[ad_1]
Read this guide to learn how to install AD DS and DNS roles in Windows Server 2022, and configure a Windows Active Directory domain.
Setup Overview
In this guide, I will create lab.infopressmedia.com AD domain for my home lab. The Domain Controller is a VMware VM with the specs specified in the table below.
| VM Name | CPU | RAM | Hard Disk |
|---|---|---|---|
| IPMvDC1 | 2 cores | 4 GB | 90 GB |
Here are the details of the VM’s network configuration
| Host Name | IP Address | FQDN |
|---|---|---|
| IPMvDC1 | 192.168.0.81 | IPMvDC1.lab.infopressmedia.com |
The sections below detail the steps to configure a new AD DS domain using Windows Server 2022 Standard.
Step 1: Install Windows Server 2022
The task of installing Windows Server 2022 is pretty straightforward. So, I’ll not provide a step-by-step guide. If you need help with this section, read my guide, How to Install and Configure Windows Server 2022 Core.
The guide in the above link is for installing a Windows Server 2022 Cor (No GUI). To install the Server with GUI, select the Desktop Experience option in the Select Image section of the installation.
After installing the Operating System, rename the Server on the OS, assign it a static IP address, change Time Zone, and install Windows Updates.
Once you finish with this boring section, let’s get to the main actions in the proceeding sections!
Step 2: Install AD DS and DNS Roles
- Sign in to the server and open PowerShell as administrator.
- Then, install the Active Directory Domain Service and DNS roles with the command below
Install-WindowsFeature -Name AD-Domain-Services, DNS -IncludeManagementTools -IncludeAllSubFeature
Step 3: Configure DNS for AD DS
Before promoting the server to a Domain Controller and creating the AD domain, you must configure DNS. Follow the steps in these subsections to get your DNS ready.
Step 3.1: Create a Forward Lookup Zone
- From Server Manager: Tools > DNS open the DNS manager.
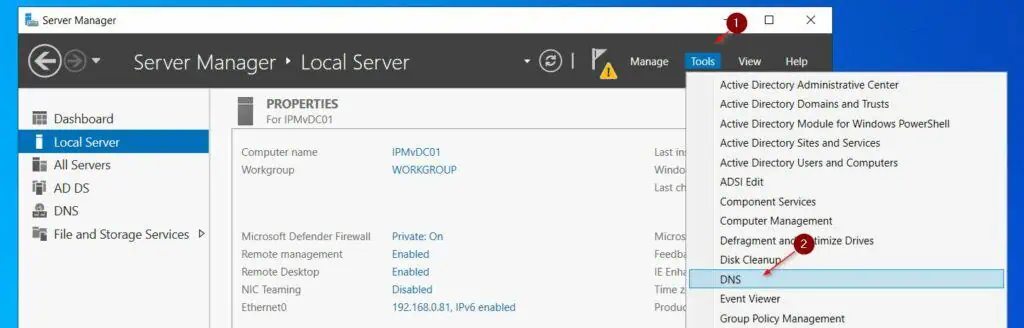
- Then, expand the server name, right-click Forward Lookup Zones, and choose New Zone. On the welcome page, click Next.
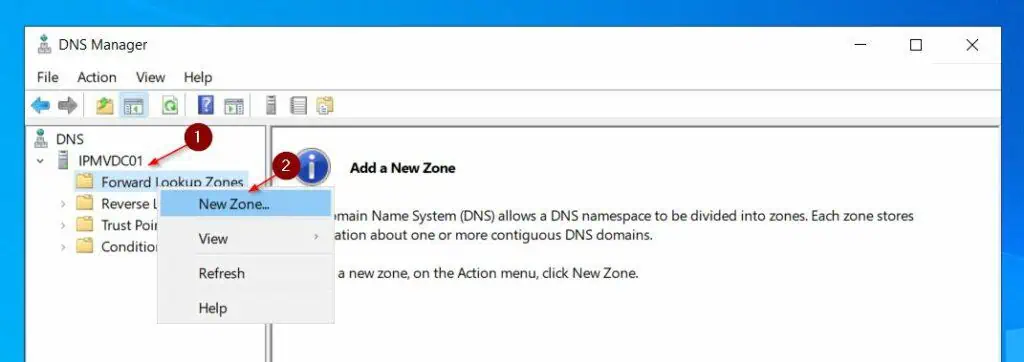

- After that, on the Zone Type page, select Primary zone.
