[ad_1]
LA PAZ, Sep 21 (IPS) – In Bolivia, more and more women have gone from being homemakers or street vendors to joining the noisy world of engines, their hands now covered in grease after learning that special touch to make a car work. But they frequently have to put up with machismo or sexism, injustice and mistrust of their skills with tools.
Automotive mechanics is traditionally associated with masculine men wearing oil-stained coveralls. In La Paz and other Bolivian cities over the years many auto repair shops have upgraded from precarious workshops on the street to modern facilities with high-tech equipment.
Vehicles have also transitioned from human-operated nut-and-gear systems to cars governed by electronics.
But openness to women has not evolved in the same way in the profession, as it is unusual to find female mechanics.
And auto repair shops do not appear in studies on informal employment in Latin America by the International Labor Organization (ILO), although mechanic shops are very much present in the informal sector.
“At the age of five I learned about fractions through tears. My father would ask me for a fork wrench (middle wrench, in Bolivia), but since I didn’t know which one it was, he would throw it at my head,” Miriam Poma Cabezas, a senior electromechanical technician, now 50 and divorced, told IPS.
Since that incident, a mixture of anecdote and forced apprenticeship, 45 years have passed, most of them dedicated to the profession of mechanics specializing in engines and now in the electronics of high-end vehicles, in a workshop of which she is co-owner in the city of El Alto, next to La Paz, the country’s political capital.
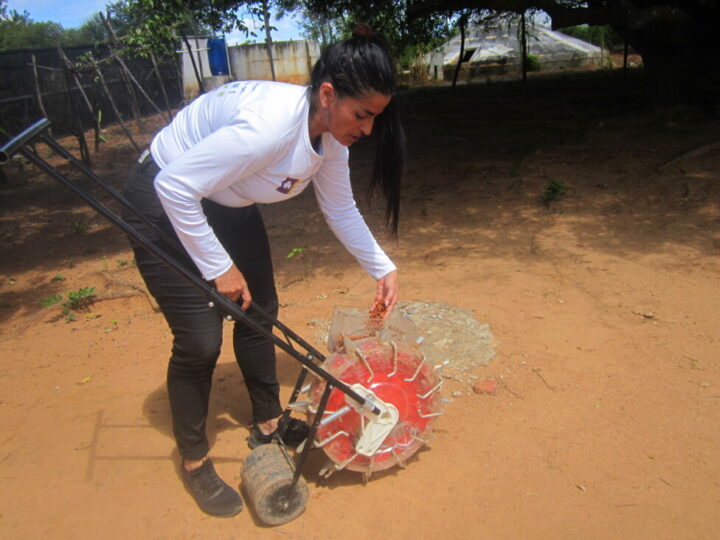
On a busy street in the La Paz neighborhood of Sopocachi, Ana Castillo uses complex techniques to dismantle rubber tires, identify the damage, and clean and apply chemicals to fix them. At 56, she is an expert in the trade.
She charges about a dollar and a half for each repaired tire, which involves exerting vigorous effort to loosen rusted lug nuts, in order to find the puncture in worn tires amidst the fine black dust that has darkened her hands for 20 years.
“God put me here and I love it because you have to use your strength. I would go crazy sitting still,” Castillo, who completed law school, though she never practiced law, tells IPS as she quickly operates a wrench that creaks as it loosens one of the nuts, stuck hard and moldy from water and dirt.
But she does not only repair tires. She is also a specialist in rebuilding classic cars, an activity for which she is becoming very well-known.
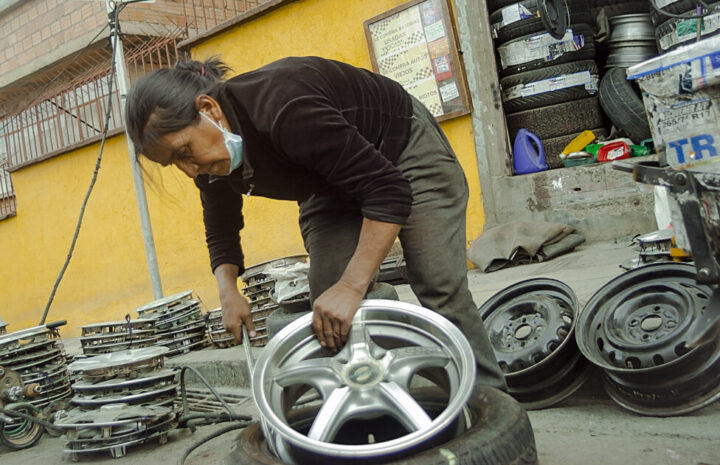

With a great deal of effort, Poma managed to set up her own high-level electromechanical repair shop, but before that she had spent years working as an informal self-employed worker, not only in automotive mechanics.
For her part, Castillo complained about the municipal seizure of a piece of land where she wanted to build the mechanic shop of her dreams, together with her husband Mario Cardona. A court ruling granted them the right to use the land and a city council resolution upheld it, but they still have not been given back the land.
