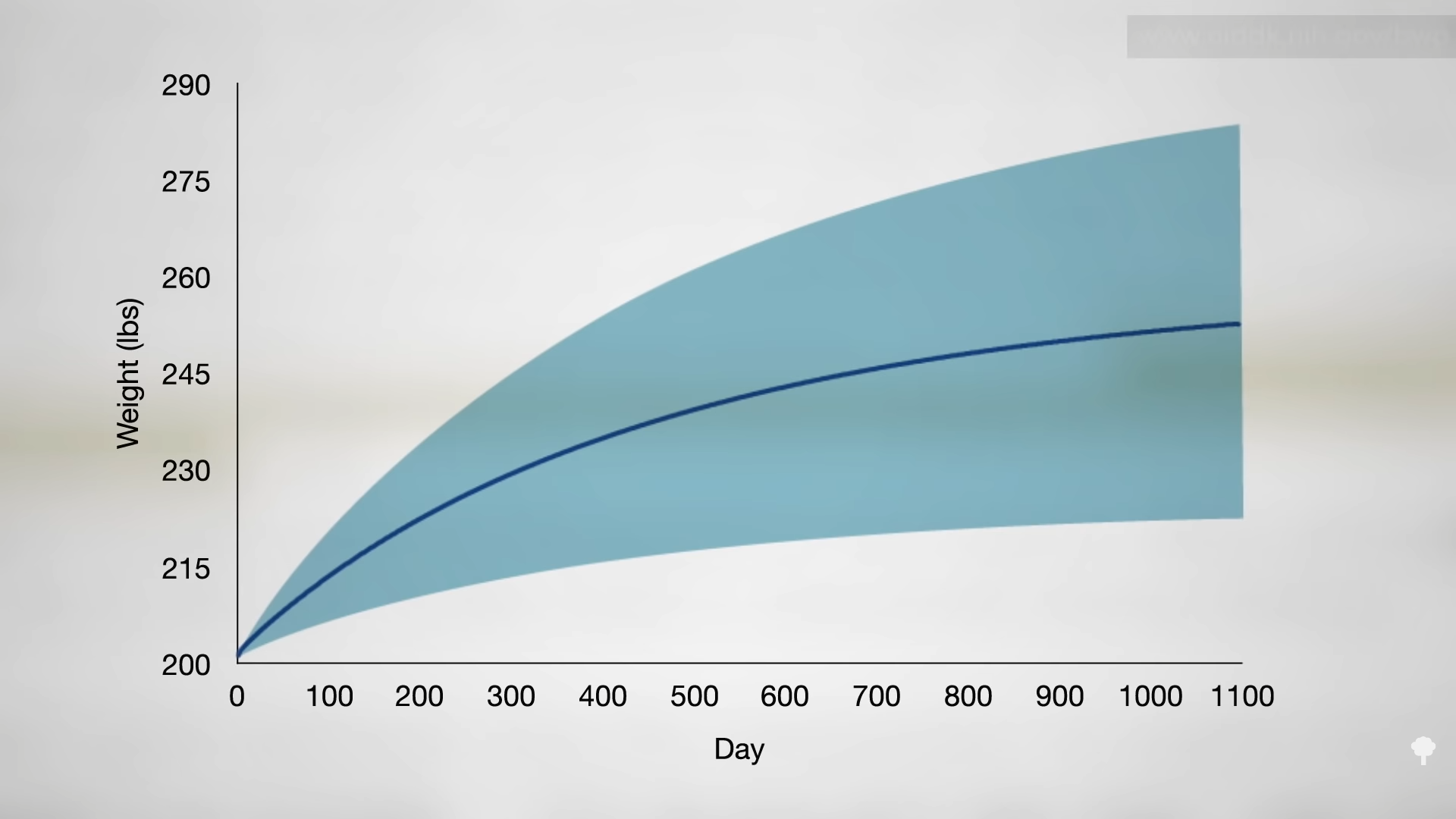
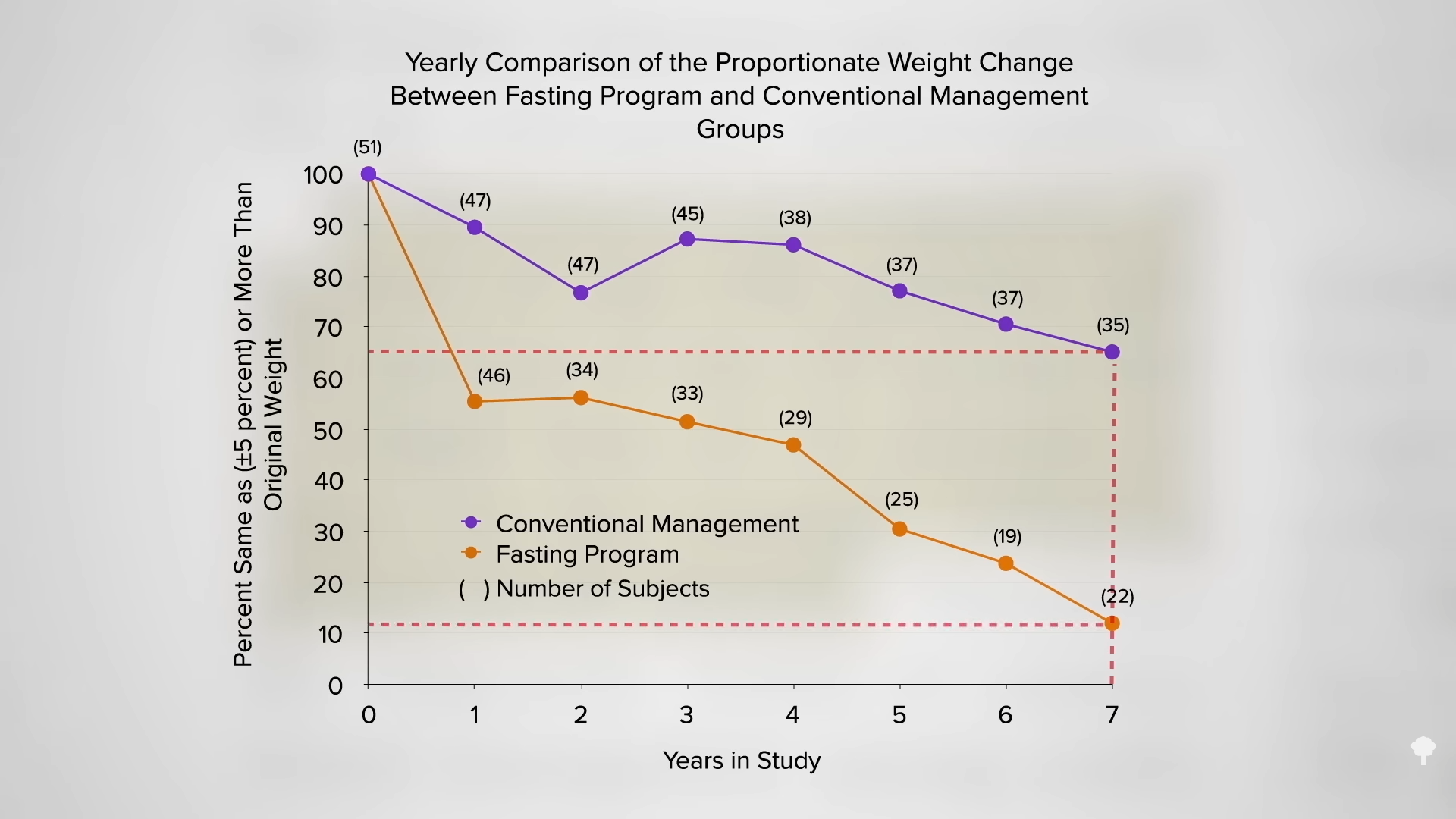
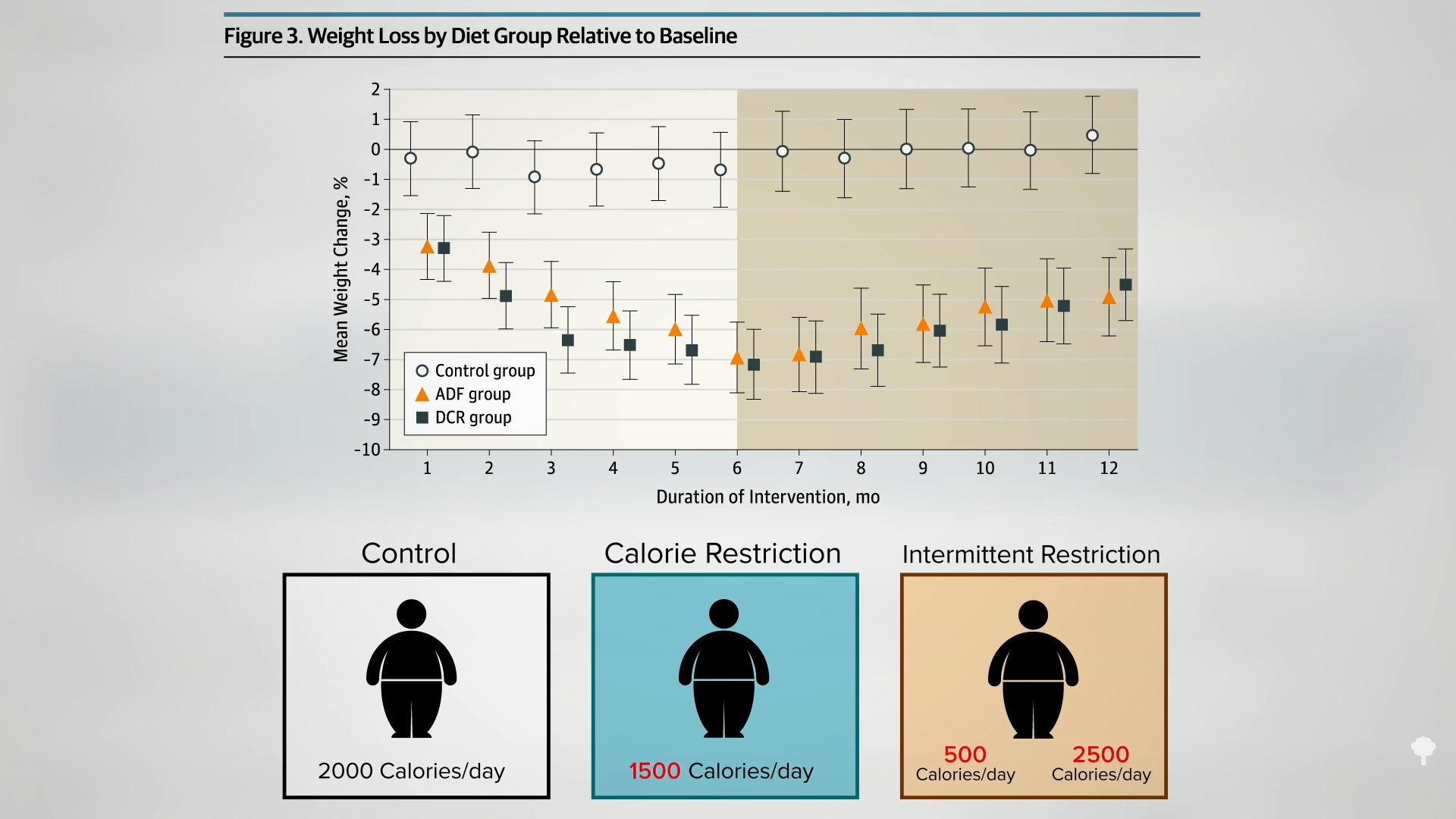
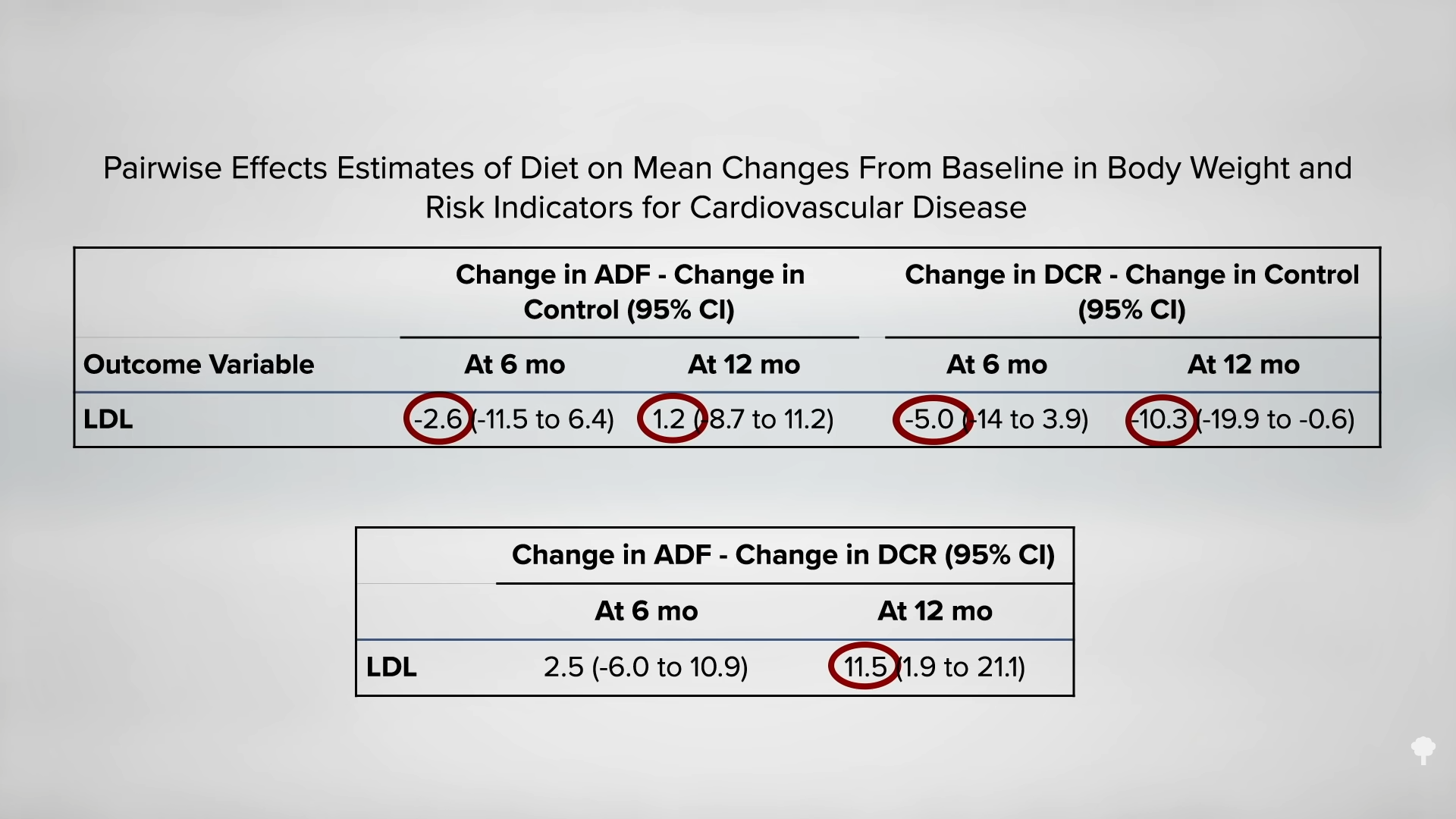
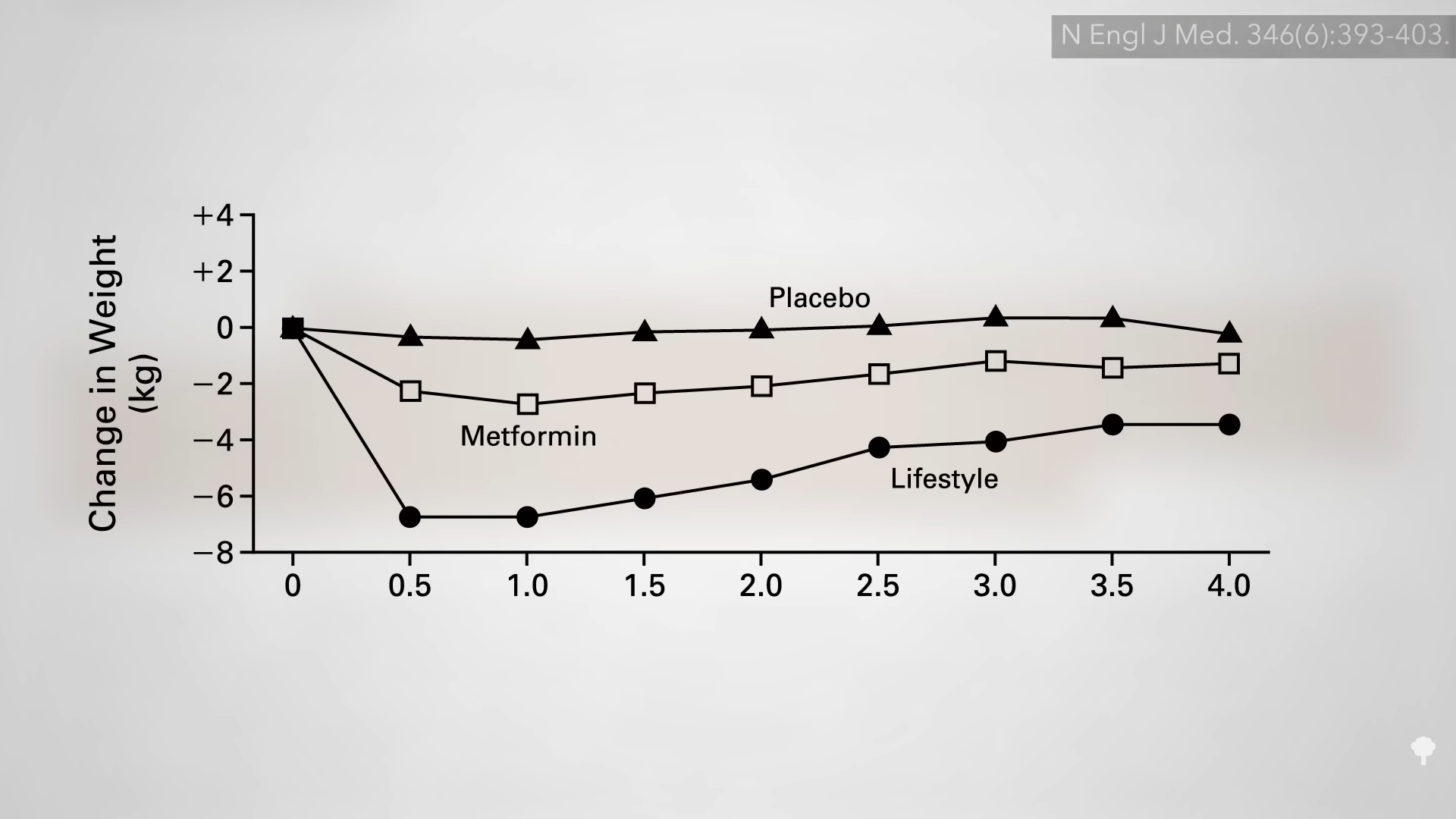
In a direct comparison of different weight-loss approaches at the same clinic, five years after initiating a conventional low-calorie approach, only about one in five was down 20 pounds compared to nearly half in the group who instead had undergone a few weeks of fasting years previously. By year seven, as you can see in the graph below and at 3:03 in my video, most of those instructed on daily caloric restriction were back up to their original weight or had even exceeded it, but that was only true for about one in ten in the fasted group. In an influential paper in the New England Journal of Medicine on seven myths about obesity, fallacy number three was identified as: “Large, rapid weight loss is associated with poorer long-term weight-loss outcomes, as compared with slow, gradual weight loss.” In reality, the opposite is true. The hare may end up skinnier than the turtle.
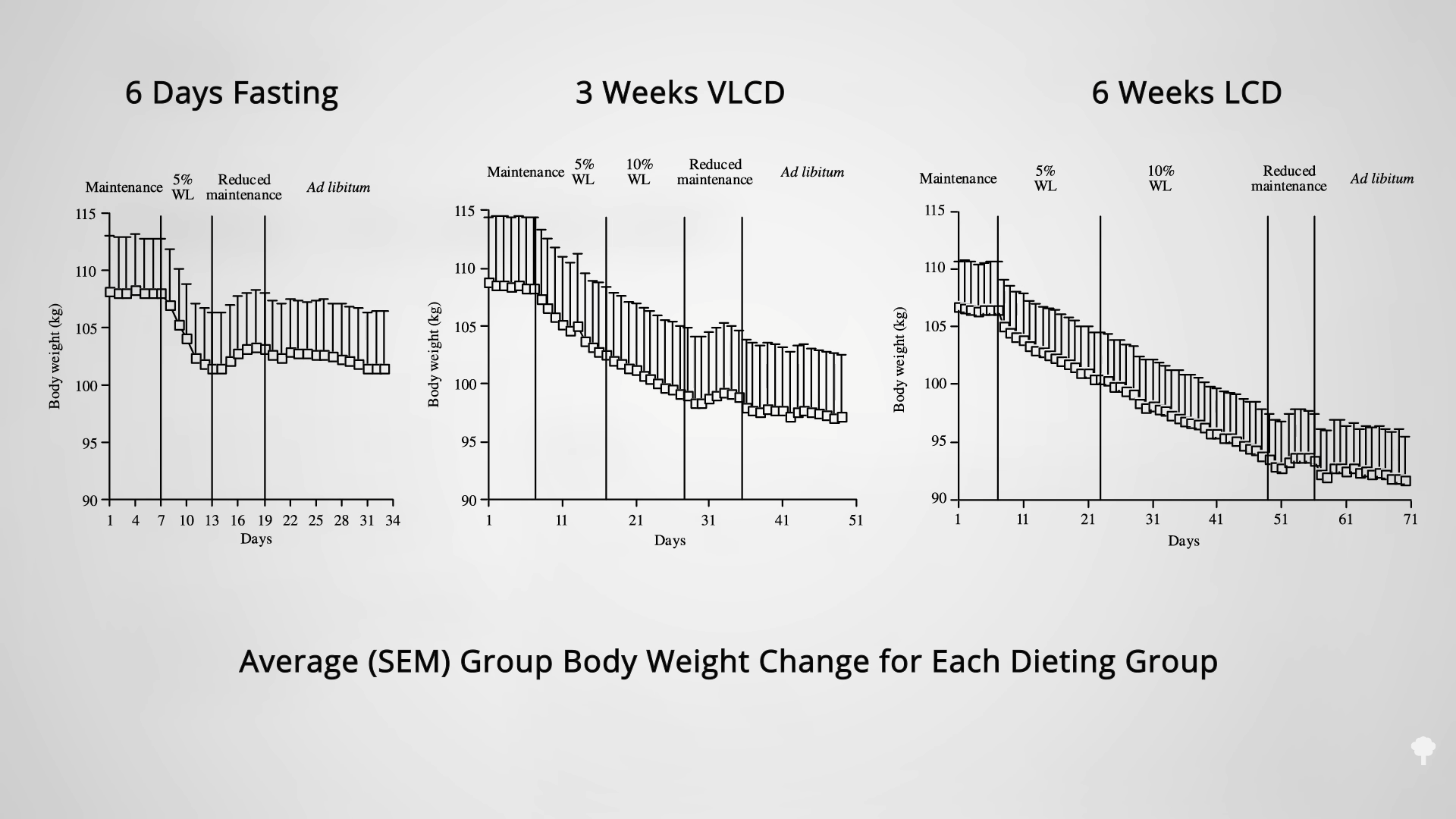
As shown in the graph below and at 3:39 in my video, researchers set up a study comparing the sustainability of weight loss at three different speeds: six days of fasting, three weeks on a very-low-calorie diet of 600 calories a day, or six weeks on a low-calorie diet of 1,200 calories a day.
