Gadgets
Run Connect-MgGraph without Browser Prompt Authentication
[ad_1]
Do you want to run the Connect-MgGraph command and avoid the browser prompting you for authentication? This is a hands-on guide where I show how to accomplish that.
You require two PowerShell modules to authenticate to the Microsoft Graph API directly on the PowerShell console. In the first section, I will discuss how to install the modules.
After that, I will explain the steps to your Azure account, retrieve the token for Microsoft Graph, and then use the token to authenticate to Microsoft Graph API.
Finally, we will discuss confirming that your Connect-MgGraph command worked by checking the available permissions. I will also show some examples.
I am executing the commands on this guide using PowerShell 7. The commands will work on PowerShell 5 but it may behave slightly differently.
Step 1: Install the Required Modules
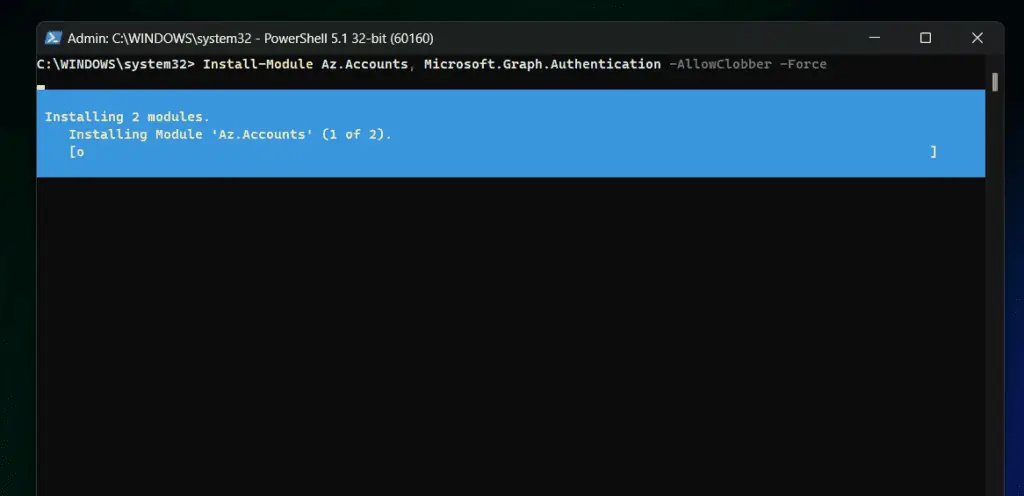
To run the Connect-MgGraph command and avoid the browser prompting authentication, you must install two PowerShell modules. Specifically, you require the Az.Accounts and Microsoft.Graph.Authentication modules.
Install-Module Az.Accounts, Microsoft.Graph.Authentication Import-Module Az.Accounts, Microsoft.Graph.Authentication
Step 2: Authenticate to Microsoft Graph
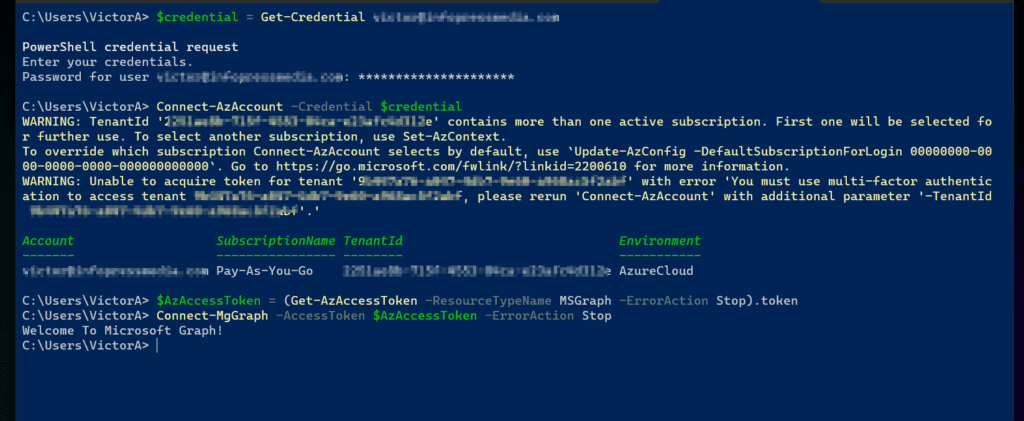