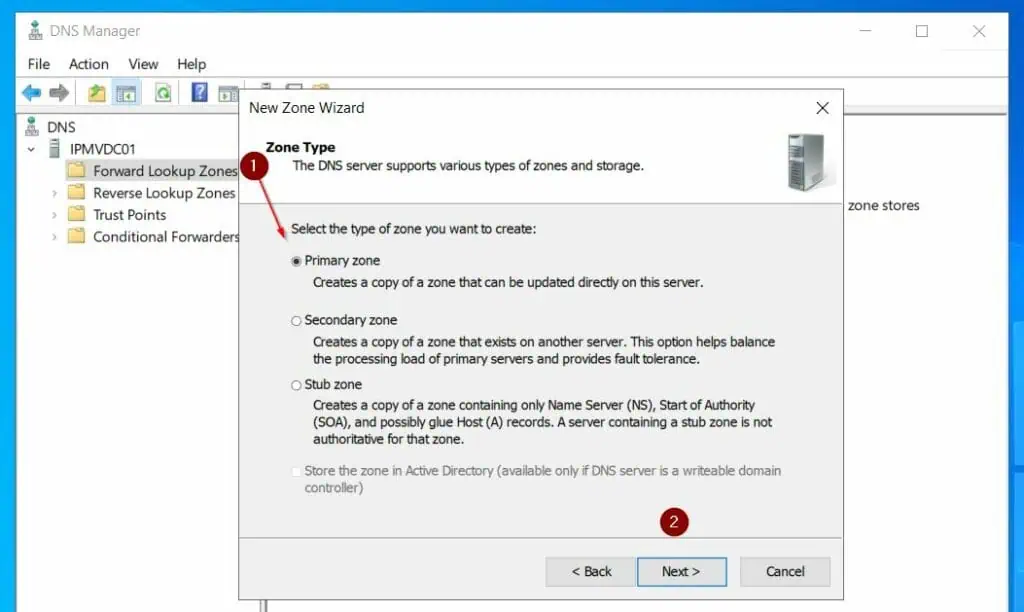

- On the Zone Name field, enter the fully qualified domain name of the AD domain you will create later. Then, accept the default zone file name on the next page.