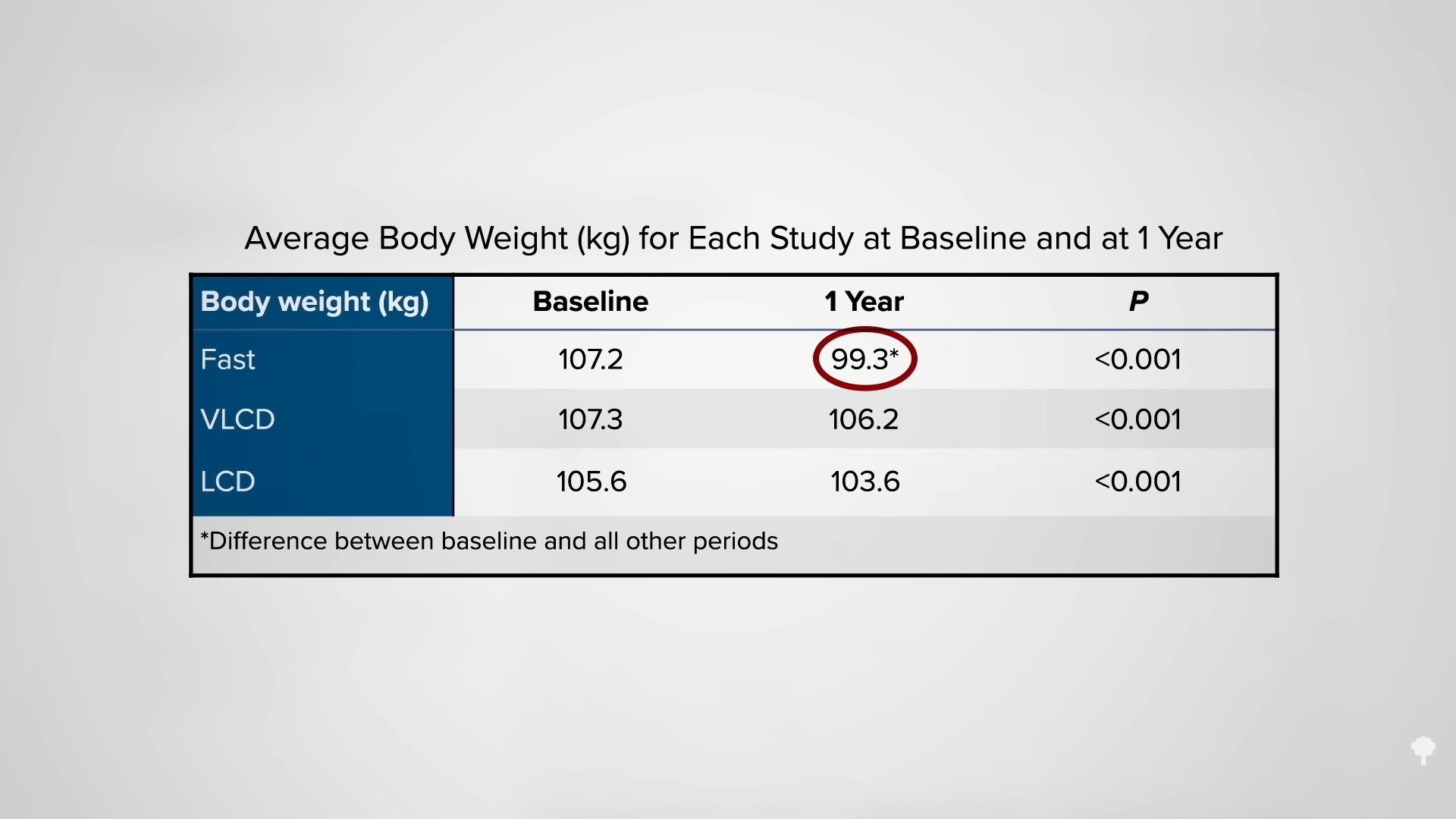
The question is: What happened a year later? At one year, the fasting group was the only one that sustained a significant loss of weight, as you can see below and at 3:55 in my video.
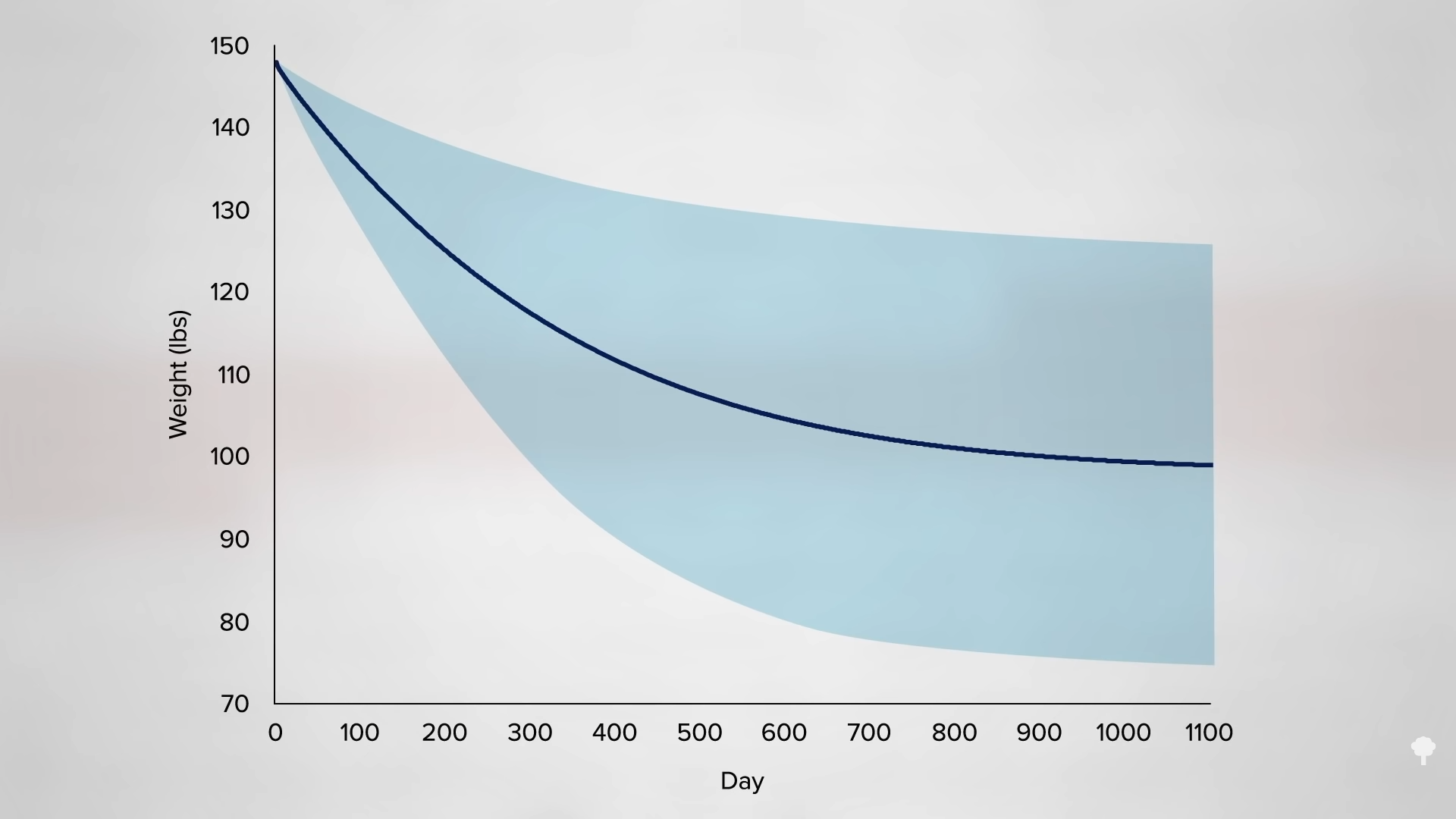
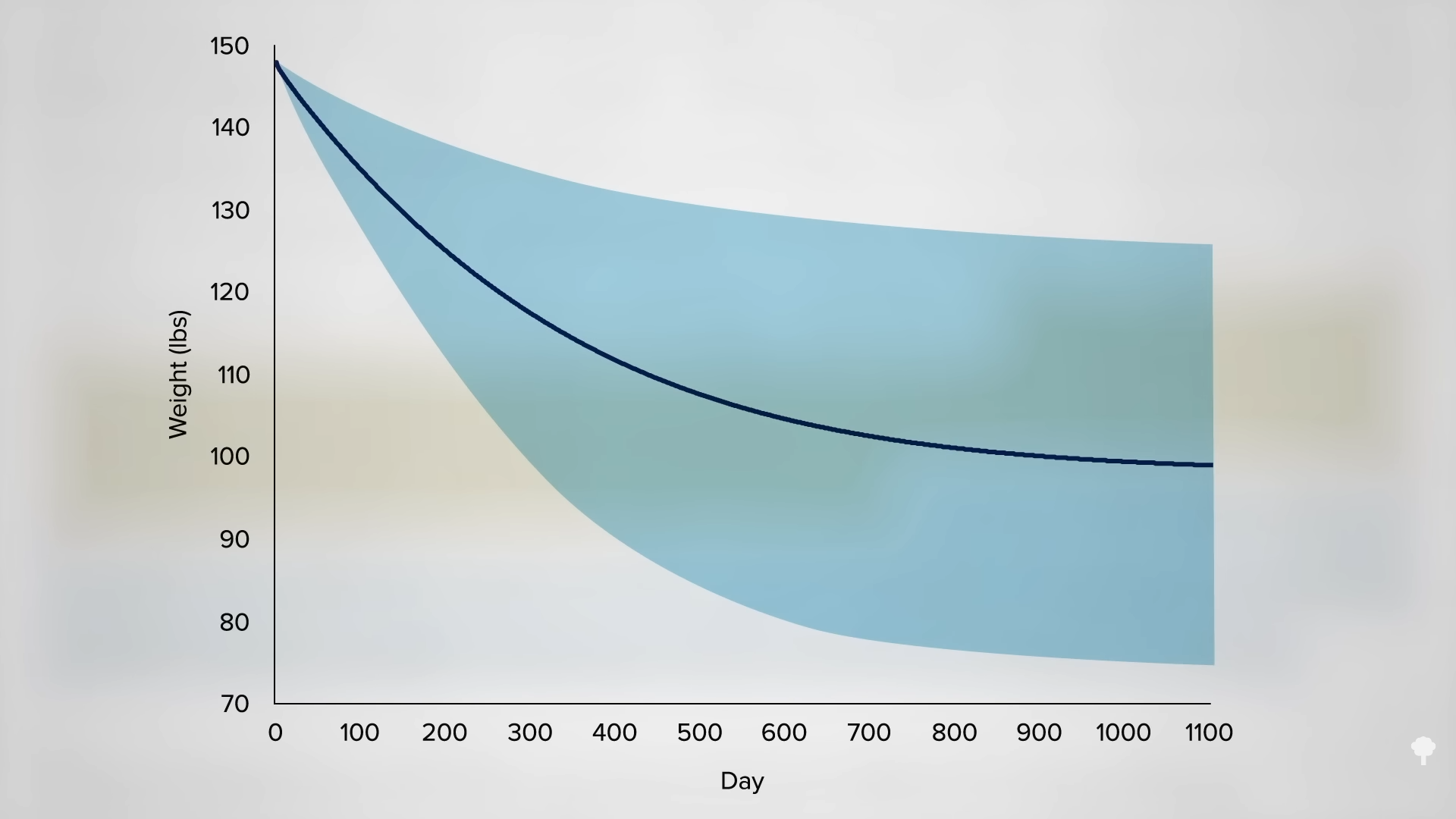
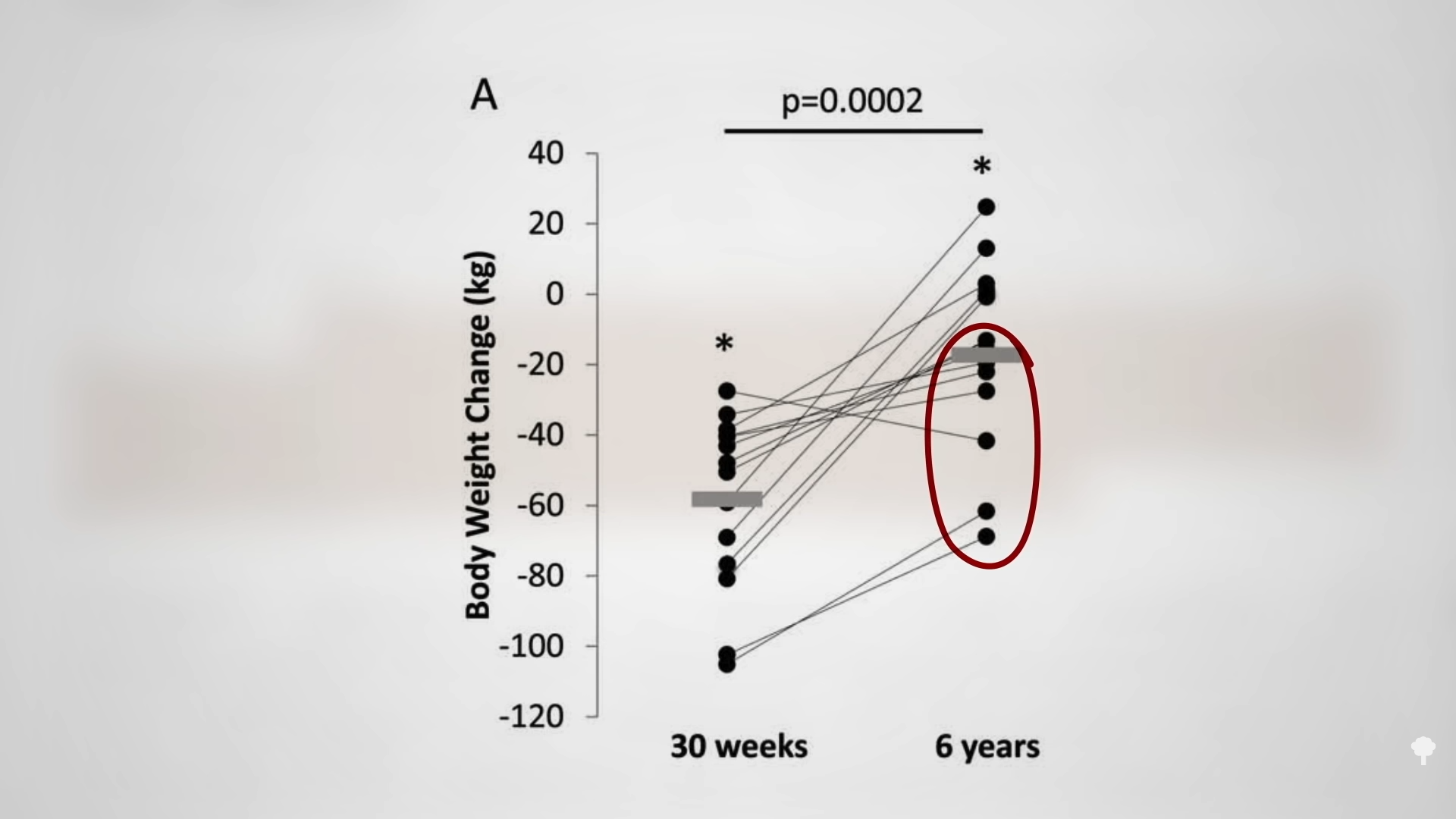
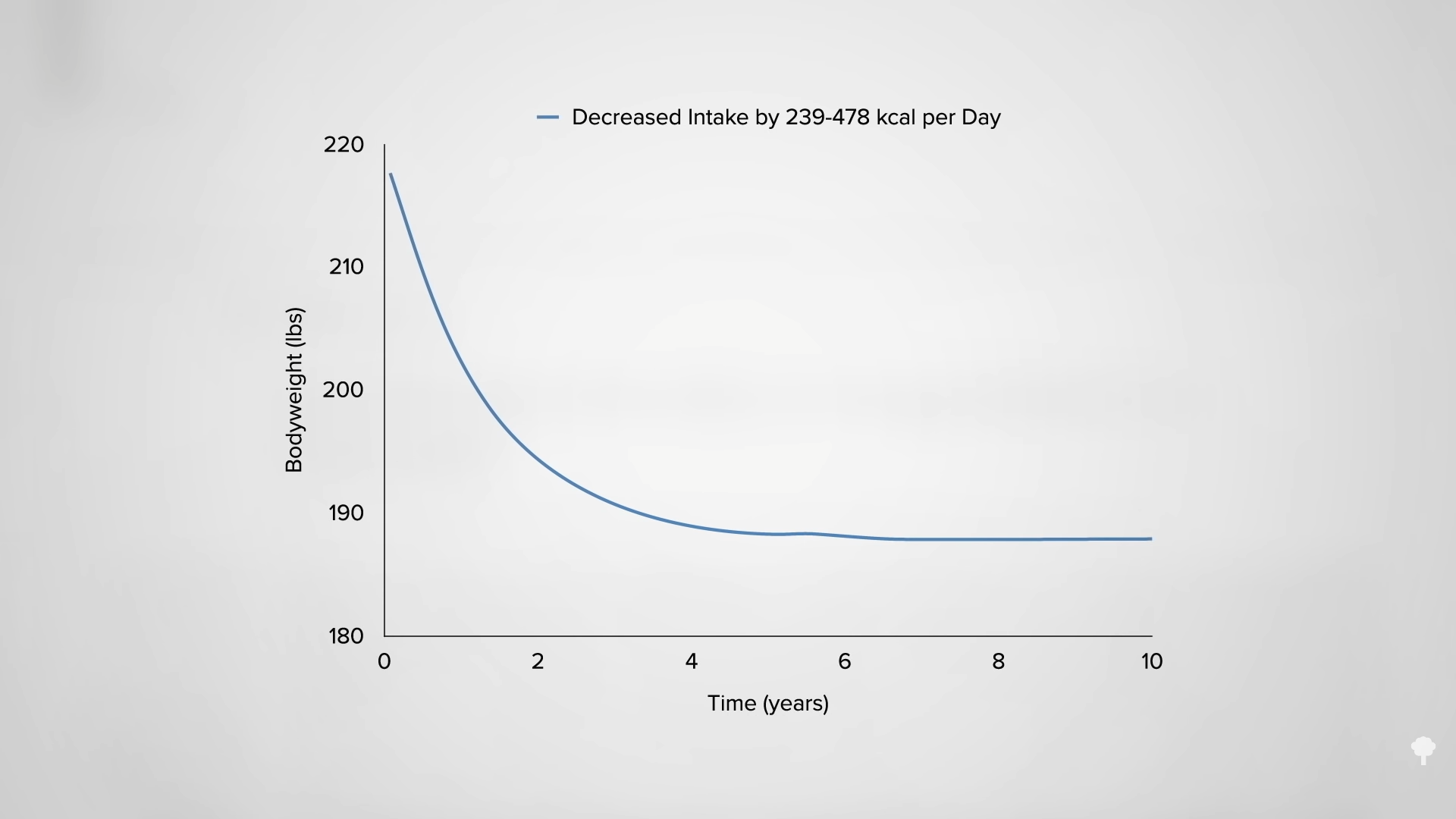
 What happened nine years later? “Therapeutic Fasting in Morbid Obesity” is the largest, longest follow-up study I could find. At least some of the fast-induced weight losses were maintained a year later by the great majority. After one year, 90 percent remained lighter than they had started, but after two years, three years, four years, and seven years, fewer and fewer patients maintained their weight loss. By nine years later, that number dropped to fewer than one in ten. By then, almost everyone had regained the weight they had initially fasted away, as you can see in the graph below and at 4:17 in my video. “Many patients thought that the temporary loss was worth the effort,” though. As a group, they had lost an average of about 60 pounds. They described improved health and quality of life and claimed that “reemployment was facilitated and earnings increased” during that period of time. But the fasting didn’t appear to result in any permanent change in eating habits for the vast majority.
What happened nine years later? “Therapeutic Fasting in Morbid Obesity” is the largest, longest follow-up study I could find. At least some of the fast-induced weight losses were maintained a year later by the great majority. After one year, 90 percent remained lighter than they had started, but after two years, three years, four years, and seven years, fewer and fewer patients maintained their weight loss. By nine years later, that number dropped to fewer than one in ten. By then, almost everyone had regained the weight they had initially fasted away, as you can see in the graph below and at 4:17 in my video. “Many patients thought that the temporary loss was worth the effort,” though. As a group, they had lost an average of about 60 pounds. They described improved health and quality of life and claimed that “reemployment was facilitated and earnings increased” during that period of time. But the fasting didn’t appear to result in any permanent change in eating habits for the vast majority.