As I hinted in my introduction, retrieving the Azure token is the first step to connecting to Microsoft Graph. This step is achieved by connecting to your Azure account.
After that, you will use the token to authenticate to Microsoft Graph. Here are the detailed steps:
- Get the credentials you require to authenticate to Azure from PowerShell by running the command below:
$credential = Get-Credential <Azure logon email>
Replace the <Azure logon email> placeholder with your actual Azure login email. When you execute the command, PowerShell will prompt you to enter the password for the Azure login.
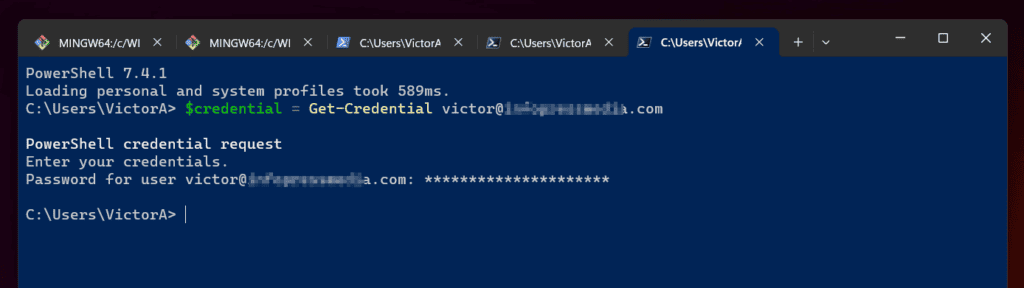

- Next step, log in to Azure with the Connect-AzAccount command…
Connect-AzAccount -Credential $credential
The above command will take a short while to complete as it authenticates to Azure using the creds saved in the $credential variable. Once you connect successfully, PowerShell displays information about your Azure tenant.
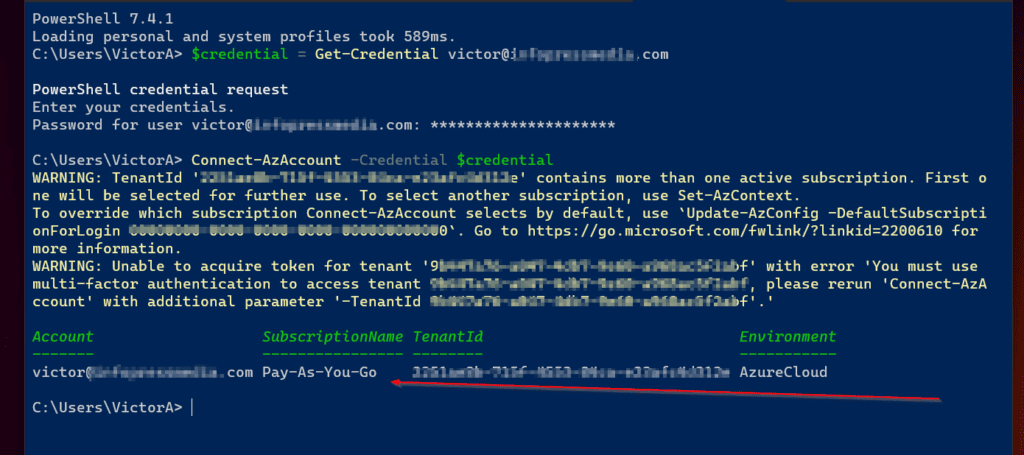