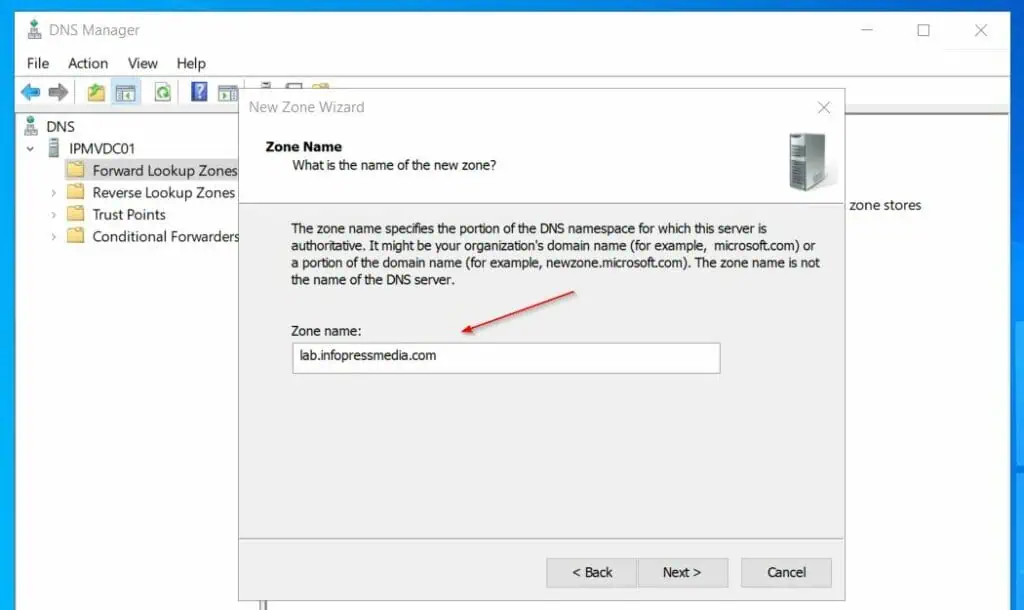

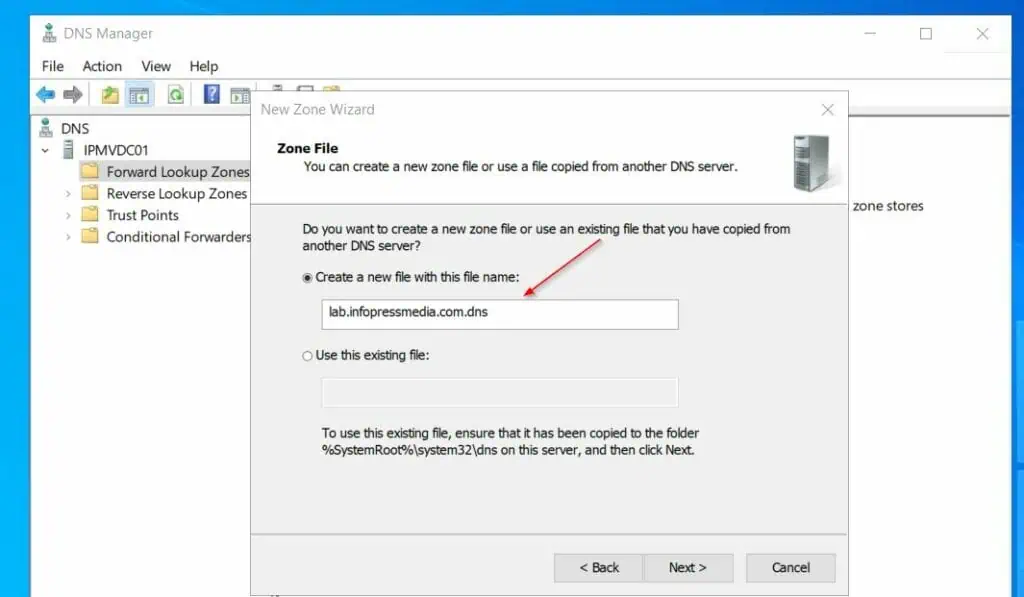

- Then, on the Dynamic Updates page, accept the default – Do not allow dynamic updates.