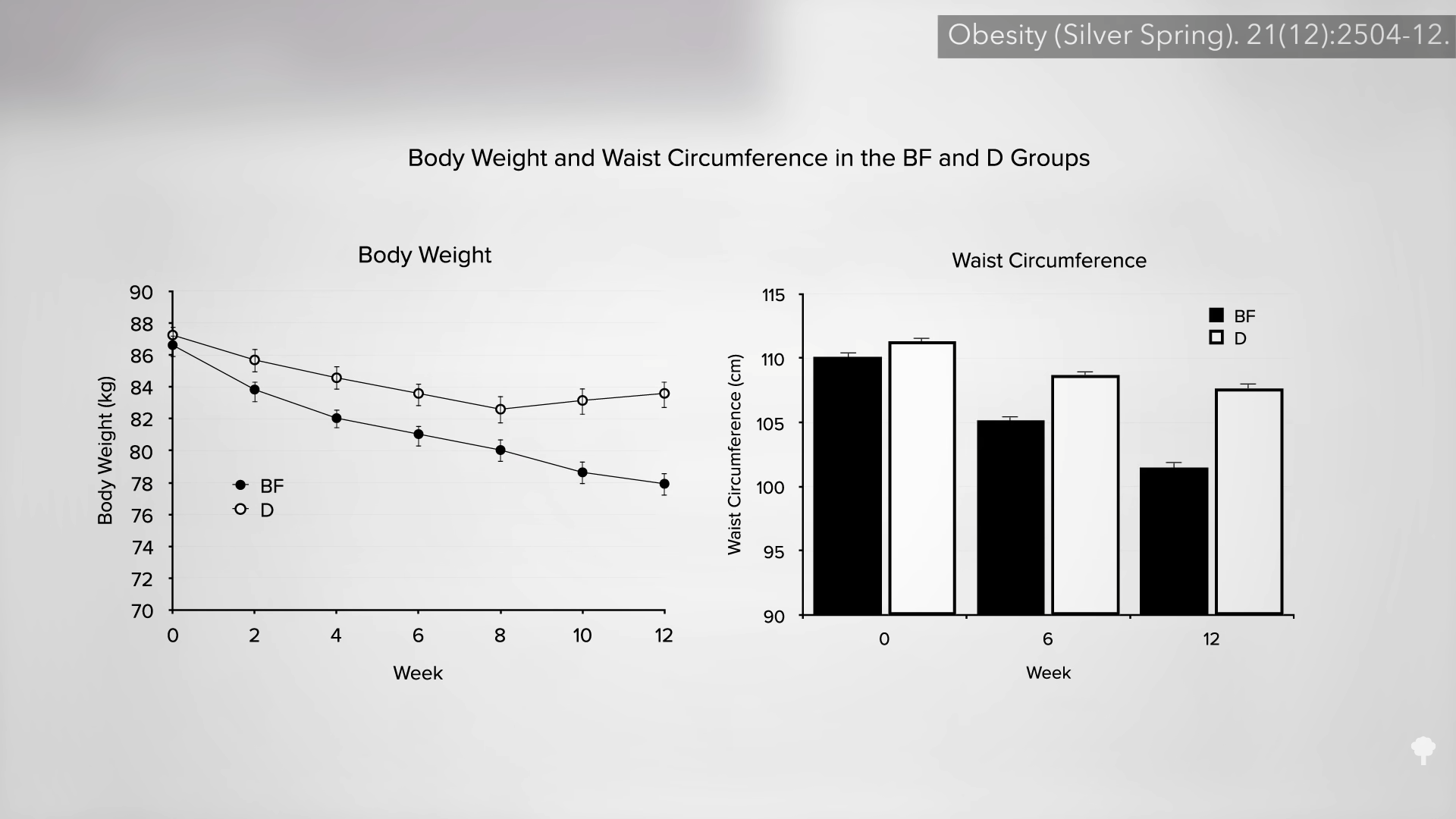
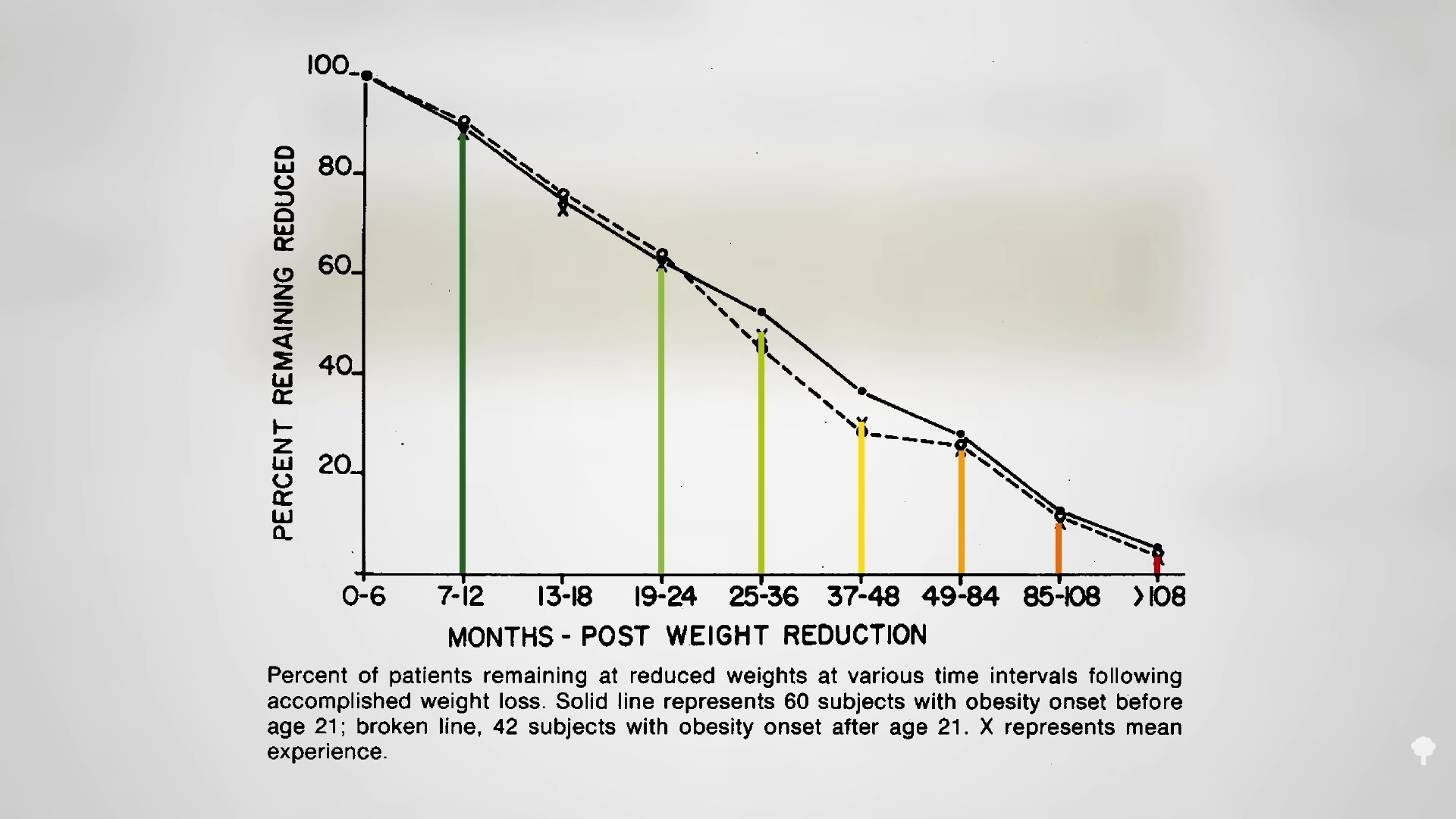 The small minority for whom fasting led to sustainable weight loss “all admit to a radical change in previous eating habits”; indeed, fasting only works long-term if it can act as a jumpstart to a healthier diet. In a retrospective long-term comparison of weight reduction after an inpatient stay at a naturopathic center, those who fasted lost more weight at the time, but they were back to the same weight at around seven years, as you can see in the graph below and at 5:14 in my video.
The small minority for whom fasting led to sustainable weight loss “all admit to a radical change in previous eating habits”; indeed, fasting only works long-term if it can act as a jumpstart to a healthier diet. In a retrospective long-term comparison of weight reduction after an inpatient stay at a naturopathic center, those who fasted lost more weight at the time, but they were back to the same weight at around seven years, as you can see in the graph below and at 5:14 in my video.
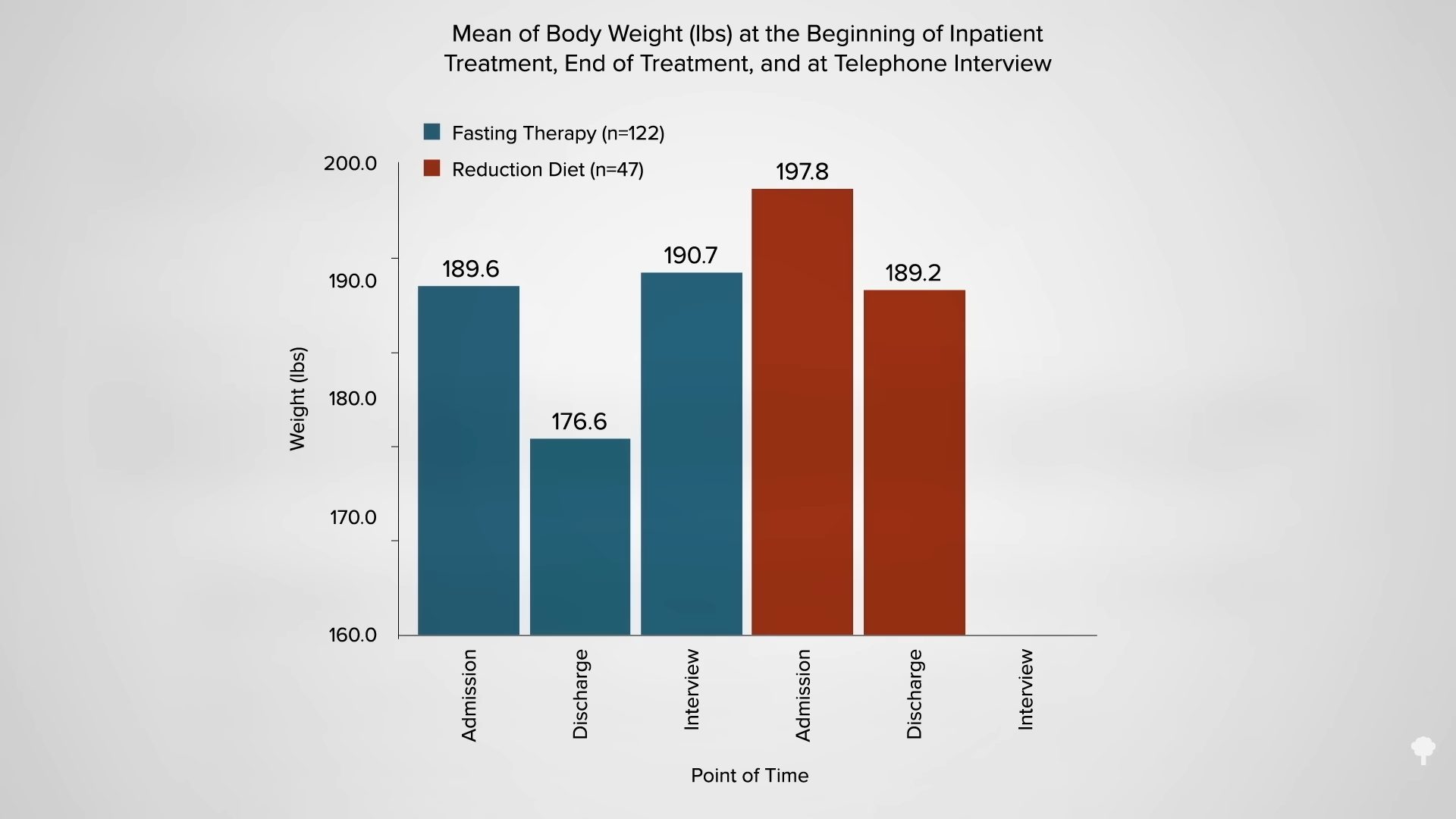
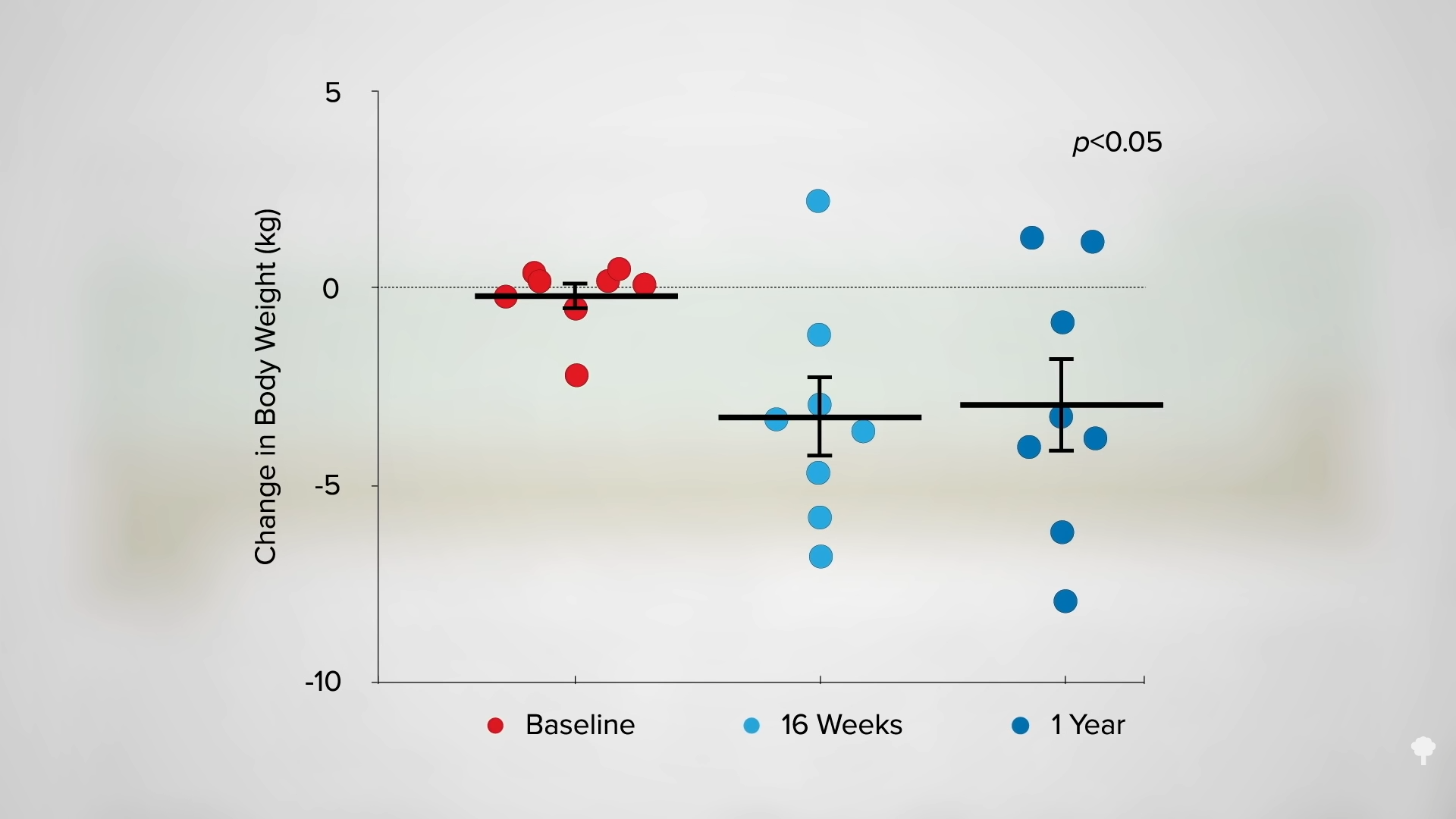
It’s no surprise since most reported returning to the same diet they had been on before. However, those who were placed instead on a healthier, more whole food, plant-based diet were more likely to make persistent changes in their eating and, seven years later, were lighter than when they started, as you can see in the graph below and at 5:36 in my video.
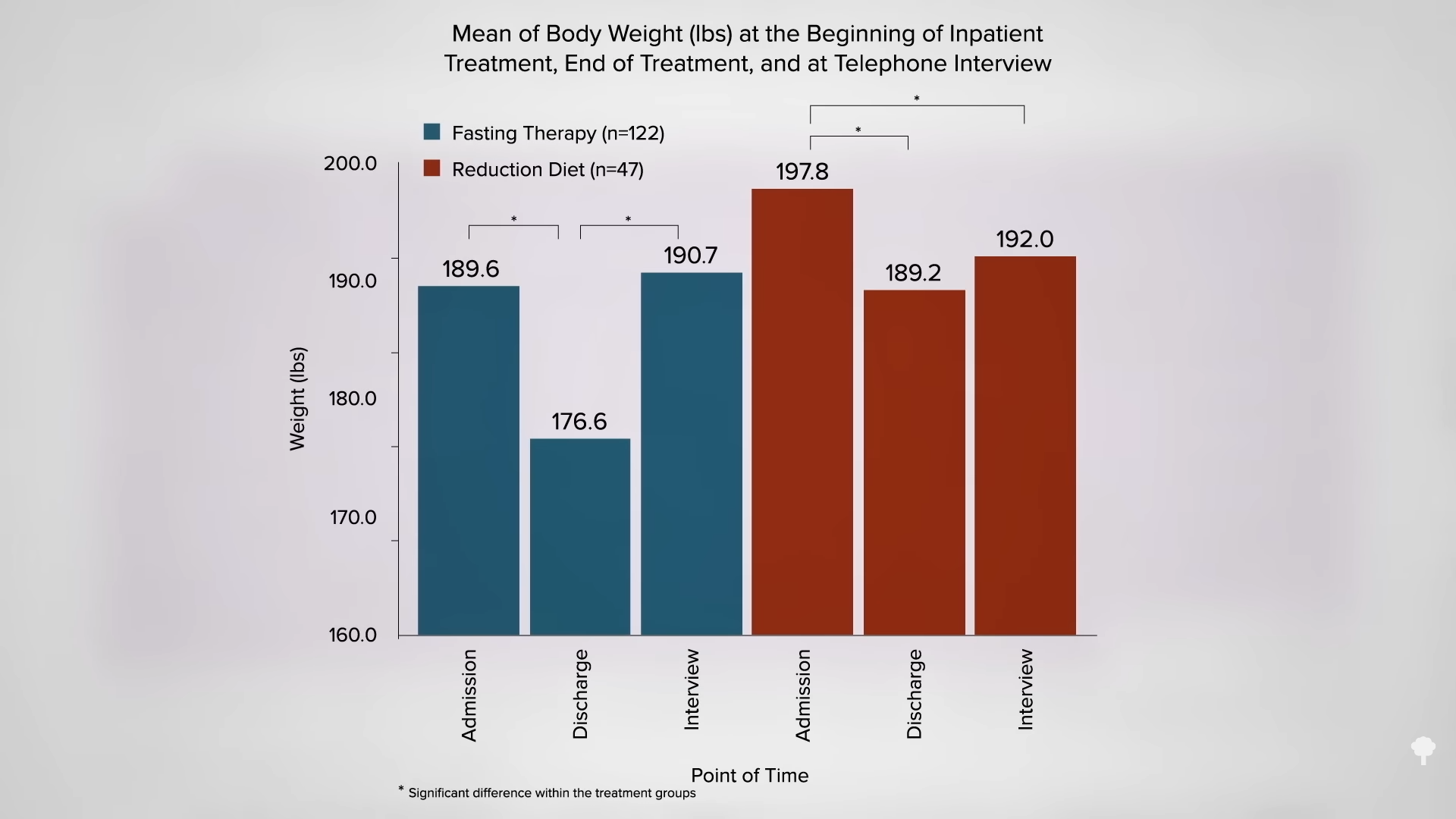
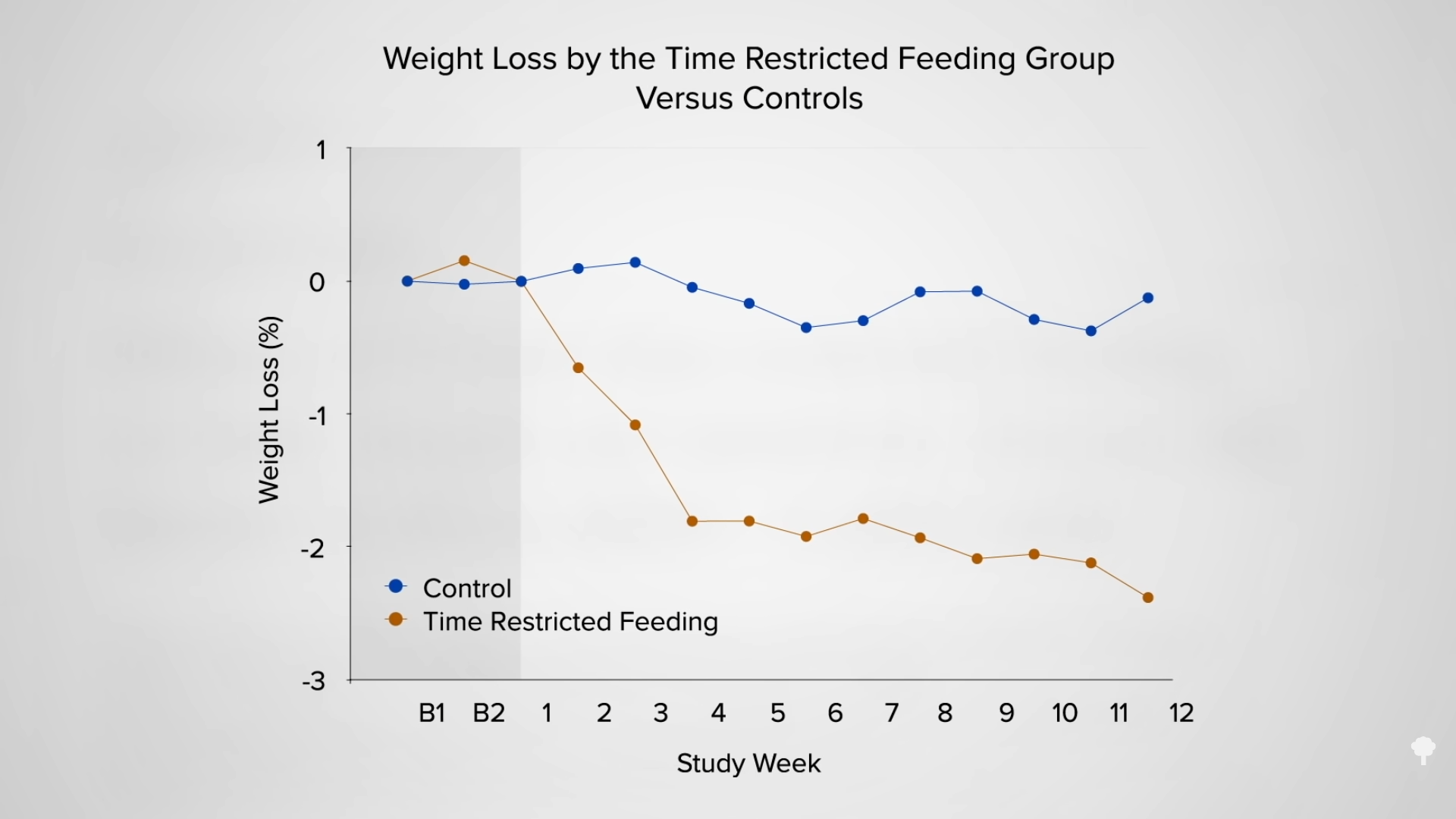
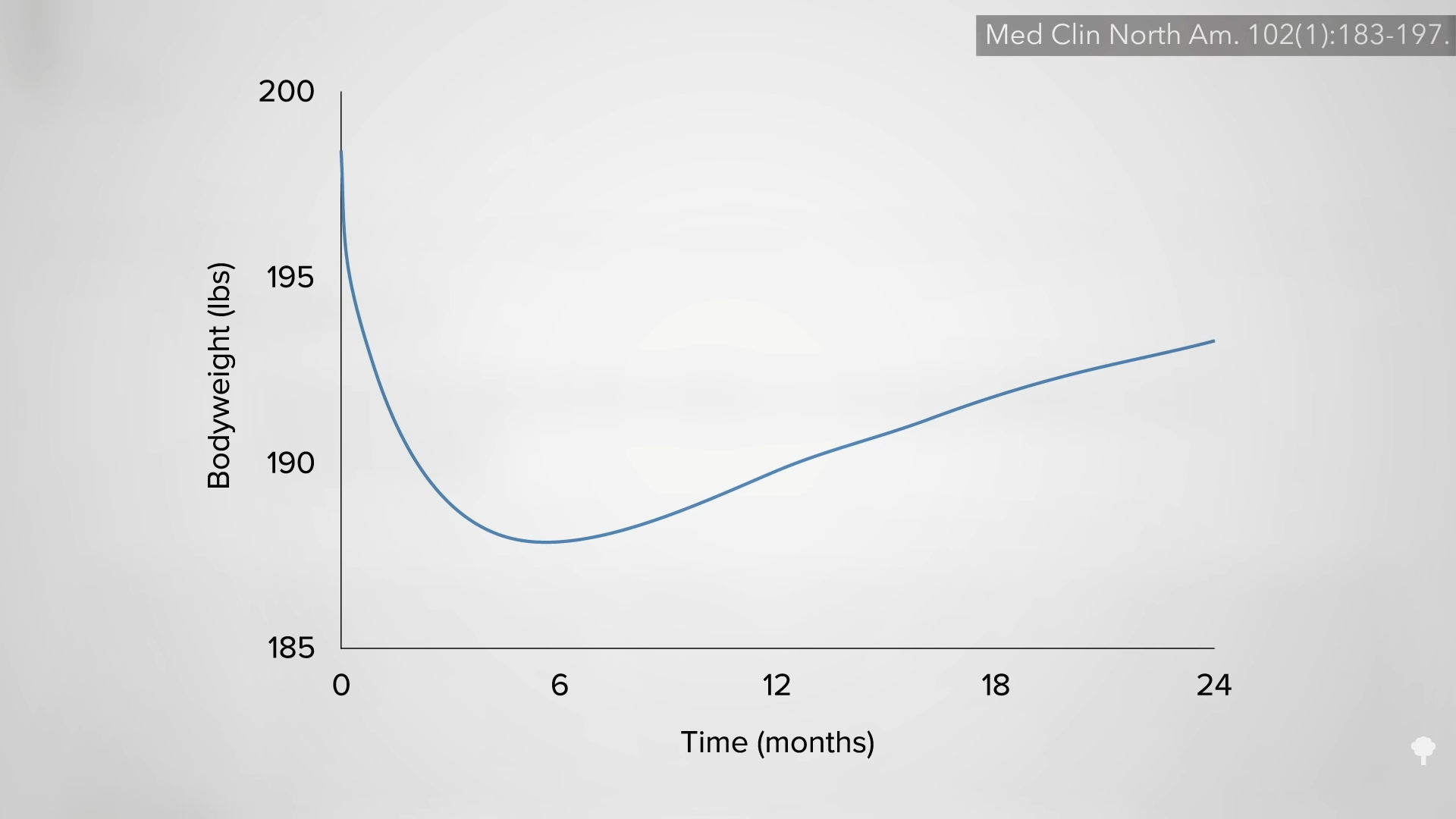
Why can’t you have it both ways, though? Use fasting to kickstart a big drop, then start a healthier diet. The problem is that the big drop is largely illusory, as you can see in the graph below and at 5:48 in my video.
