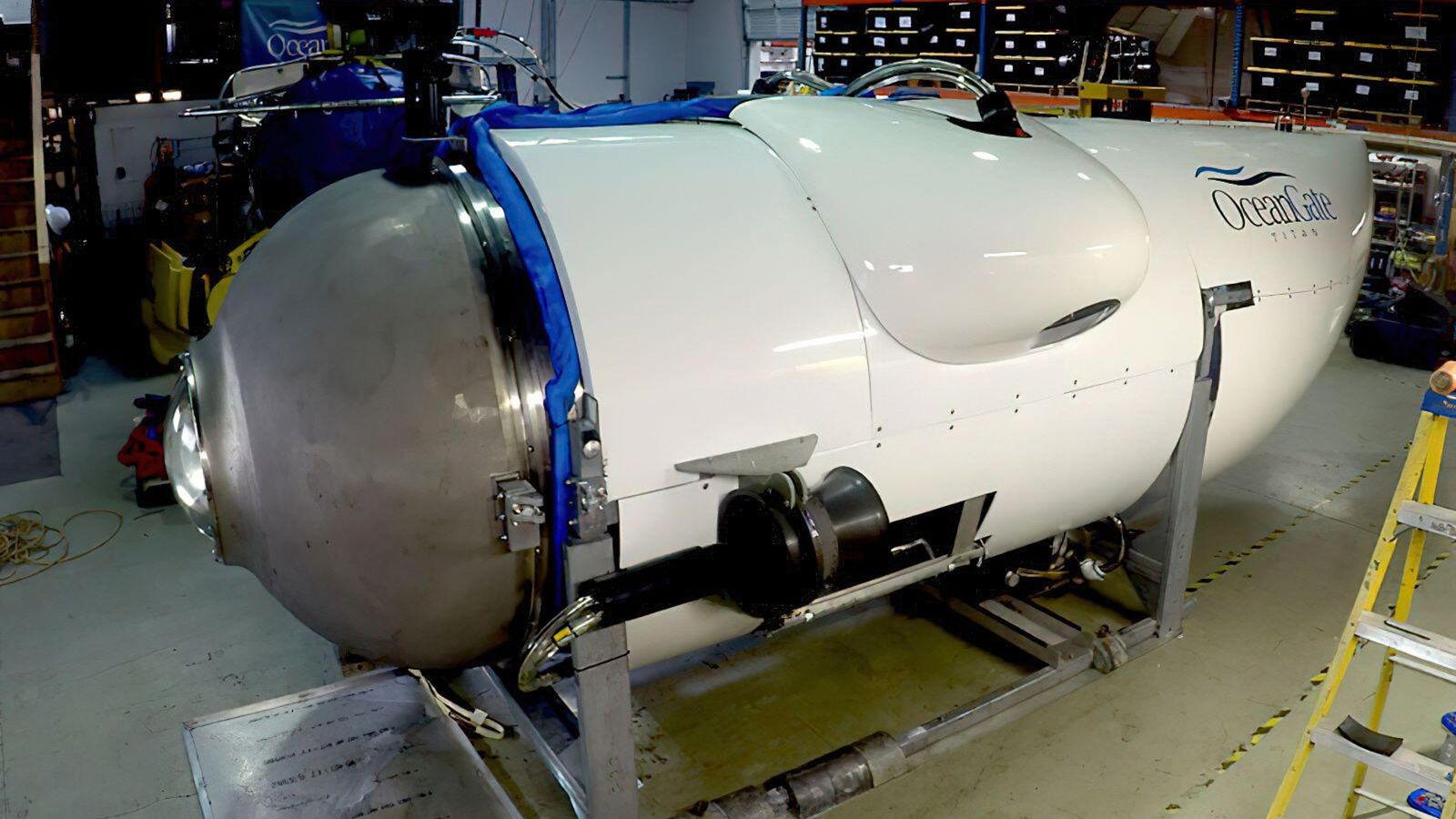
An investigation into underwater noises coming from the area of the search for the missing Titan submersible have come up “negative”, officials have said.
Regular banging sounds were picked up by a Canadian plane with underwater sonar capabilities after it was deployed in the search for the missing vessel.
The banging sounds were detected every 30 minutes on Tuesday – and were picked up again when search teams deployed more radars in the area.
Read more:
Hunt for missing submersible after search teams pick up ‘banging noises’ – latest updates
But the US Coast Guard said on Wednesday an investigation of the noises by specialist underwater equipment had “yielded negative results”.
“Additionally, the data from the aircraft has been shared with our US Navy experts for further analysis, which will be considered in future search plans,” the US Coast Guard added in a post on Twitter.
The noises were initially picked up by a Canadian P-3 aircraft using sonobuoys – a special type of buoy with underwater sonar capabilities.
It comes after a former employee of the missing Titan submersible operator has revealed he had raised “safety concerns” over the vessel but was reportedly “met with hostility” before later being sacked, according to court documents.
OceanGate’s former director of marine operations, David Lochridge, had raised concerns over “safety and quality control issues regarding the Titan to OceanGate executive management”, according to the filings.
In the August 2018 court document, it claims chief executive and founder of OceanGate Expeditions Stockton Rush, asked Mr Lochridge to conduct a “quality inspection” report on the vessel following the “issues of quality control”.
Read more:
‘This is how it is going to end’ – Scientist recounts trapped Titanic submersible experience over 20 years ago
What we know about the search for the vessel and those on board
Mr Lochridge “identified numerous issues that posed serious safety concerns” but he was reportedly “met with hostility and denial of access” to necessary documents.
The court filing claims he was worried about a “lack of non-destructive testing performed on the hull of the Titan”, and that he “stressed the potential danger to passengers of the Titan as the submersible reached extreme depths”.
Mr Lochridge was later fired from the company, wrongfully he claims.
OceanGate’s icebreaker, Polar Prince, which was supporting Titan, reportedly lost contact with the vessel about an hour and 45 minutes after it submerged.
The five men on board are Stockton Rush, British billionaire Hamish Harding, Pakistani businessman Shahzada Dawood and his son Suleman, and French submersible pilot Paul-Henri Nargeolet.
They had “about 40 hours of breathable air” left, the US Coast Guard said on Tuesday night.
A race-against-time search and rescue operation is taking place some 435 miles south of Newfoundland, Canada.
The wreckage of the Titanic, which sank in 1912 after hitting an iceberg, lies at a depth of about 12,500 feet (3,810 metres).
The Titan submersible usually takes two hours to descend to the wreck.