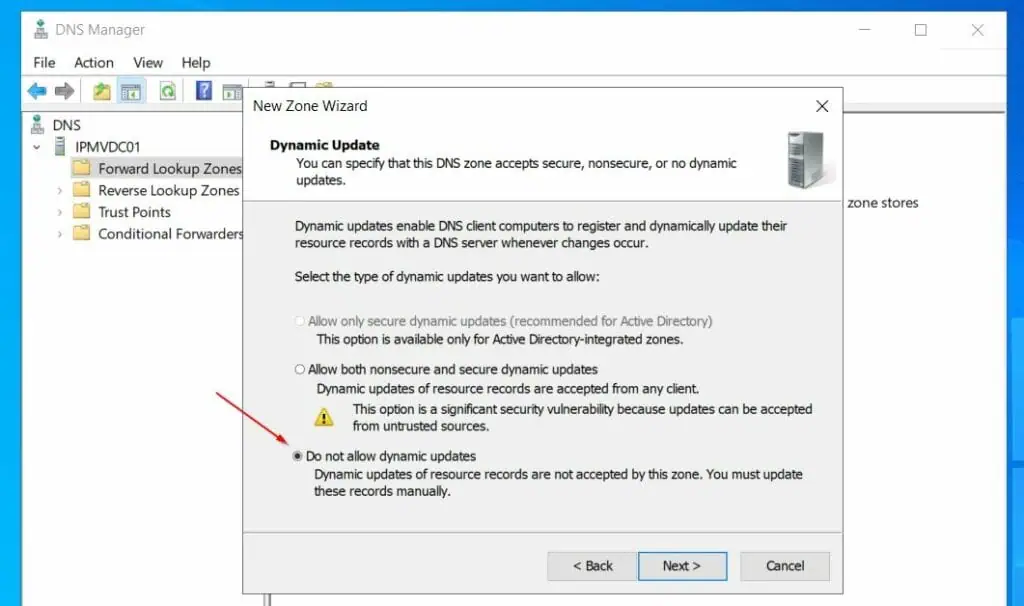

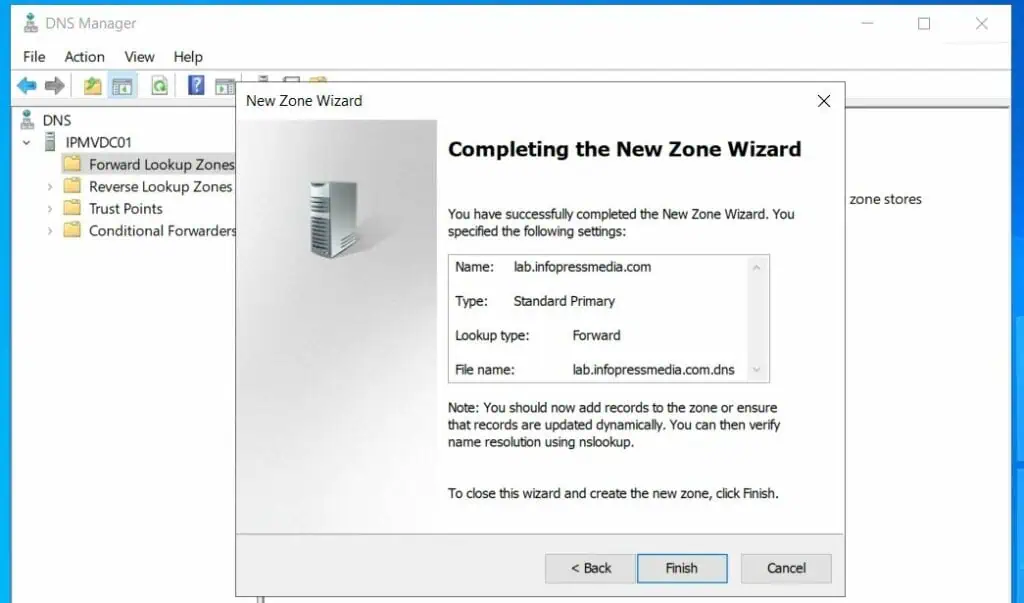
- Finally, review your selections and settings and click Finish to create the forward lookup zone.