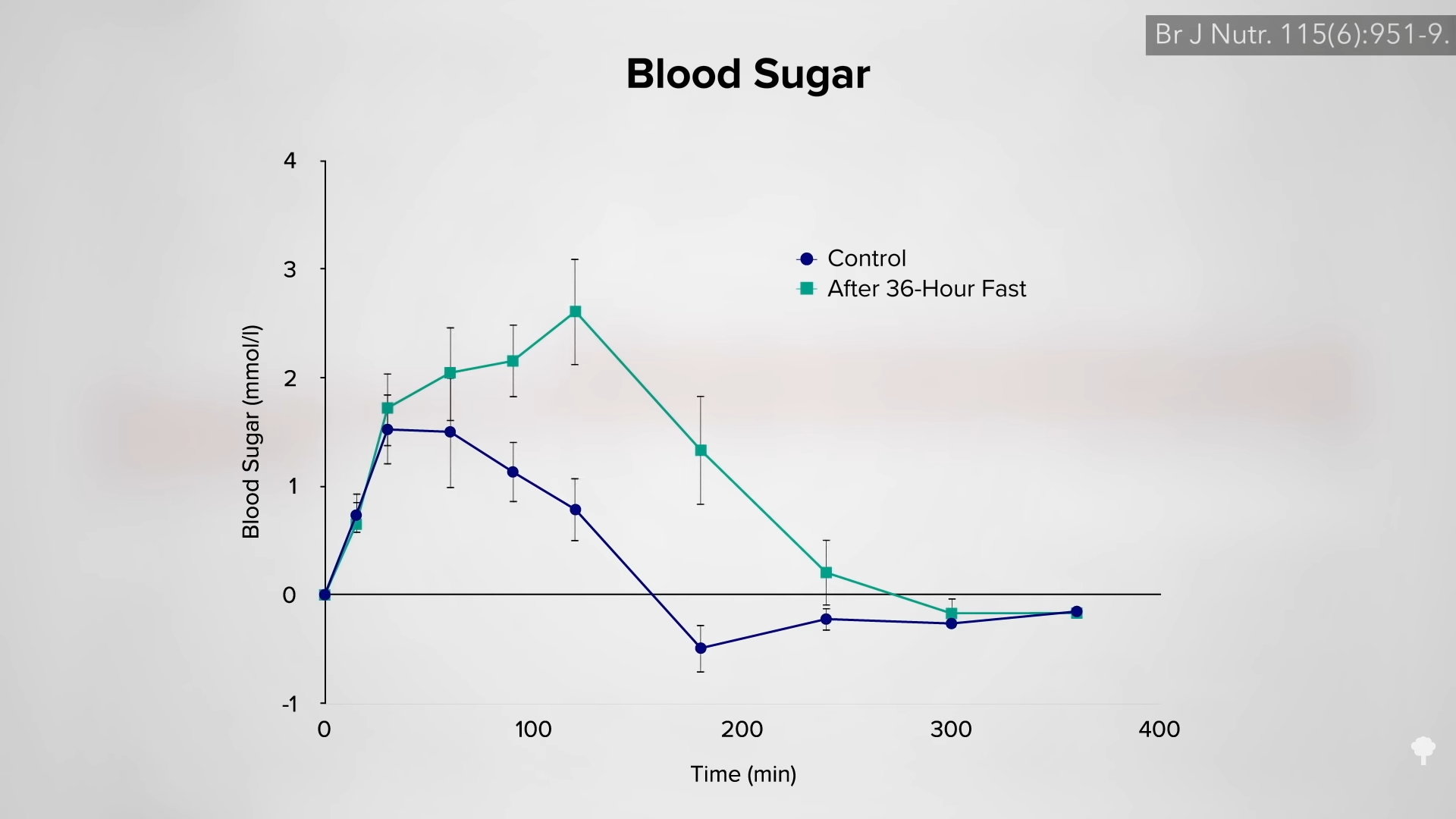
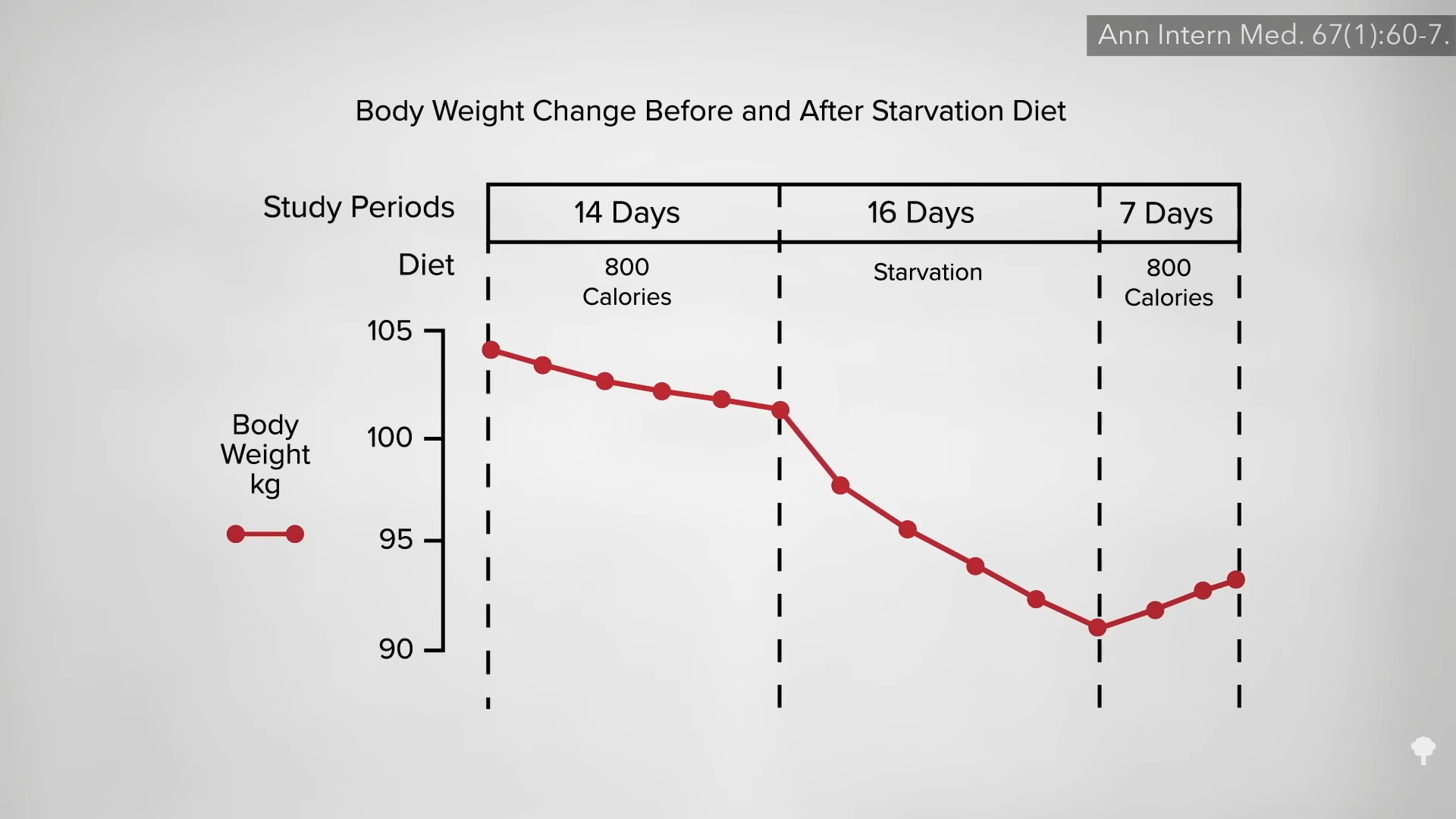 Fasting for a week or two can cause more weight loss than caloric restriction, but, paradoxically, it may actually lead to less loss of body fat. How can eating fewer calories lead to less fat loss? Because during fasting, your body starts cannibalizing itself and burning more of your own protein for fuel. Emperor penguins, elephant seals, and hibernating bears can survive by just burning fat without dipping into their muscles, but our voracious big brains appear to need at least a trickle of blood sugar. If we aren’t eating any carbohydrates, our body is forced to start turning our protein into sugar to burn. Even getting just a few grams of carbs—from adding honey to water when fasting, for instance—can cut protein loss up to 50 percent.
Fasting for a week or two can cause more weight loss than caloric restriction, but, paradoxically, it may actually lead to less loss of body fat. How can eating fewer calories lead to less fat loss? Because during fasting, your body starts cannibalizing itself and burning more of your own protein for fuel. Emperor penguins, elephant seals, and hibernating bears can survive by just burning fat without