- Now that you’ve signed in to Azure, the next step of this section is to retrieve the Azure Access token you require to authenticate to Microsoft Graph API.
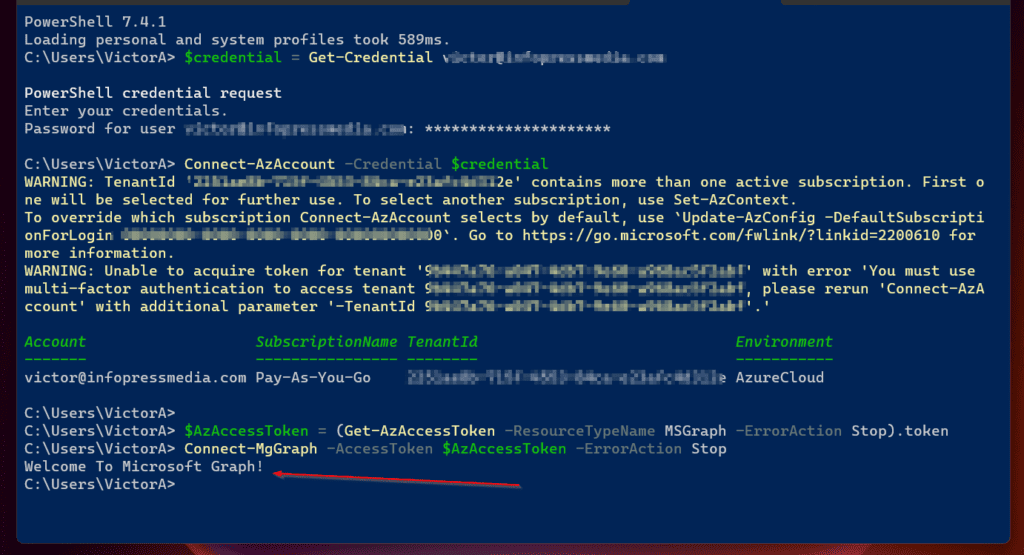
$AzAccessToken = (Get-AzAccessToken -ResourceTypeName MSGraph -ErrorAction Stop).token
- Finally, execute the Connect-MgGraph command specifying the $AzAccessToken variable – this provides the auth you require and stops the command prompting you to authenticate via the browser.
Connect-MgGraph -AccessToken $AzAccessToken -ErrorAction Stop
To confirm that you’ve successfully authenticated to Microsoft Graph, you will receive a “Welcome To Microsoft Graph!” message.

Step 3: Manage Azure with the Microsoft Graph Commands

Having shown how to run the Connect-MgGraph command and bypass the browser prompt for authentication, I have met the purpose of this article.
However, I like to share a few Azue tasks that you can perform using the Microsoft Graph module cmdlets. I decided to include these examples as a way to confirm that the Microsoft Graph API connection worked.
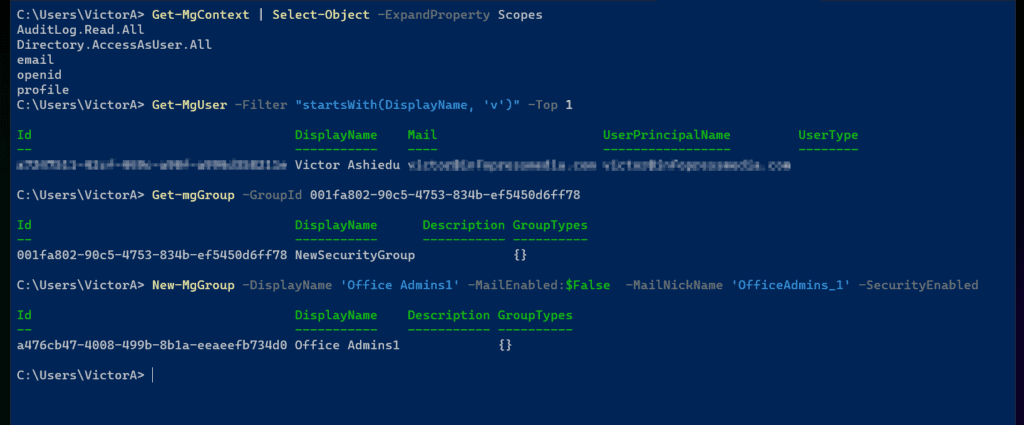
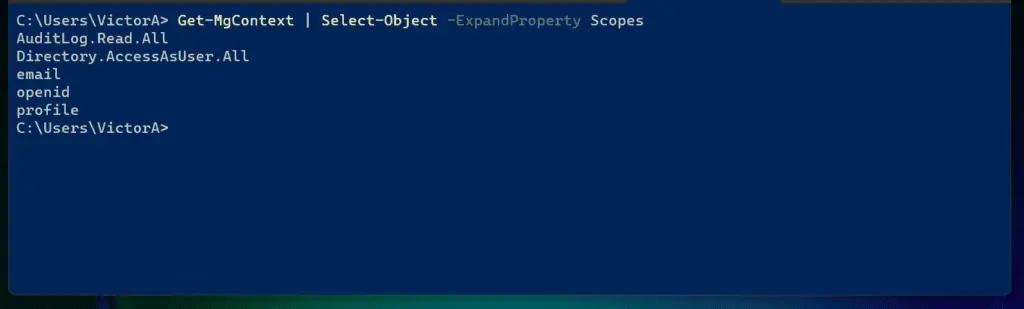
Let’s start by running the Get-MgContext command. This command displays the scope of the session.
Get-MgContext | Select-Object -ExpandProperty Scopes
The screenshot below shows the result of the above command. To learn more about Microsoft Graph scopes, read the Microsoft Graph permissions reference.