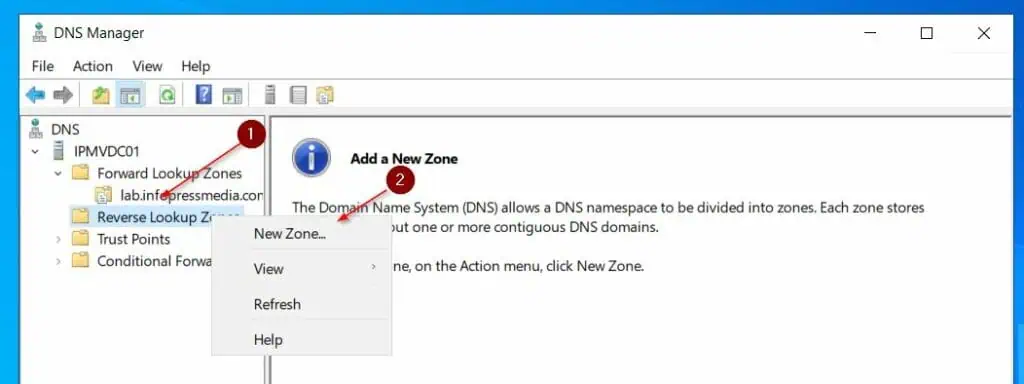
Step 3.2: Create a Reverse Lookup Zone
- Right-click Reverse Lookup Zones and select New Zone. Then, click Next on the welcome page.

- After that, choose Primary zone. Then, IPv4 Reverse Lookup Zone.
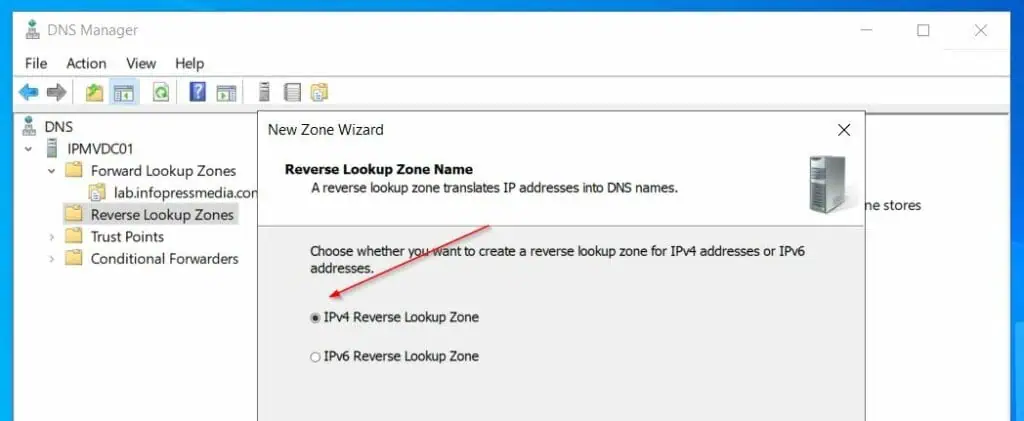

- On the Reverse Lookup Zone Name, enter the Network ID portion of the IP address of the server – mine is 192.168.0. On the Zone file name page, accept the default.
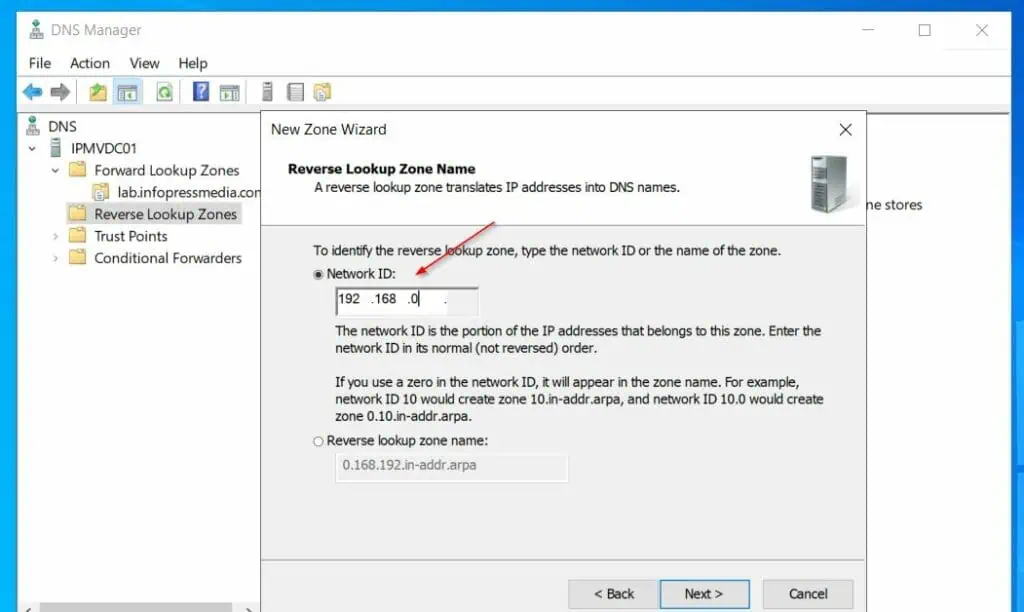

- Then, choose the “Do not allow dynamic updates” option on the next page, then create the reverse lookup zone.