dipping into their muscles, but our voracious big brains appear to need at least a trickle of blood sugar. If we aren’t eating any carbohydrates, our body is forced to start turning our protein into sugar to burn. Even getting just a few grams of carbs—from adding honey to water when fasting, for instance—can cut protein loss up to 50 percent.
What about adding exercise to prevent the loss of lean tissues during a fast? That may make it worse! At rest, most of your heart and muscle energy needs can be met with fat, but if you start exercising, some of the blood sugar meant for your brain starts getting snatched up and your body may have to break down even more protein.
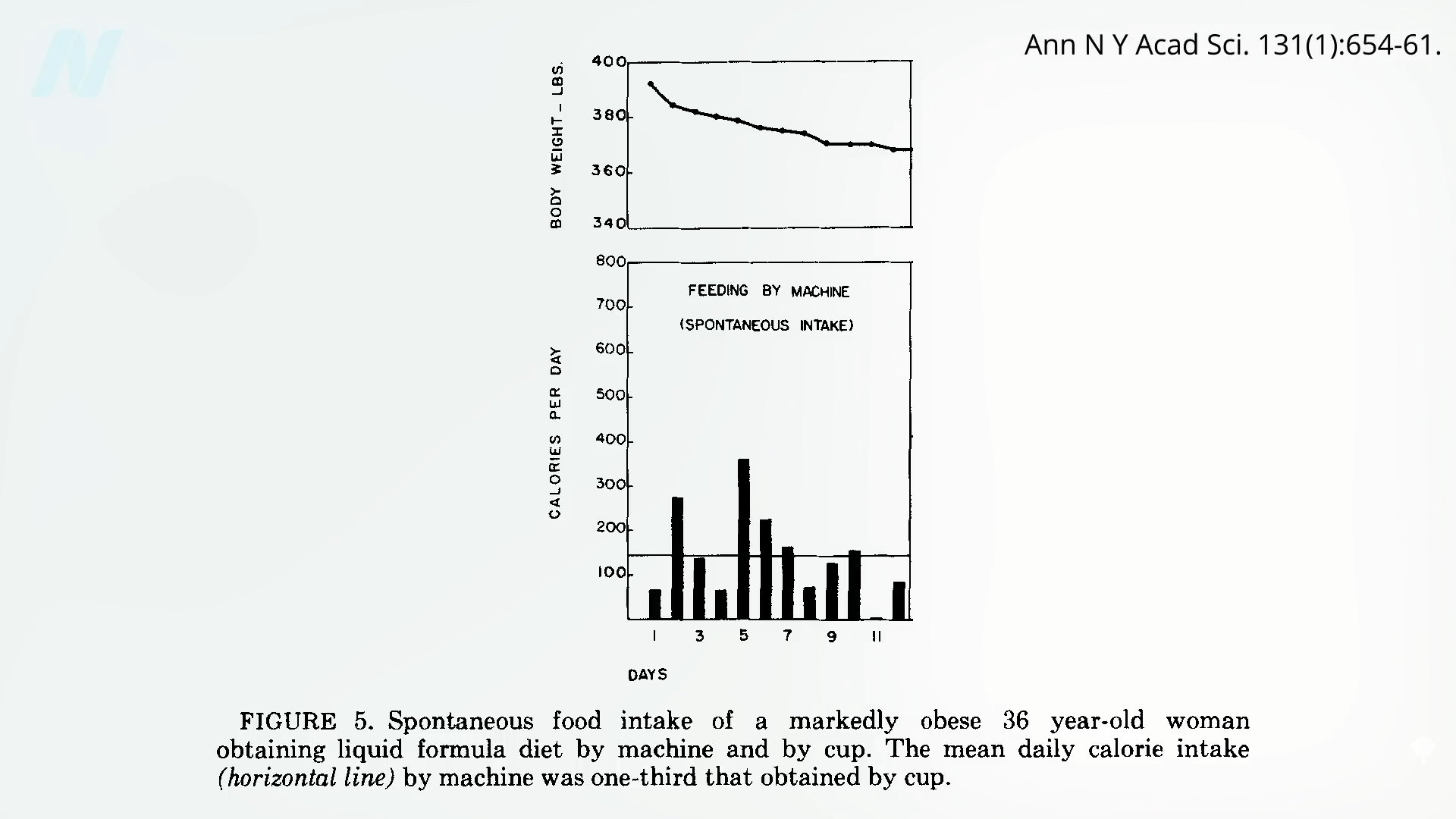
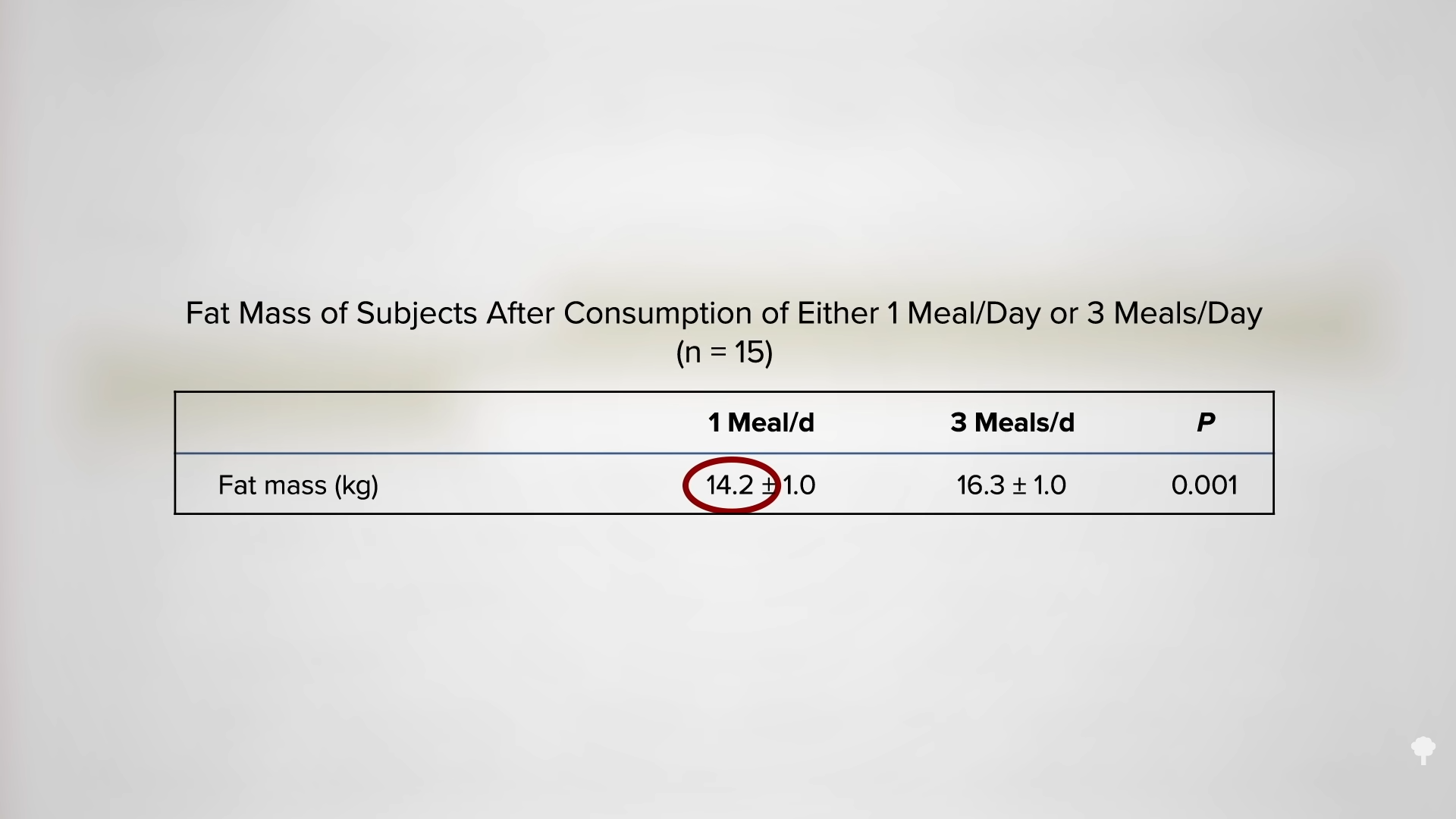
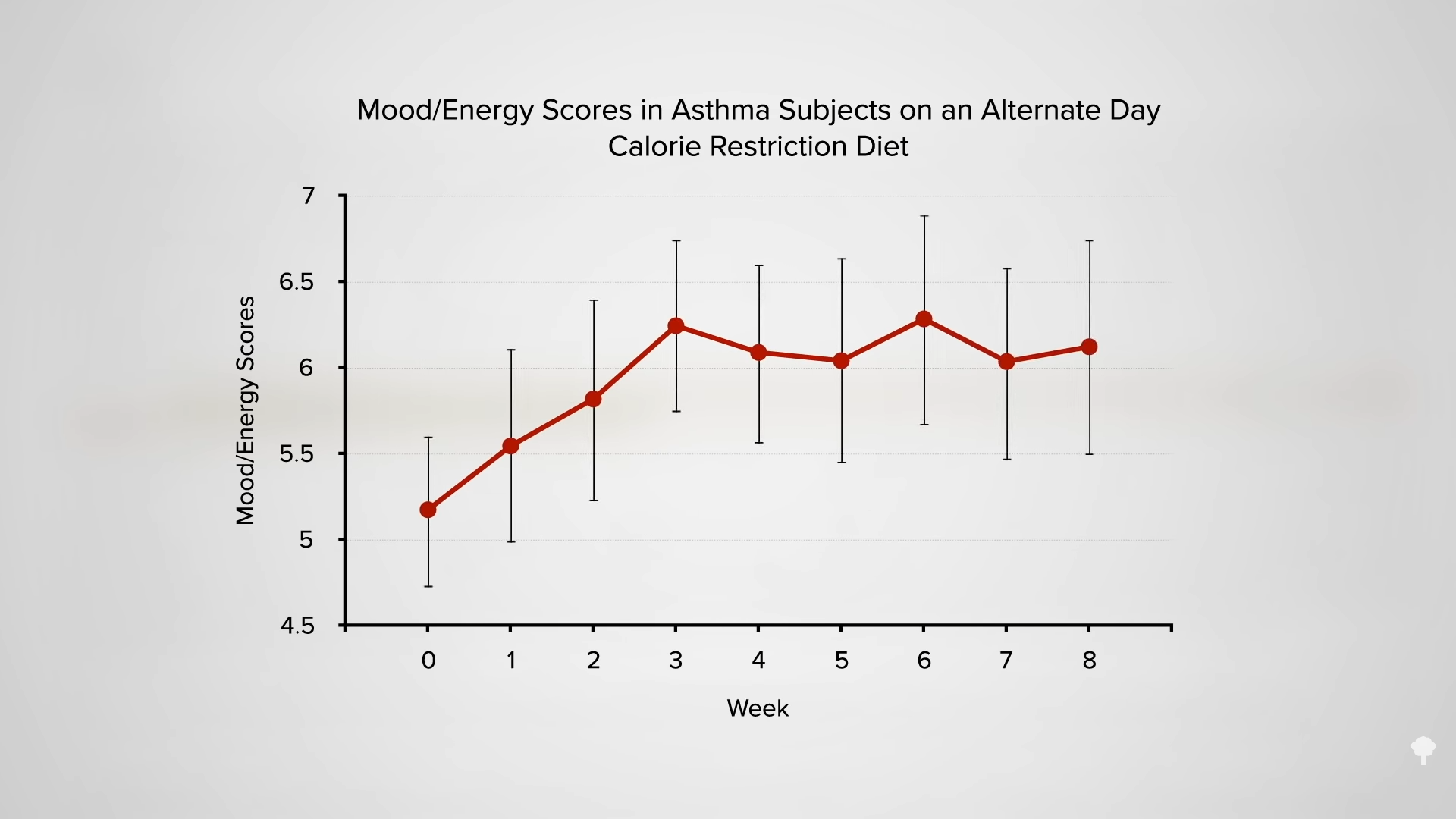
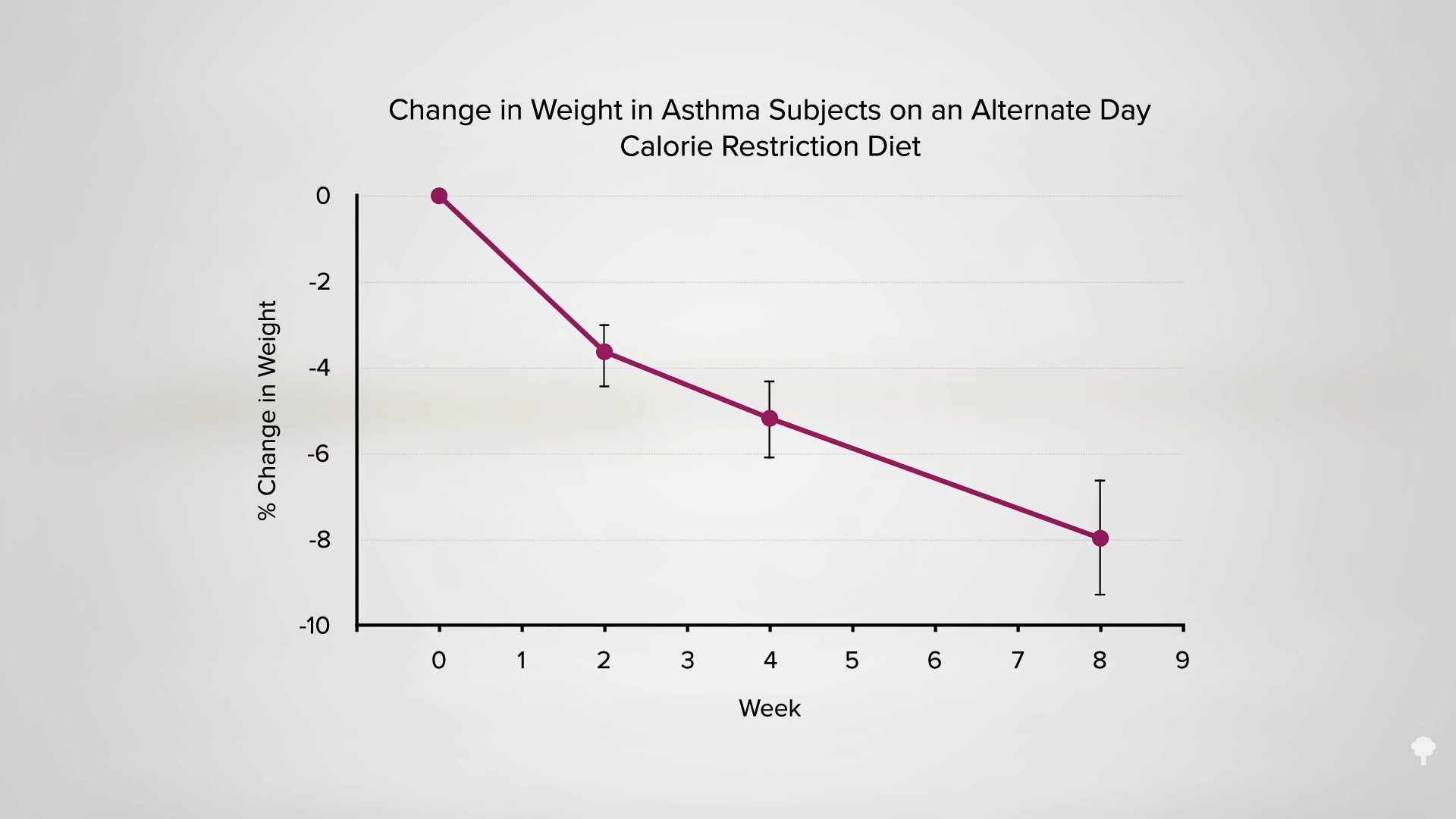
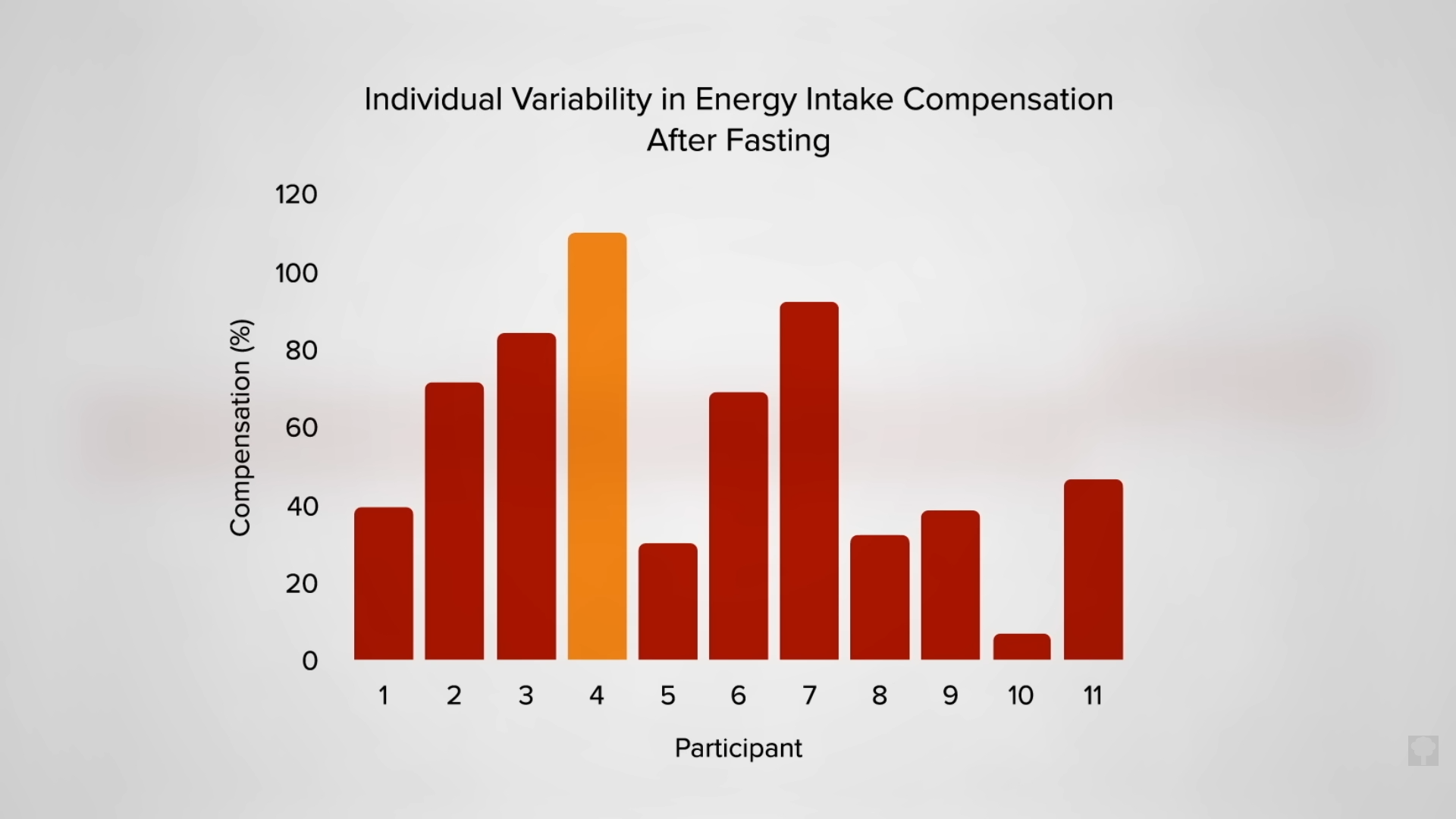
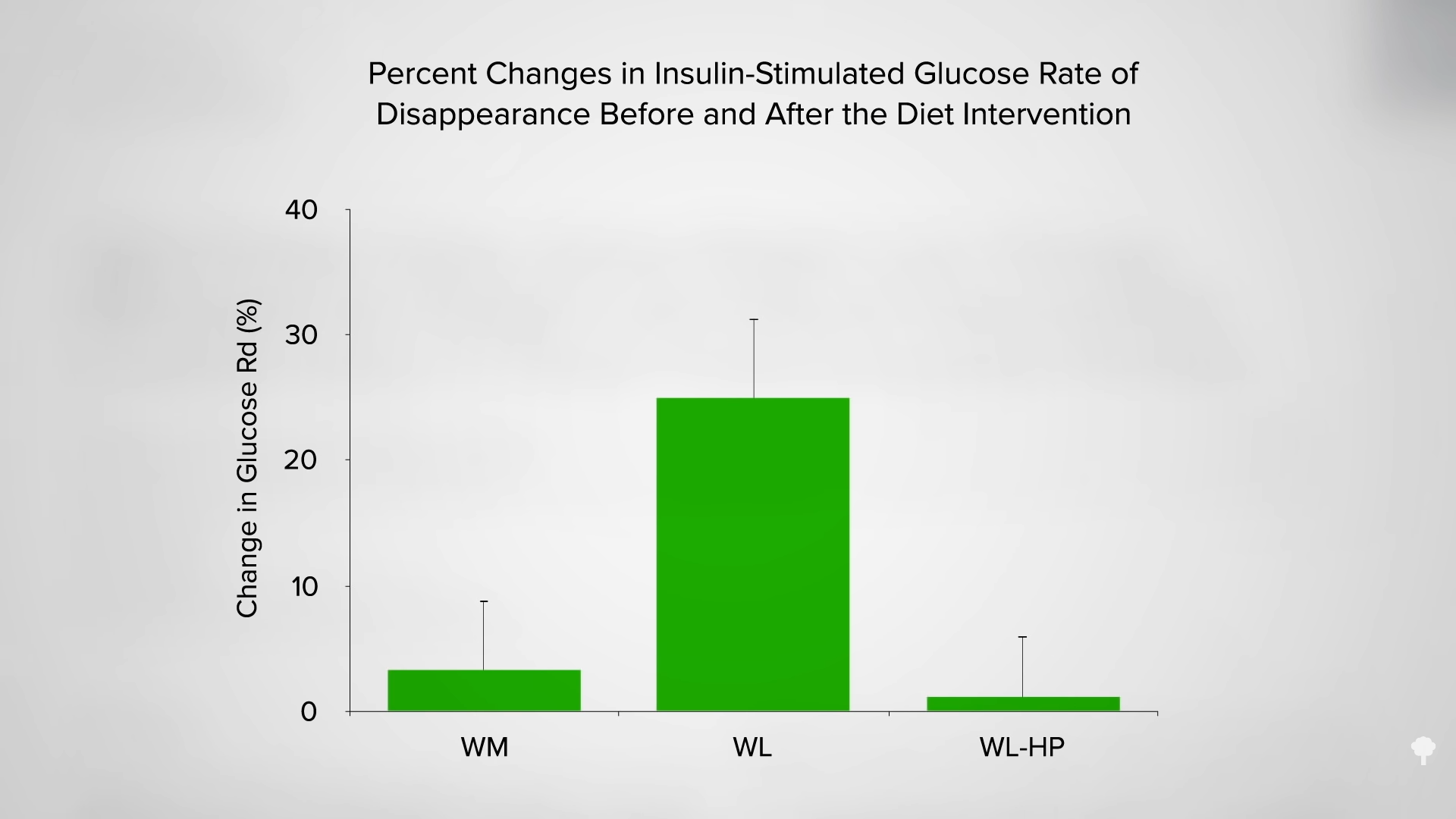
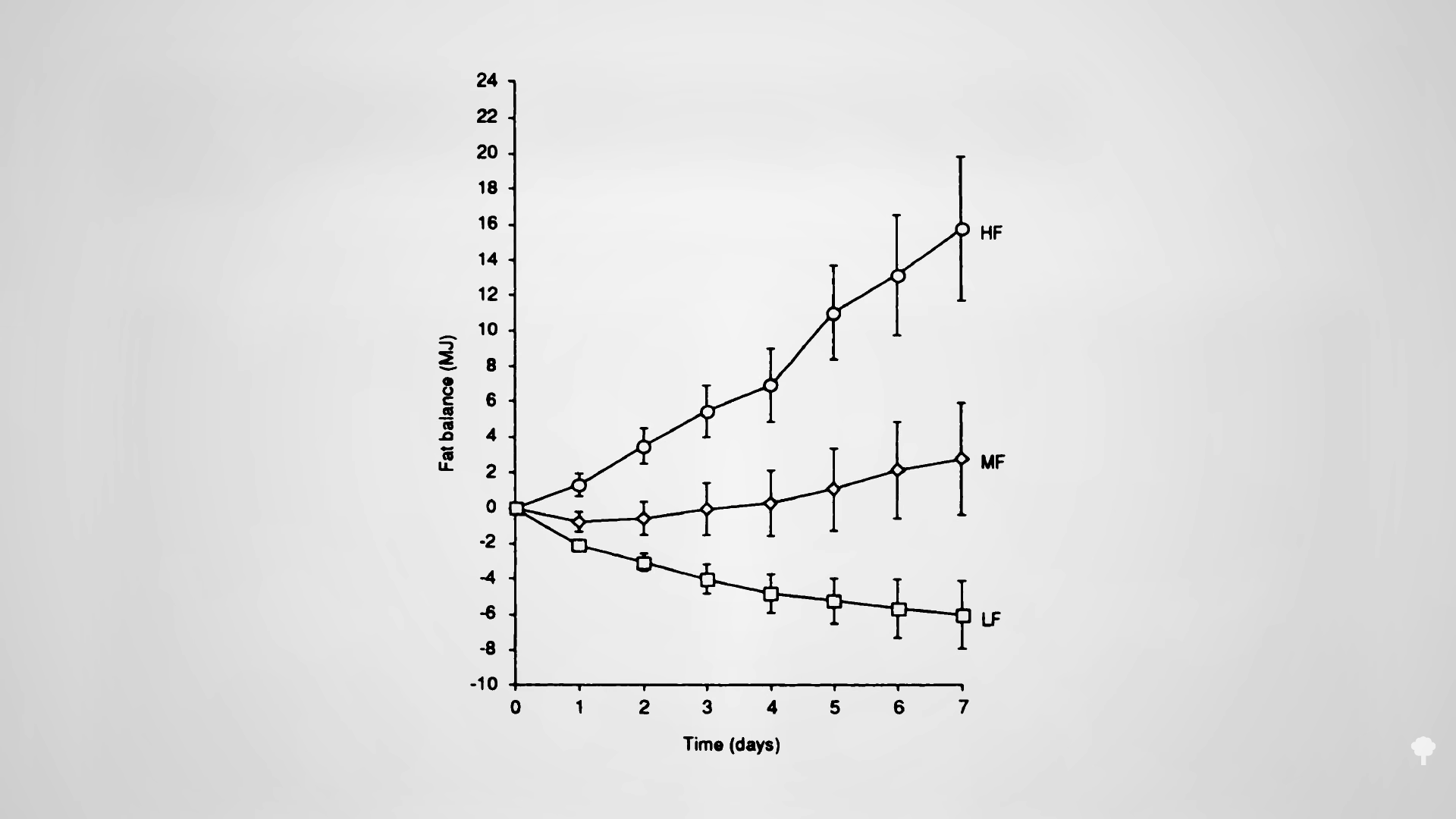
As you can see in the graph below and at 7:00 in my video, less than half of the weight loss during the first few weeks of fasting ends up coming from your fat stores. So, even if you double your daily weight loss on a fast, you may be actually losing less body fat.