A case like so many others
The automotive mechanics sector is just one example of those in which the participation of Bolivian women is particularly difficult, because they are seen as traditionally male professions and there is strong resistance to women breaking into the field, whether out of necessity or a sense of vocation.
The 2018 Annual Report of the UN Women agency, based on figures from the National Institute of Statistics, states that seven out of 10 women in Bolivia are economically active, work in informal conditions and lack labor rights, which makes it difficult to specifically identify how many work as mechanics.
UN Women highlights that Bolivia “is the third country in the world, after Rwanda and Cuba, with the highest political participation of women”: 51 percent in the Chamber of Deputies and 44 percent in the Senate.
But this high female presence in politics in this South American country of 12.3 million inhabitants does not translate into a boost for women in other areas, particularly business and formal employment.
The president of the Chamber of Businesswomen of Bolivia (Camebol), Silvia Quevedo, told IPS that there is no “state incentive (for women’s participation) in any particular job” and encourages “women themselves to forge their own way, based on the quality of their work.”
Camebol emerged in the department of Santa Cruz, the most economically developed in the country, and has since spread to six of Bolivia’s nine regions. It has a thousand members and its purpose, together with strengthening its institutional framework, is to influence public policies to promote equal opportunities in business.
A study conducted by the ILO on Bolivian self-employed women workers in the informal sector shows that the department of La Paz accounts for 31.8 percent of this segment, with an average age of 45 years and eight years of schooling, below the 12 years of compulsory basic education.
In the city of La Paz, 75 percent of self-employed women work in commerce, 15 percent in manufacturing and eight percent in community services. In the other two largest cities in the country, Cochabamba and Santa Cruz, the proportions are similar, according to the report.
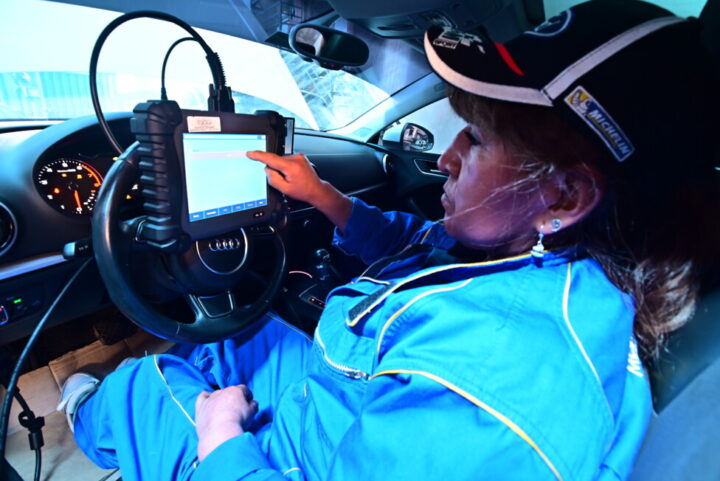

Experienced hands
Miriam Poma told IPS that she began to create her own source of employment at the age of 16, on the bustling commercial Huyustus Street in La Paz, where thousands of vendors sell all kinds of merchandise. She sold shoes and handbags.
But soon after, she decided to devote herself full time to repairing Volkswagen vehicles, and ended up as head mechanical assistant to her father, Marcelino Poma, who competed in rally races until he was 70 years old.
Creativity to adapt at a young age to the opportunities of street commerce led Ana Castillo to sell pork sandwiches. She was 14 years old at the time, forced by the responsibility of caring for her two younger brothers after they had all been abandoned by their mother.
“I know how to make everything: sausages, pickles, sauces; I’m not afraid to start from scratch,” Castillo, who helped her two younger brothers earn degrees in business administration and social communication, told IPS enthusiastically.
In the formal economy, “foreign trade has a woman’s face,” said Quevedo, the president of Camebol, based on surveys of the participation of its members in export companies.
Quevedo is an economist with extensive knowledge in agriculture who specializes in exports.
In 2022, international sales of non-traditional products amounted to 9.7 billion dollars, according to the Bolivian Institute of Foreign Trade (IBCE), in a country with a GDP of 41 billion dollars.
But there are still prejudices about women’s efficiency in men’s jobs, as the two women mechanics noted.
Poma said the customers in her father’s repair shop initially did not trust her to tune their engines, and tried to keep her from working on their vehicles.
Her brother, Julio Poma, would say he had done the work, and only after the client expressed complete satisfaction would he reveal that the work was actually done by his sister.
Recently, Poma tried to pass on her knowledge to men in the field of motor electronics, but no one was interested in a female instructor who was also a racing driver in 2006. In order to attract students, she had to hire a foreign expert.
A study carried out by the Women’s Institute of La Paz, belonging to the city government, indicated the level of interest in learning gastronomy, computer technology, cell phone use and education in small business finances.
Among the non-conventional trades, the respondents called for training in masonry, plumbing and electricity, a spokesperson for the Institute told IPS. The Institute conducts training workshops for 1,450 low-income women heads of households between the ages of 25 and 70.
© Inter Press Service (2023) — All Rights ReservedOriginal source: Inter Press Service
[ad_2]
Global Issues
Source link