Step 3.3: Configure Forwarder
For the DNS server to resolve internet addresses, configure a forwarder on the DNS Manager with these steps:
- From the DNS Manager, right-click the Server and choose Properties.
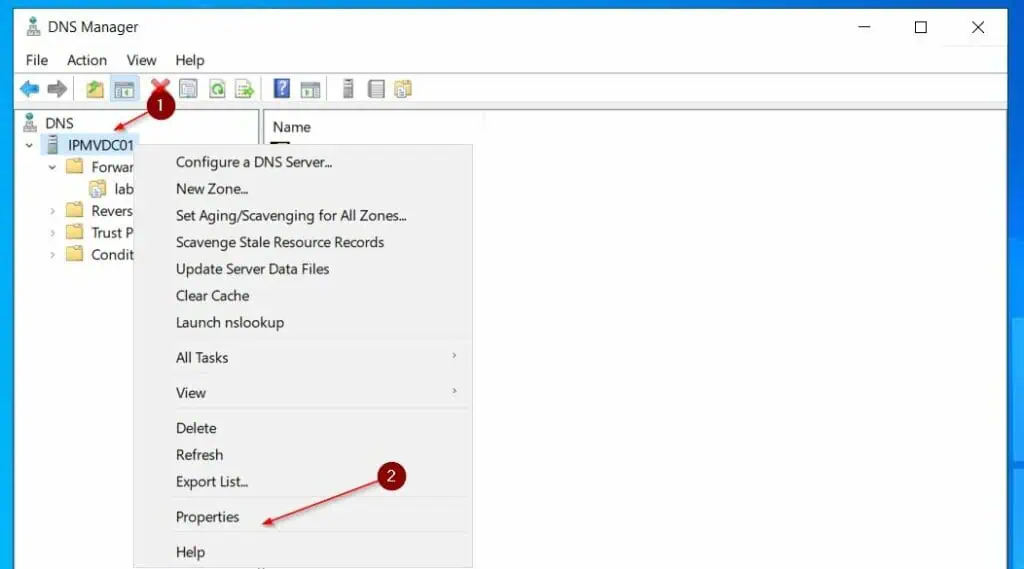

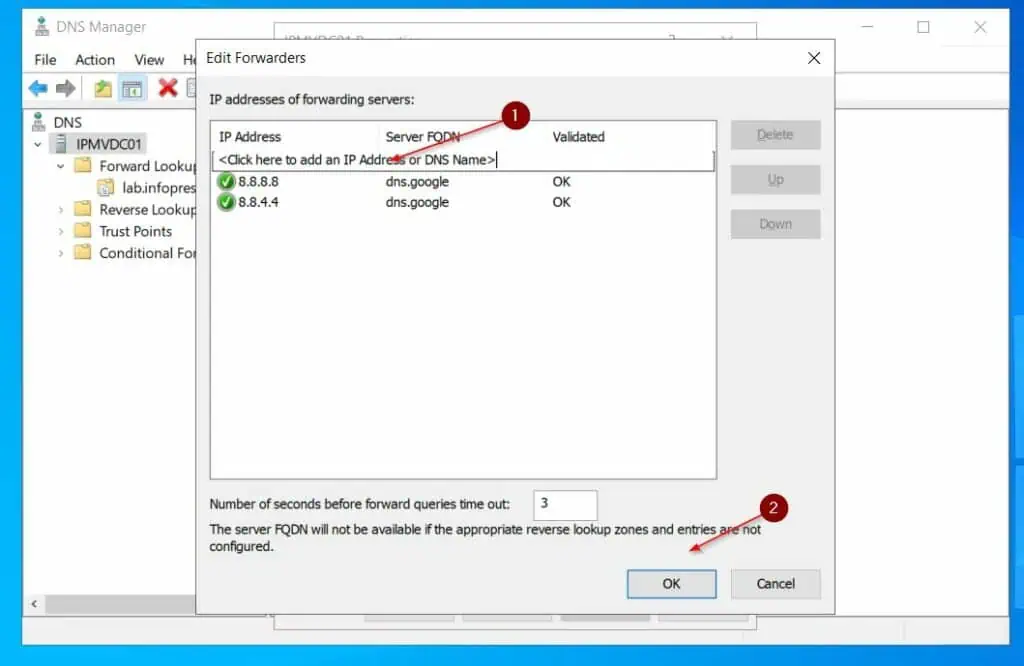
- Then, on the Forwarders tab, click Edit, then enter 8.8.8.8, and press Enter to