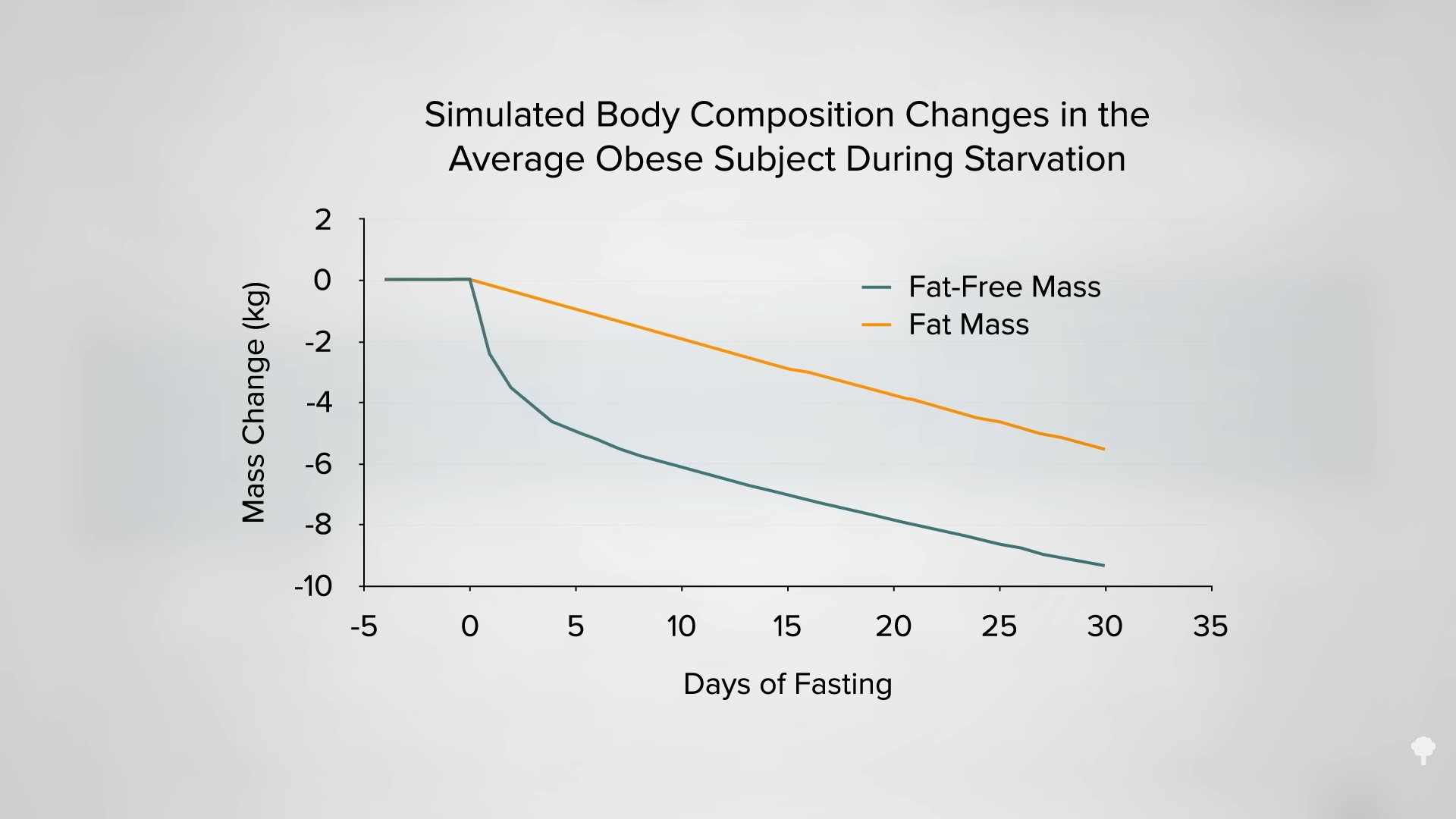
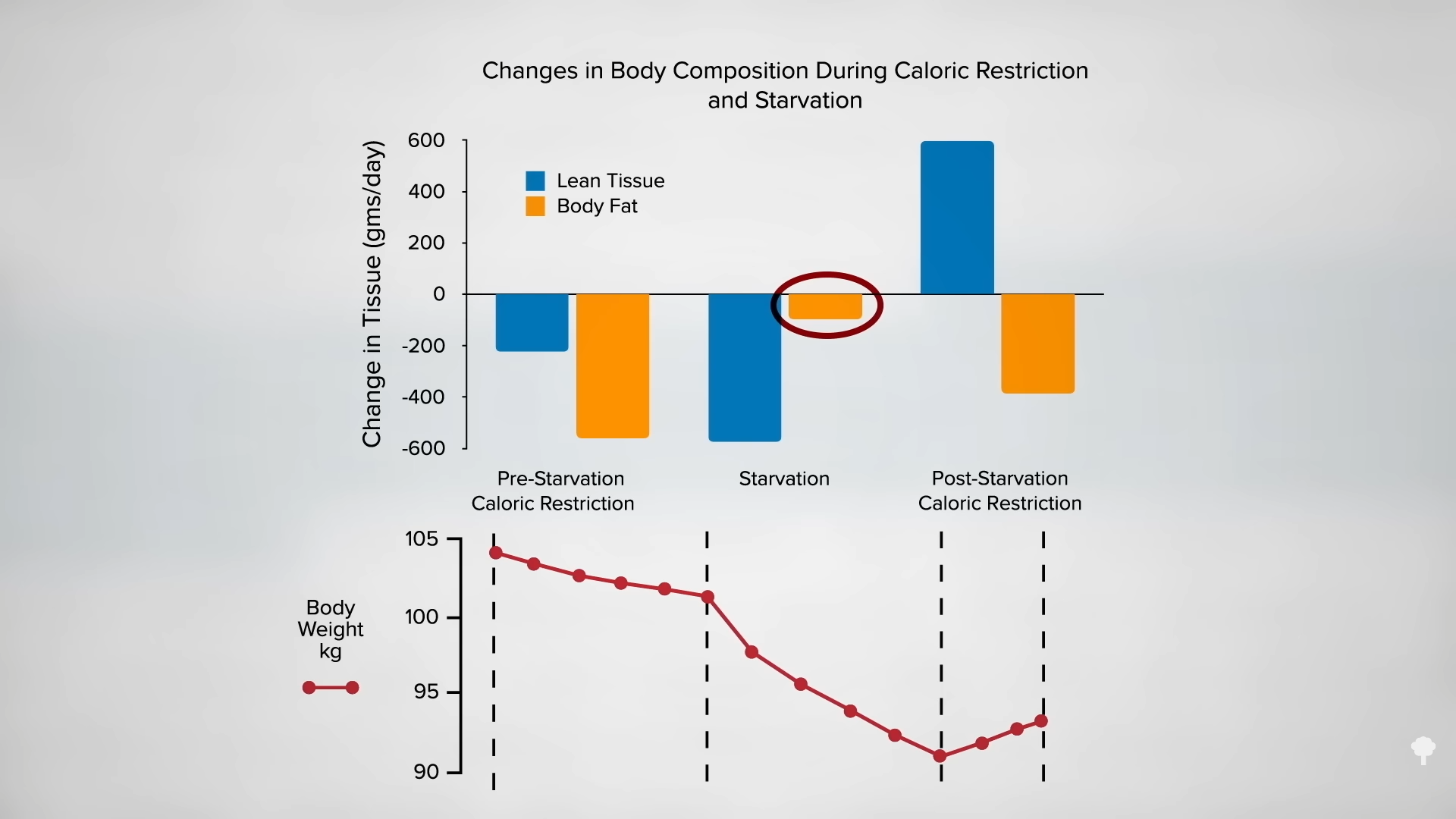
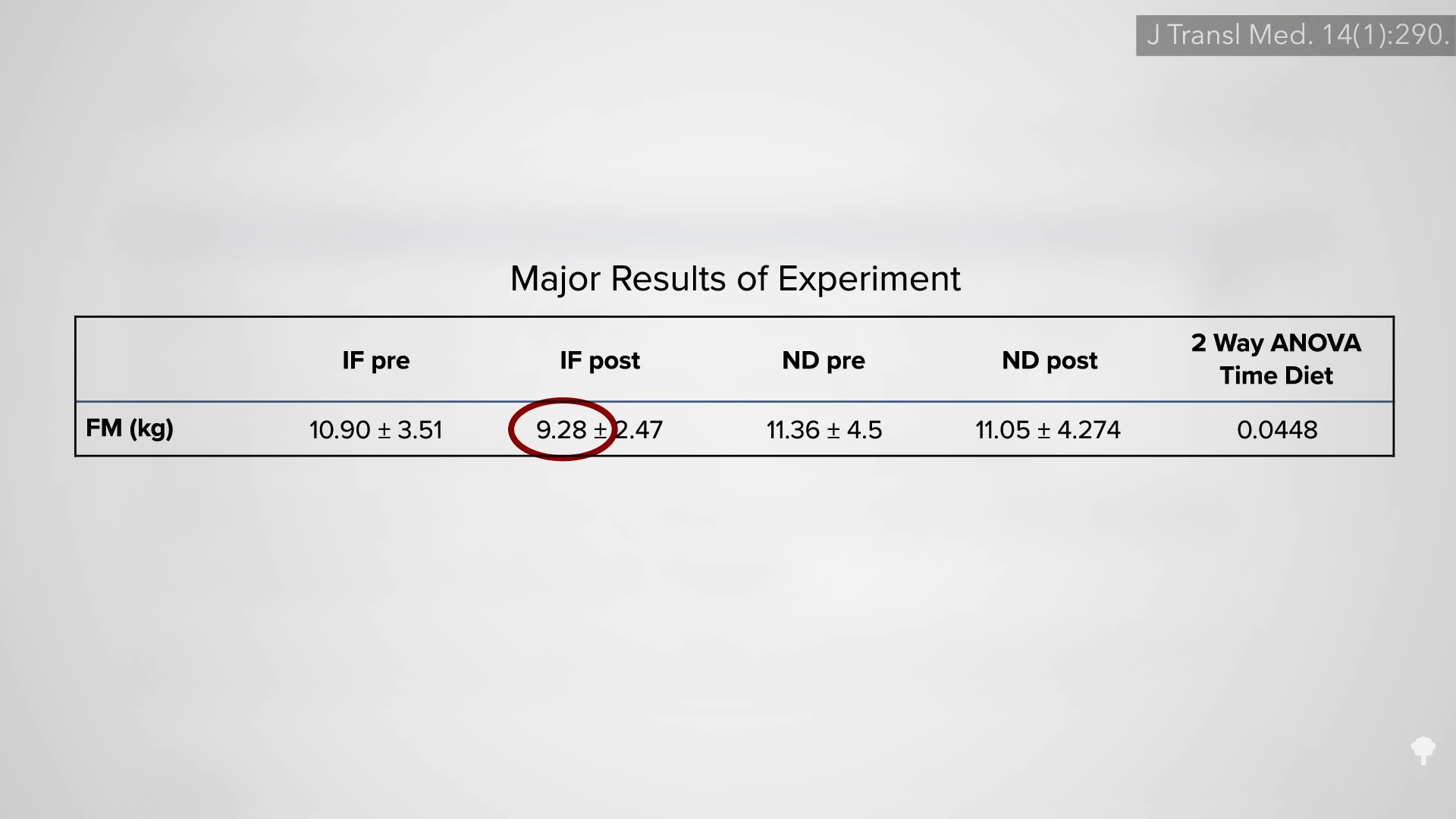
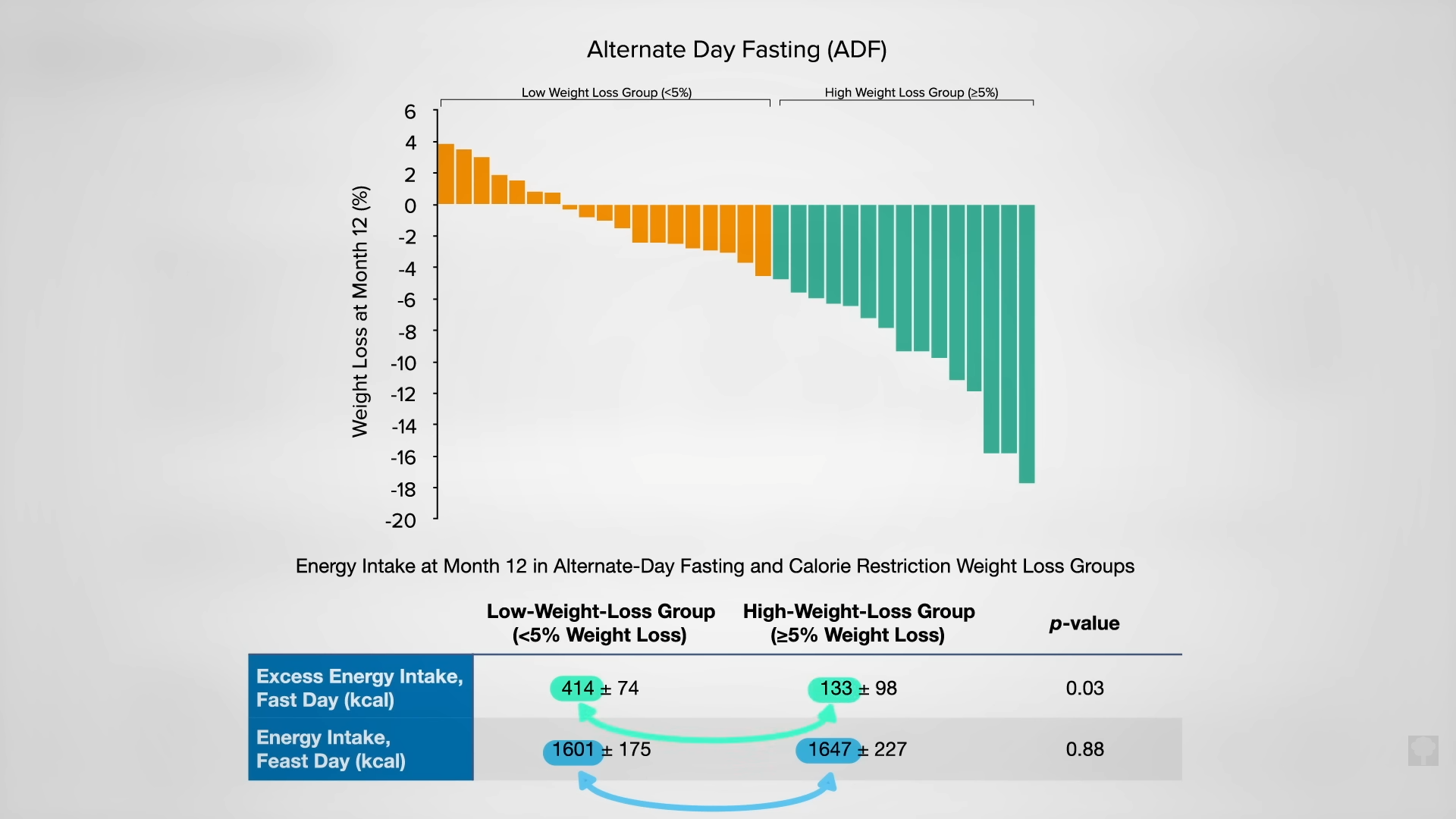
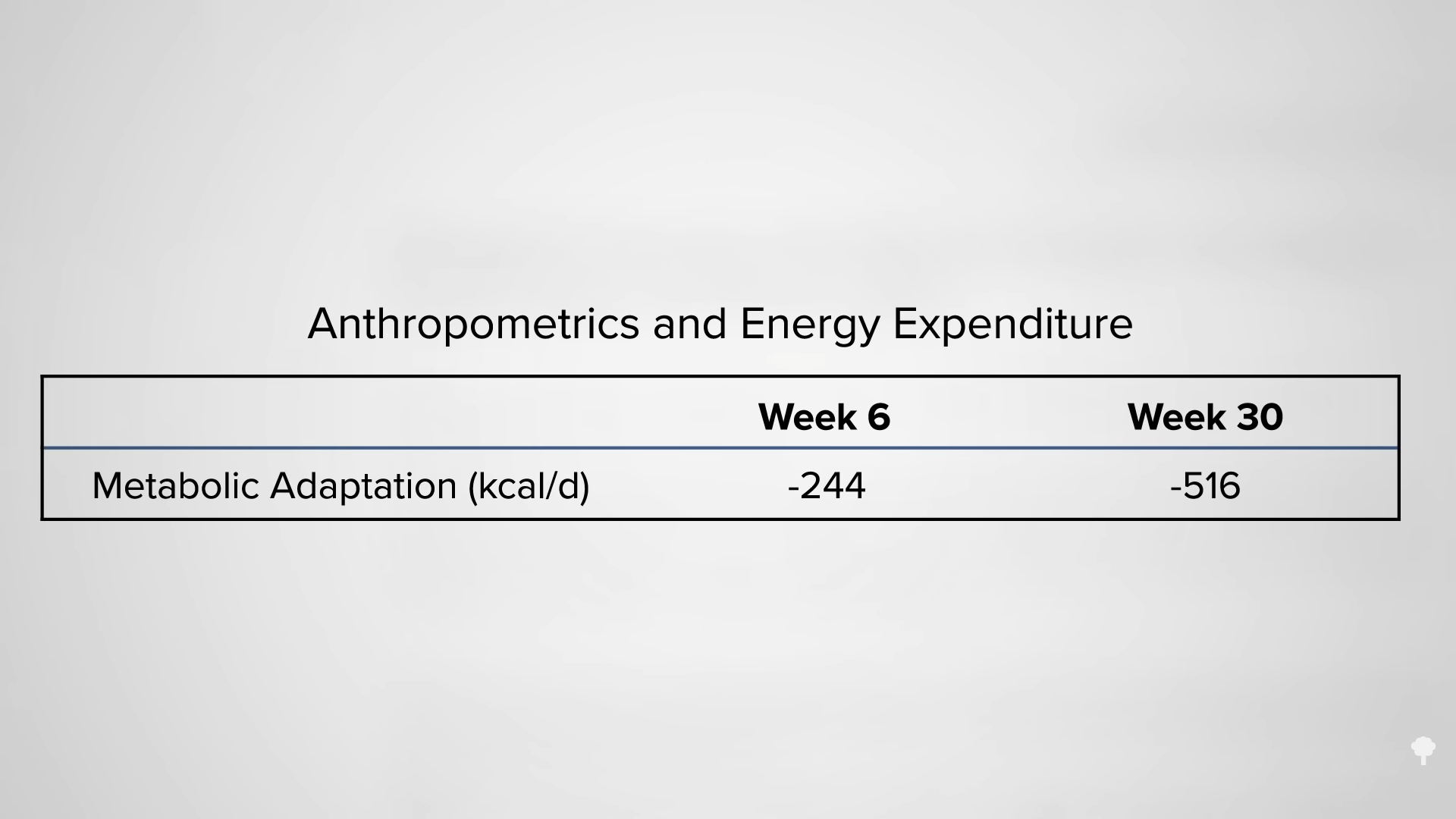
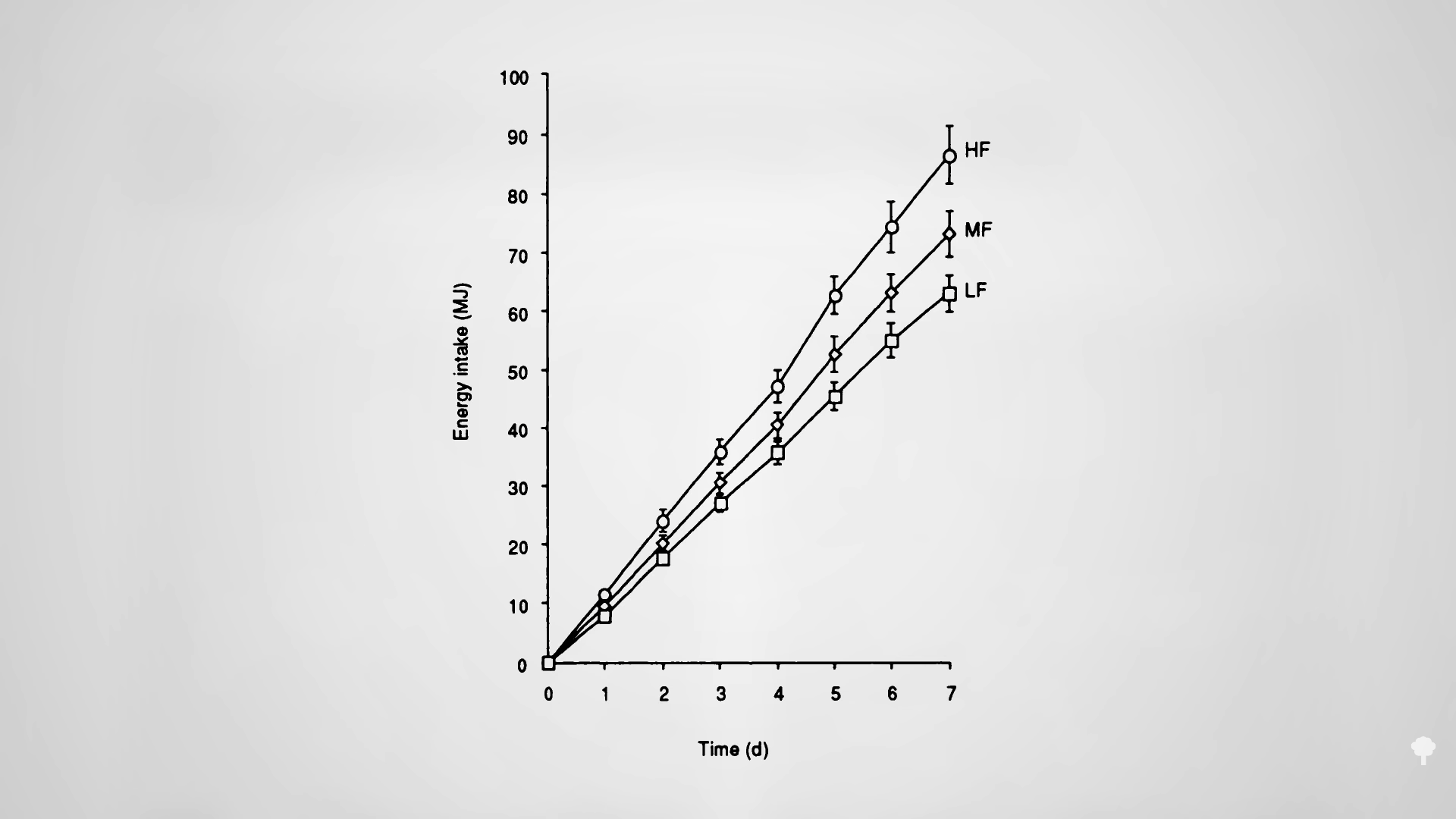
In an NIH-funded study, obese individuals were placed on an 800-calorie-a-day diet for two weeks and steadily lost about a pound of body fat a day. They were then switched to about two weeks of zero calories and started losing more protein and water. On average, though, they only lost a few ounces of fat daily. When they were subsequently switched back to the initial 800-calories-a-day diet for a week, they rapidly replaced the protein and water, so the scale registered their weight as going up, but their body fat loss accelerated back to the approximate pound a day. The scale made it look as though they were doing better when they were completely fasting, but the reality is they were doing worse. So, during the five-week experiment, they would have lost even more body fat had they stuck with their calorie-restricted diet rather than completely stopping eating in the middle. They would have lost more body fat by eating more calories. Fasting for a week or two can interfere with the loss of body fat, rather than accelerate it. You can see a series of graphs depicting this from 7:13 in my video, including the one below.
 This is the follow-up to Benefits of Fasting for Weight Loss Put to the Test. It seems fasting may only work long-term if it can act as a jumpstart to a healthier diet, and just fasting for a week or two can be counterproductive, like the keto diet. Is it even safe to fast longer than that? Find out in Is Fasting for Weight Loss Safe?.
This is the follow-up to Benefits of Fasting for Weight Loss Put to the Test. It seems fasting may only work long-term if it can act as a jumpstart to a healthier diet, and just fasting for a week or two can be counterproductive, like the keto diet. Is it even safe to fast longer than that? Find out in Is Fasting for Weight Loss Safe?.
For more on the keto story and more on fasting for weight loss, see related videos below.
I’ve done my third live webinar on fasting, Fasting and Cancer. Those videos are also on NutritionFacts.org.