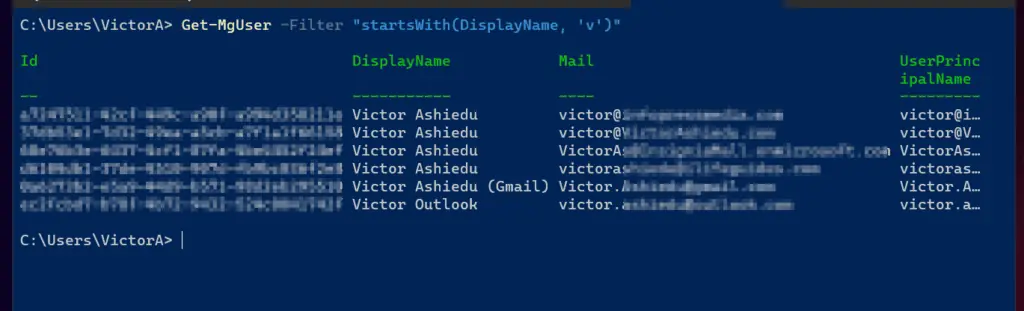
Another command task we can perform is to find an Azure AD user with the Get-MgUser command. In my example below, I want to return Azure AD users with DisplayNames that start with “v.”
Get-MgUser -Filter "startsWith(DisplayName, 'v')"

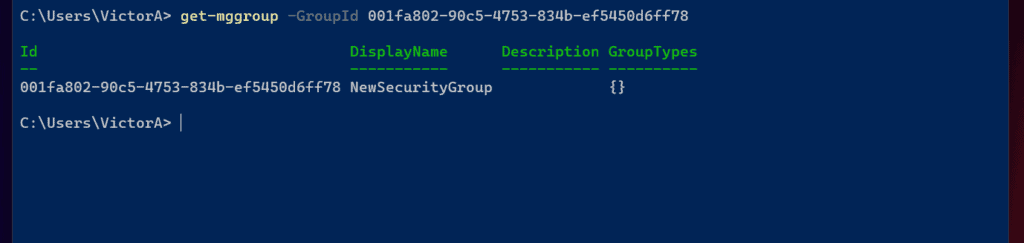
Another great example of managing Azure AD with Microsoft Graph is displaying and creating groups. To view an Azure AD group, run the Get-mgGroup command.
My example below returns a group with the specified Id.
Get-mgGroup -GroupId 001fa802-90c5-4753-834b-ef5450d6ff78

Finally, I can create a new Azure AD security group with the New-MgGroup command. See my command below for a sample command that creates a group called Office Admins.
New-MgGroup -DisplayName 'Office Admins' -MailEnabled:$False -MailNickName 'OfficeAdmins' -SecurityEnabled
Frequently Asked Questions
As far as I am aware, the valid cmdlet is Connect-MgGraph, which is from the Microsoft.Graph PowerShell module.
If the Connect-MsGraph cmdlet exists, it may be from another PowerShell module, not officially related to the MS Graph API module.
The faster method to connect to Microsoft Graph via PowerShell is by running the Connect-MgGraph command.
Run the Disconnect-mgGraph command to disconnect from the Microsoft Graph PowerShell session.
The Azure AD PowerShell module is used to manage Azure Active Directory only. On the other hand, the Microsoft Graph PowerShell module can be used to manage Azure AD and other Microsoft Cloud resources.
By running the Connect-MgGraph command.
Other Useful Resources
- How to connect to the Microsoft Graph API using saved user credentials (doitpsway.com)
- How to connect to Microsoft Graph without prompt – Microsoft Q&A
- Az.Accounts Module | Microsoft Learn
- PowerShell Gallery | Microsoft.Graph.Authentication 2.0.0
- Using Microsoft Graph PowerShell authentication commands | Microsoft Learn
- Microsoft Graph permissions reference – Microsoft Graph | Microsoft Learn
[ad_2]
Victor Ashiedu
Source link