 We appear to
We appear to 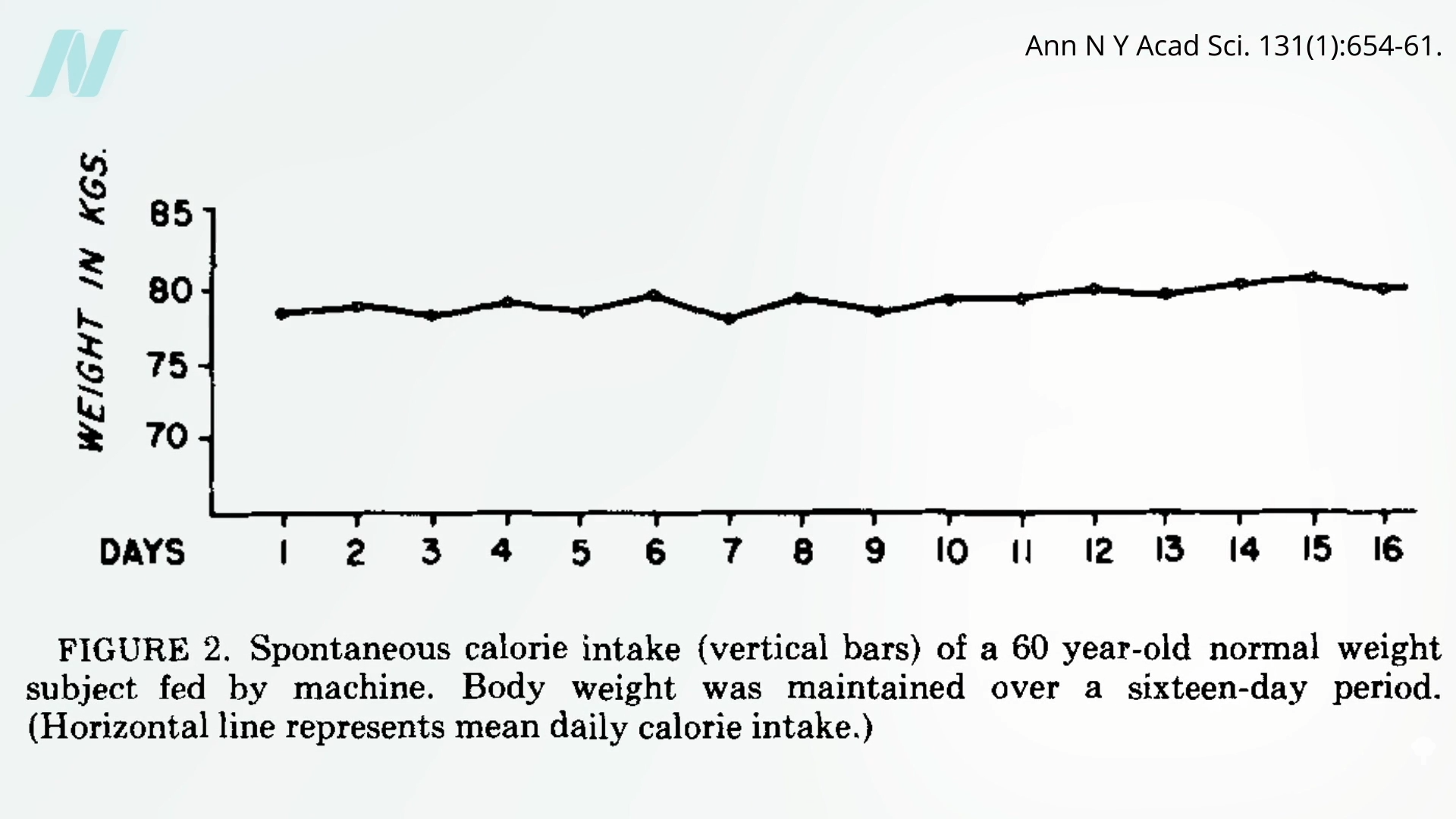
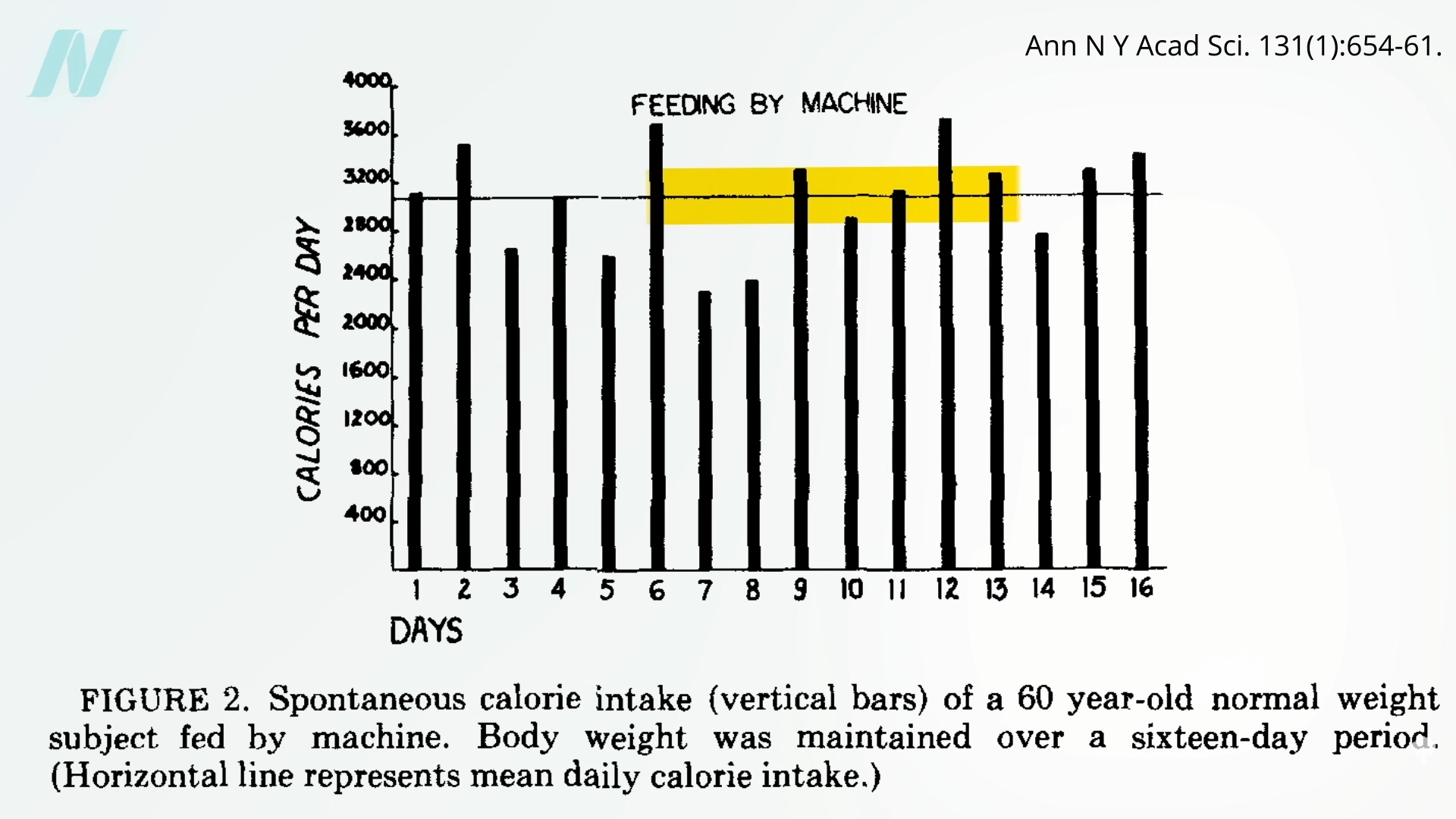
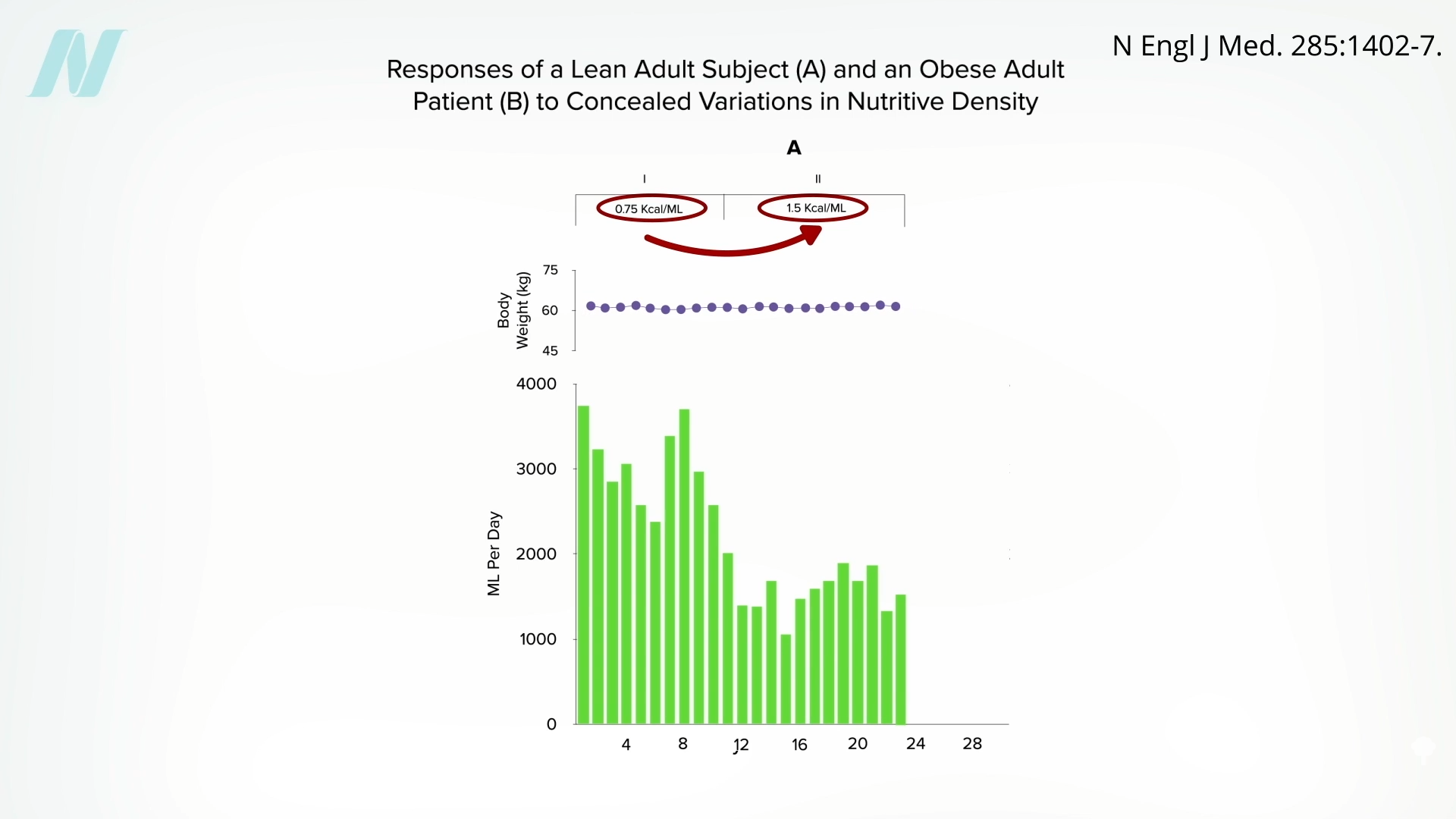
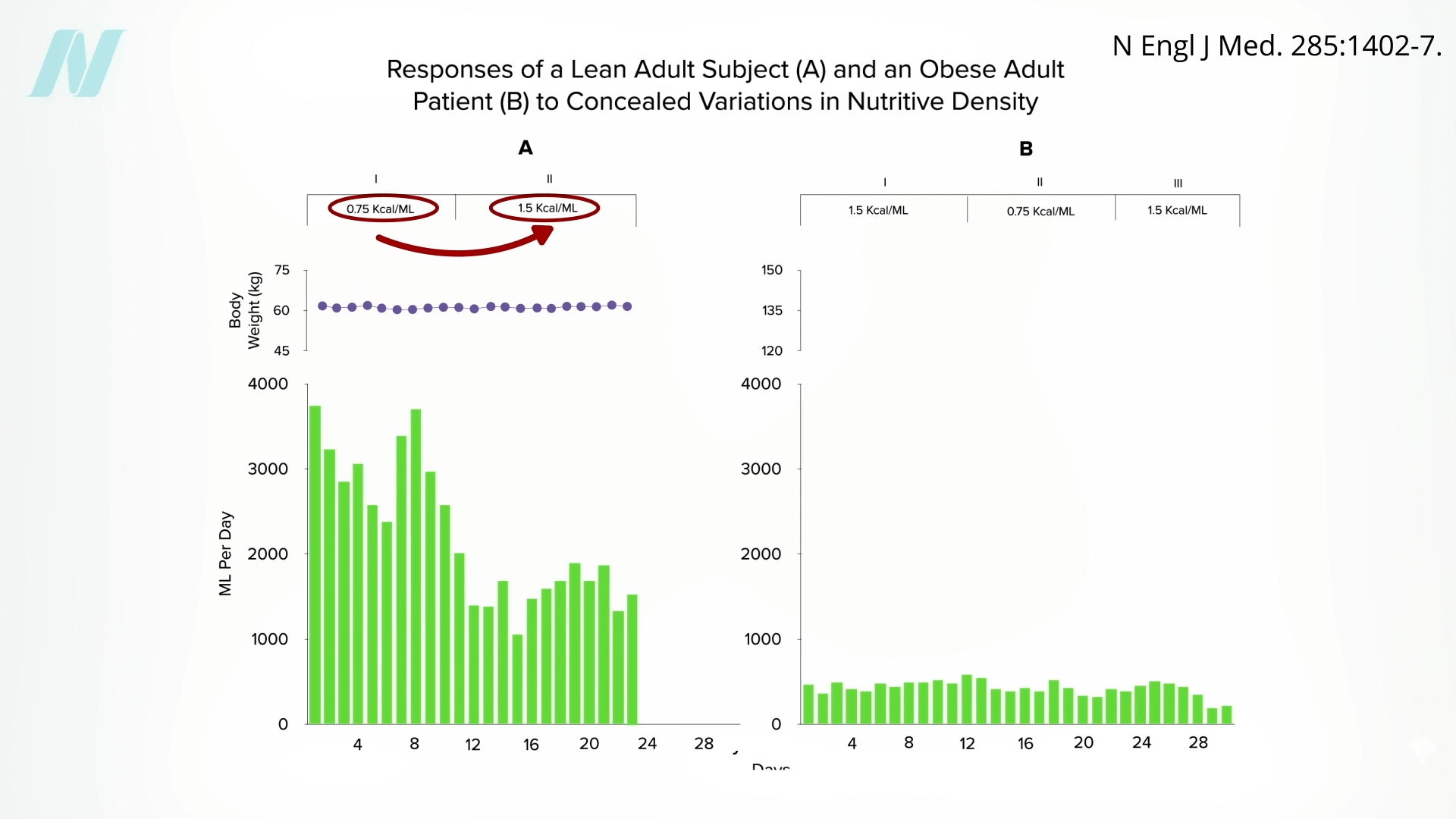 Might the brains of persons with obesity somehow
Might the brains of persons with obesity somehow 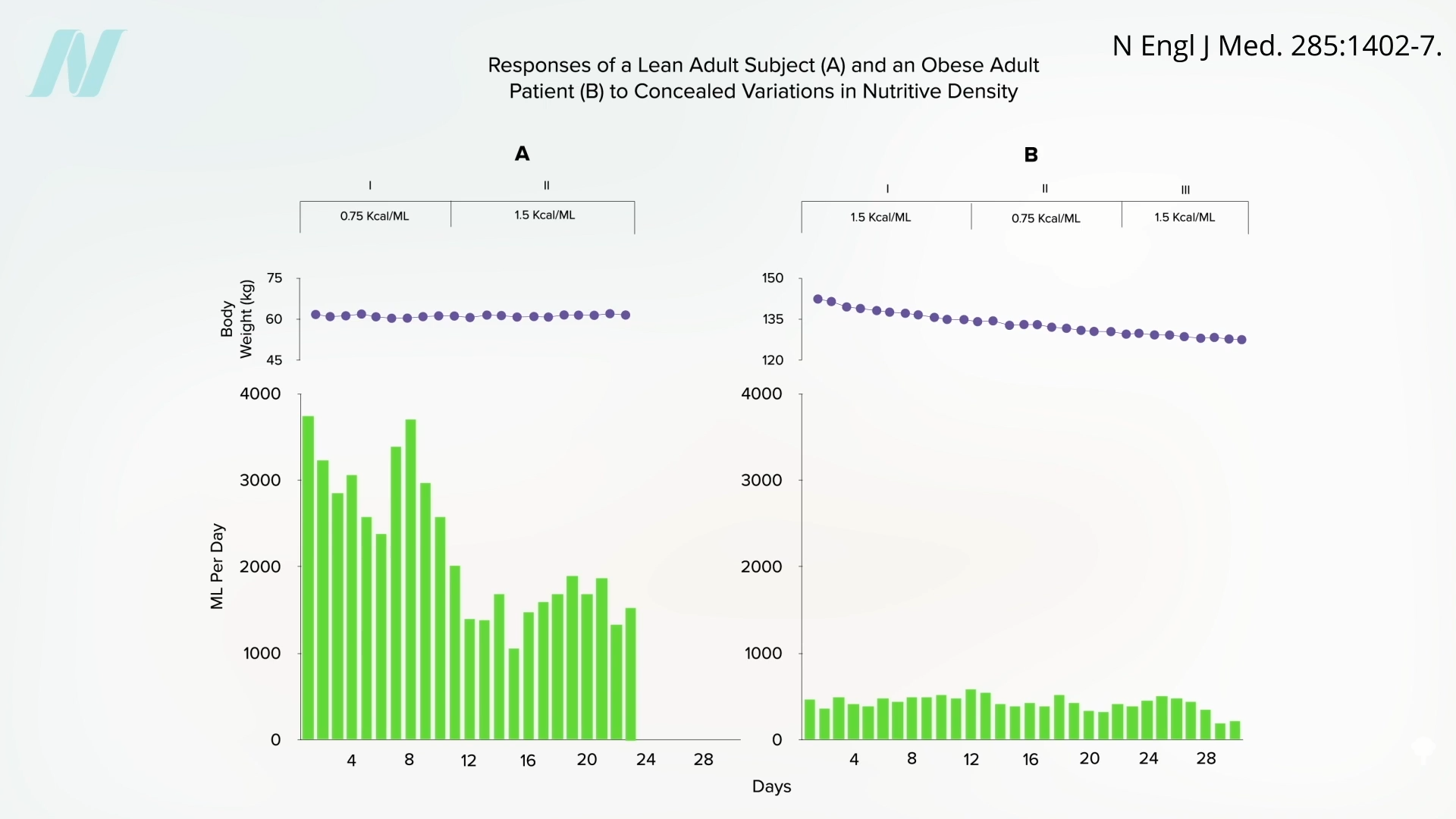 It would be interesting to see if they regained the ability to respond to changing calorie intake once they reached their ideal weight. Regardless, what can we apply from these remarkable studies to facilitate weight loss out in the real world? We’ll explore just that question next.
It would be interesting to see if they regained the ability to respond to changing calorie intake once they reached their ideal weight. Regardless, what can we apply from these remarkable studies to facilitate weight loss out in the real world? We’ll explore just that question next.
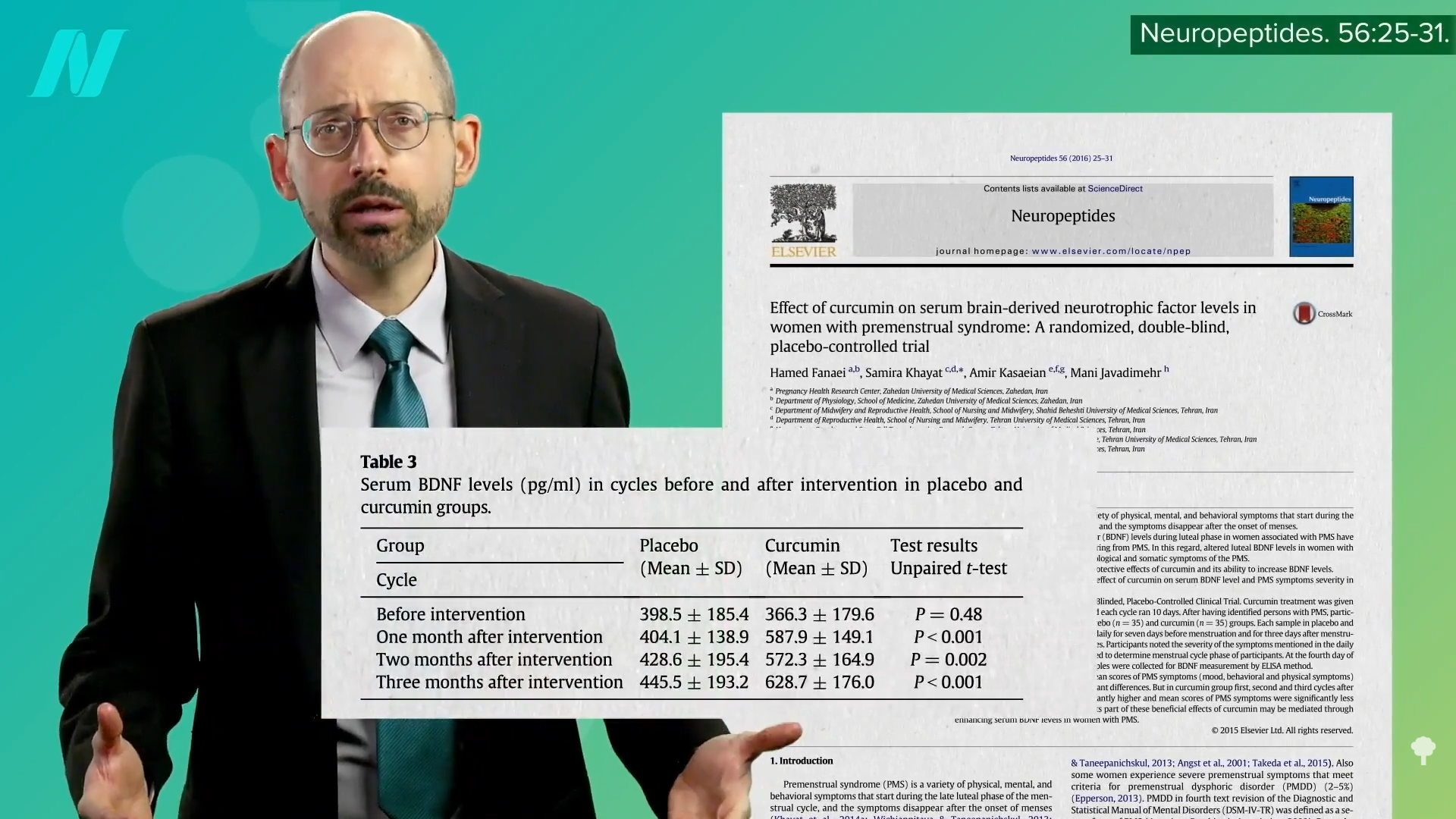

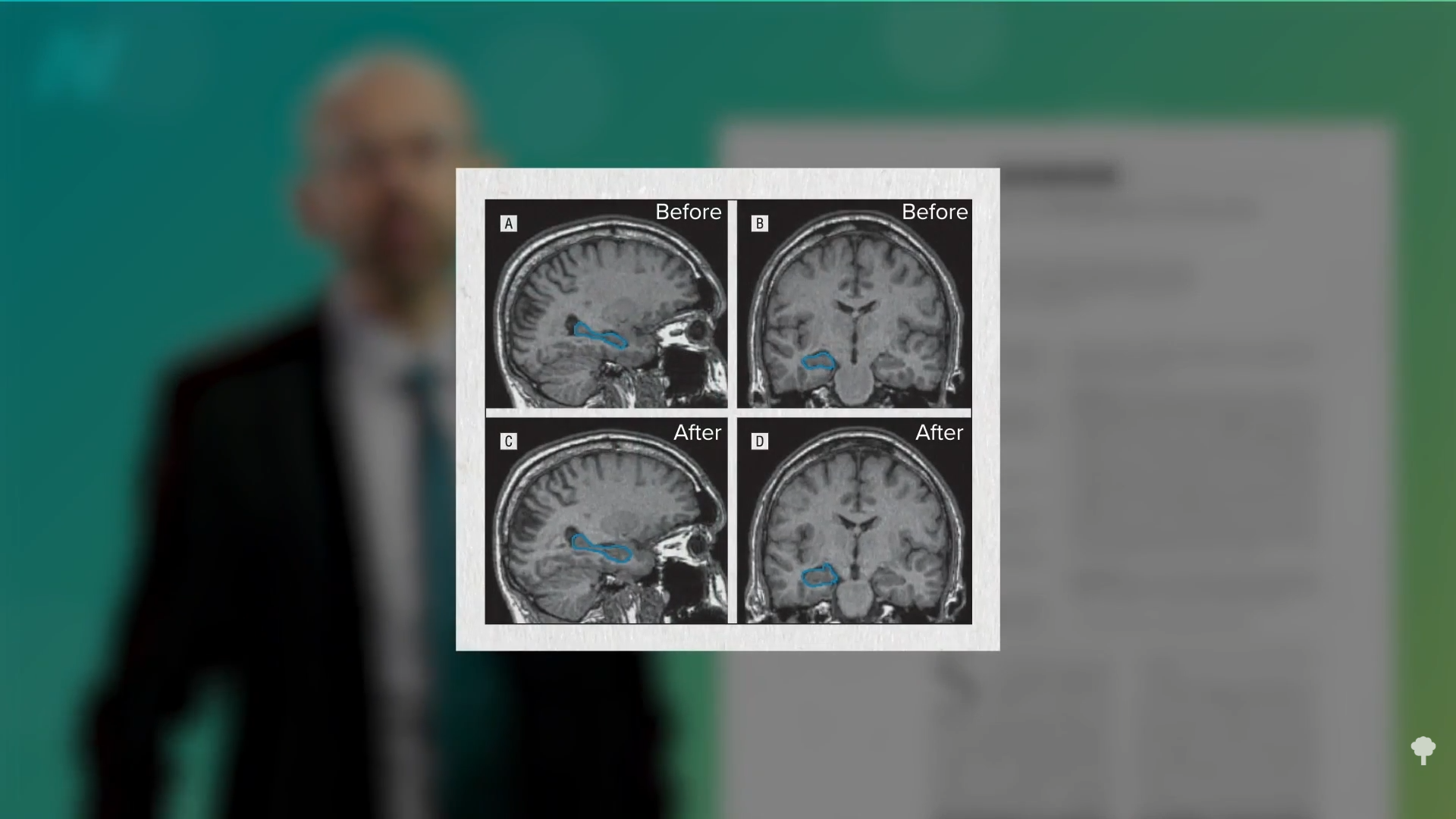



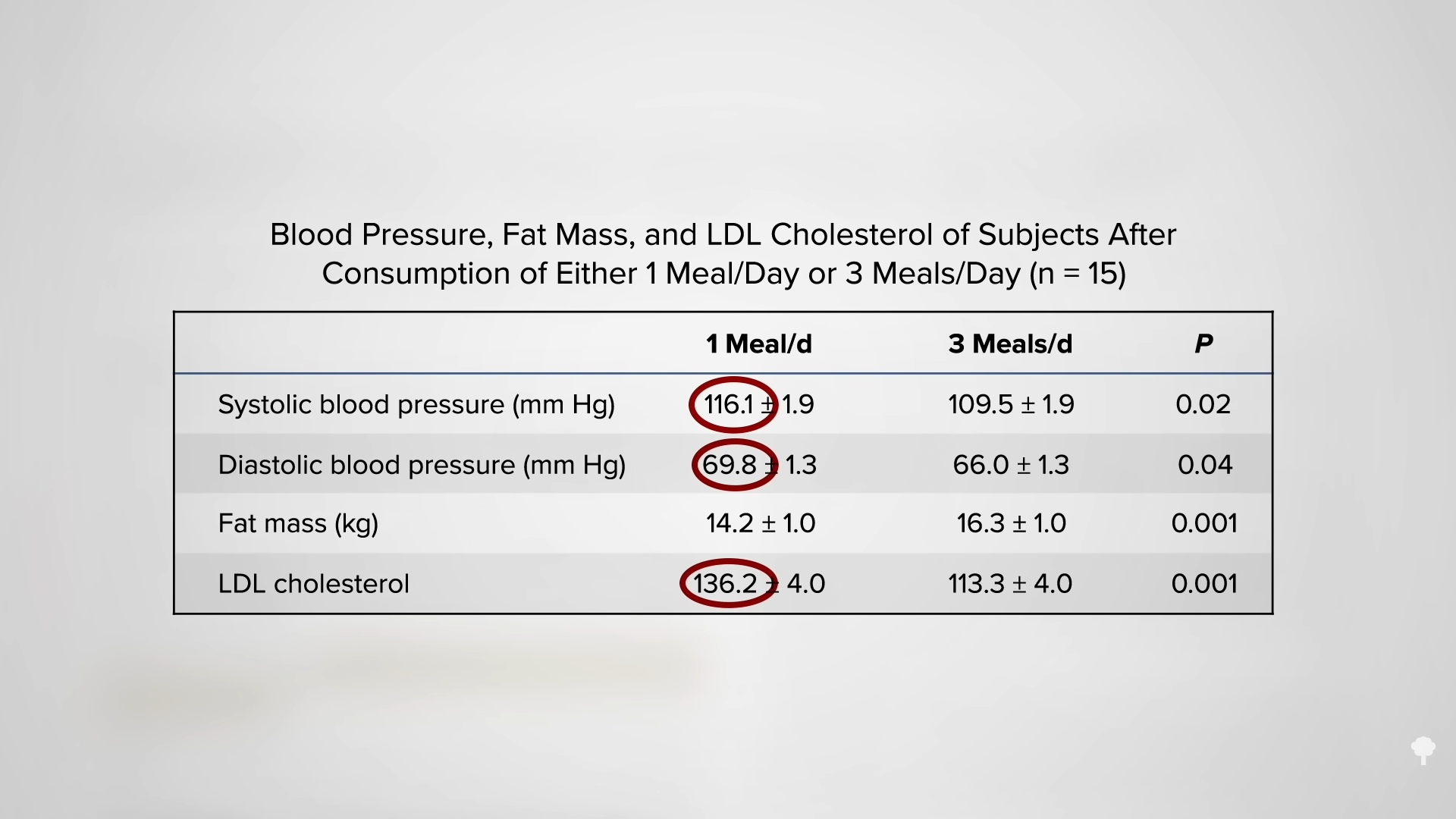

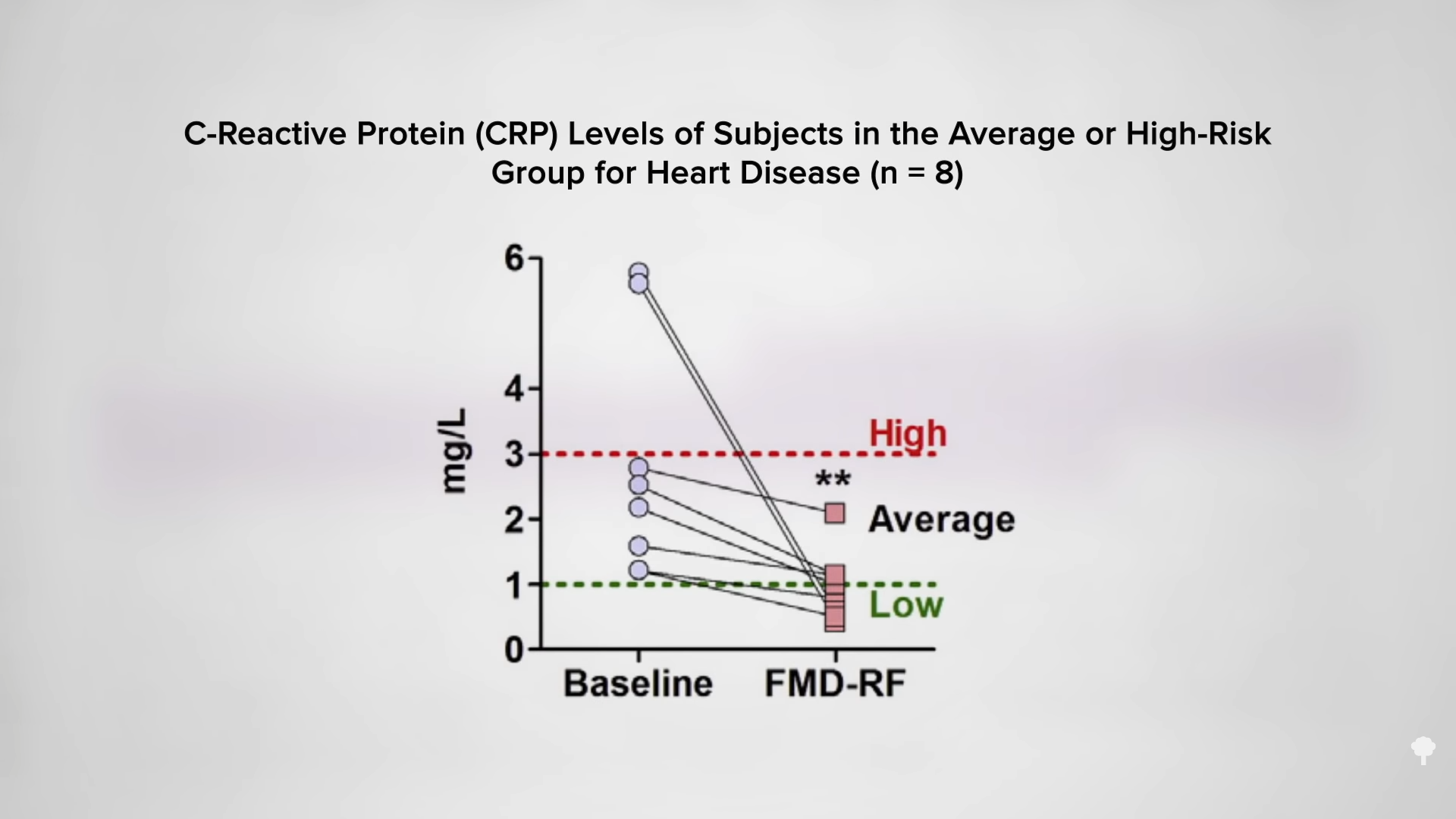
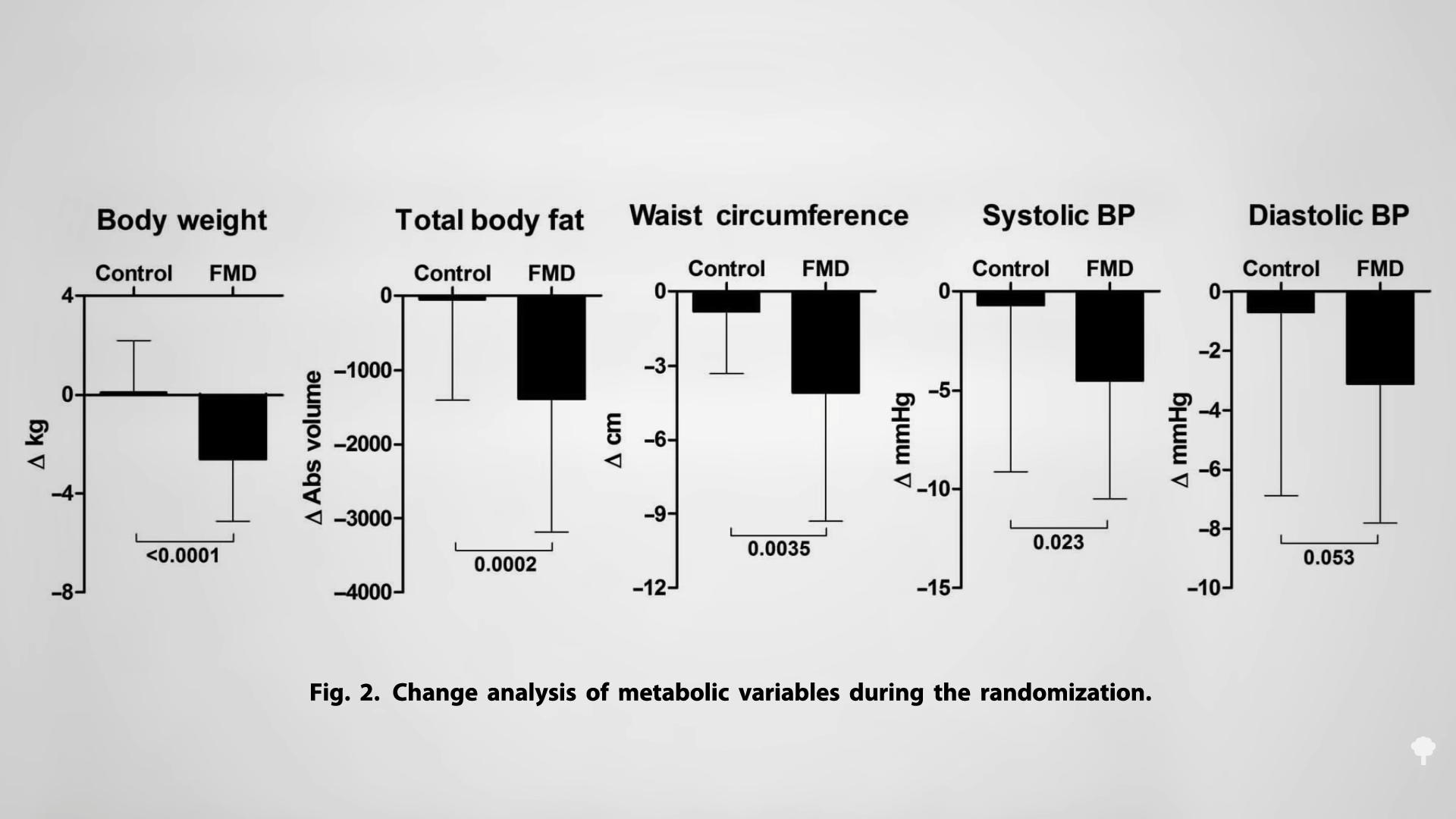
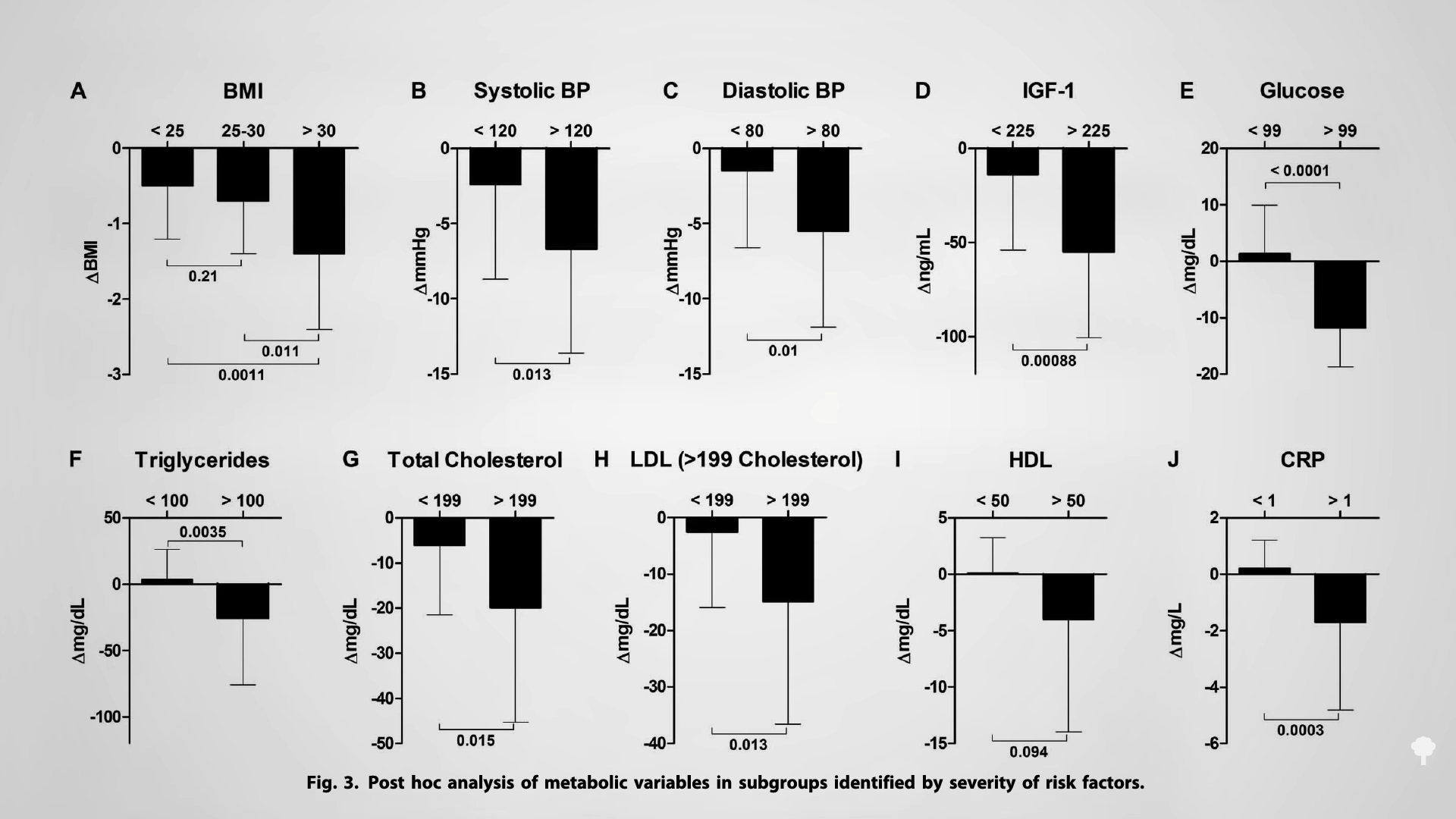






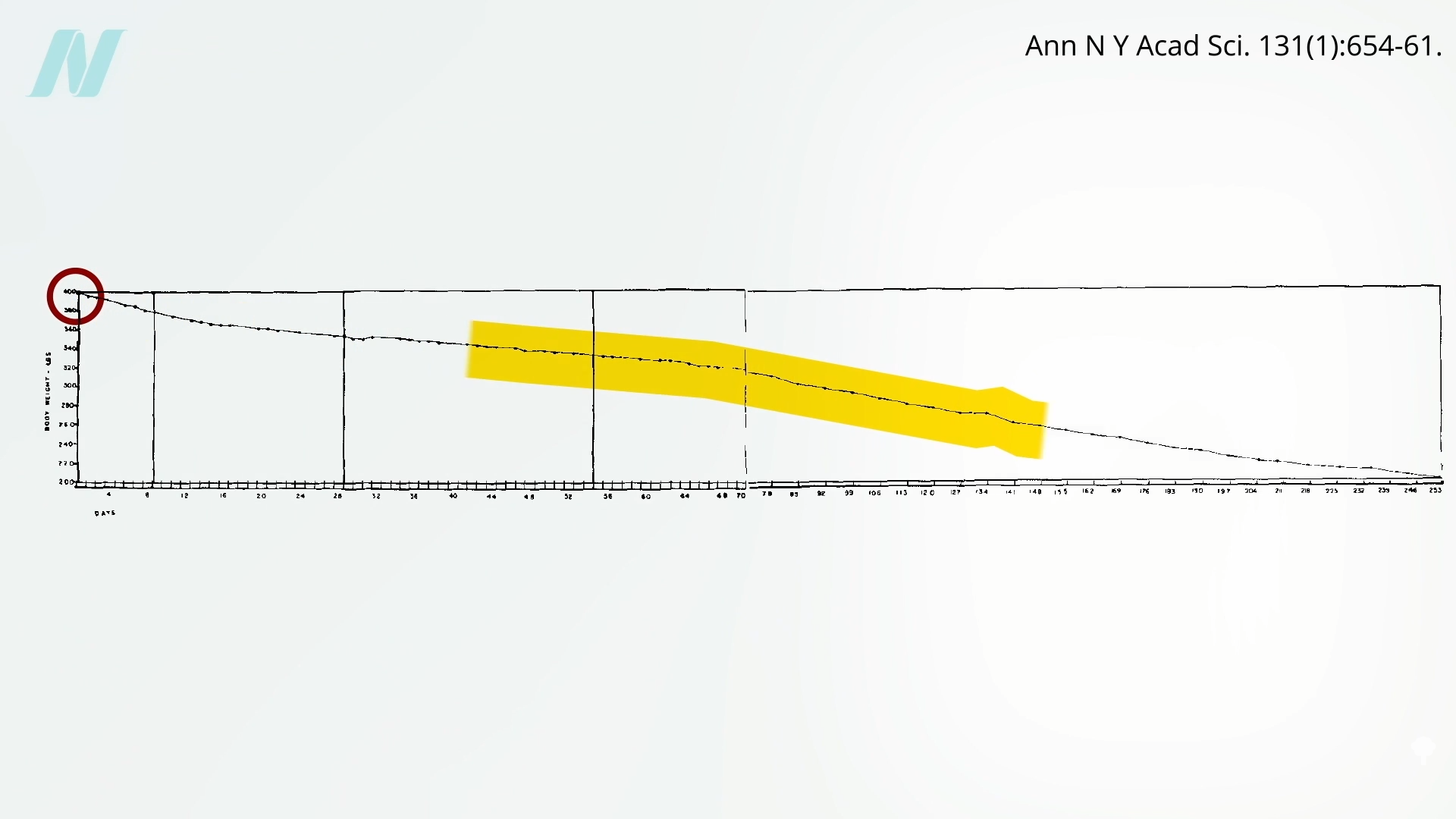
 Medically-supervised fasting has
Medically-supervised fasting has “
“







 What happened nine years later? “Therapeutic Fasting in Morbid Obesity”
What happened nine years later? “Therapeutic Fasting in Morbid Obesity”  The small minority for whom fasting
The small minority for whom fasting 



 This is the follow-up to
This is the follow-up to 





 In my previous video, I dive into how
In my previous video, I dive into how