load the entry. After that, enter 8.8.4.4 and press enter.
When you finish, click OK. DO NOT close the server’s Properties sheet as you will need it in the remaining subsections below.
8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4 are Google’s public DNS servers. My DNS server will use these to resolve internet DNS names.
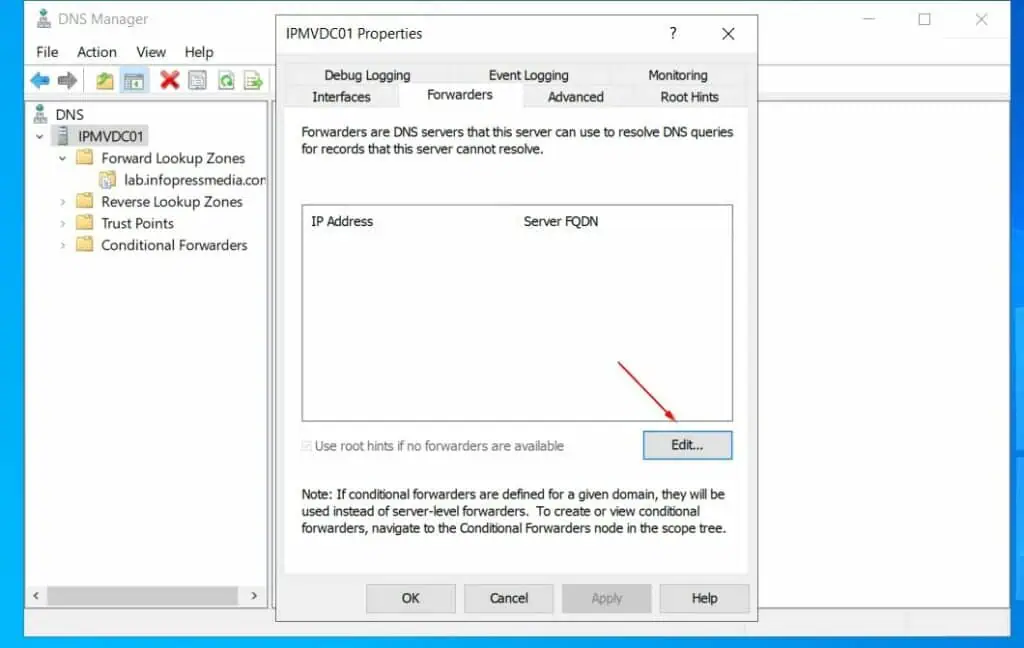


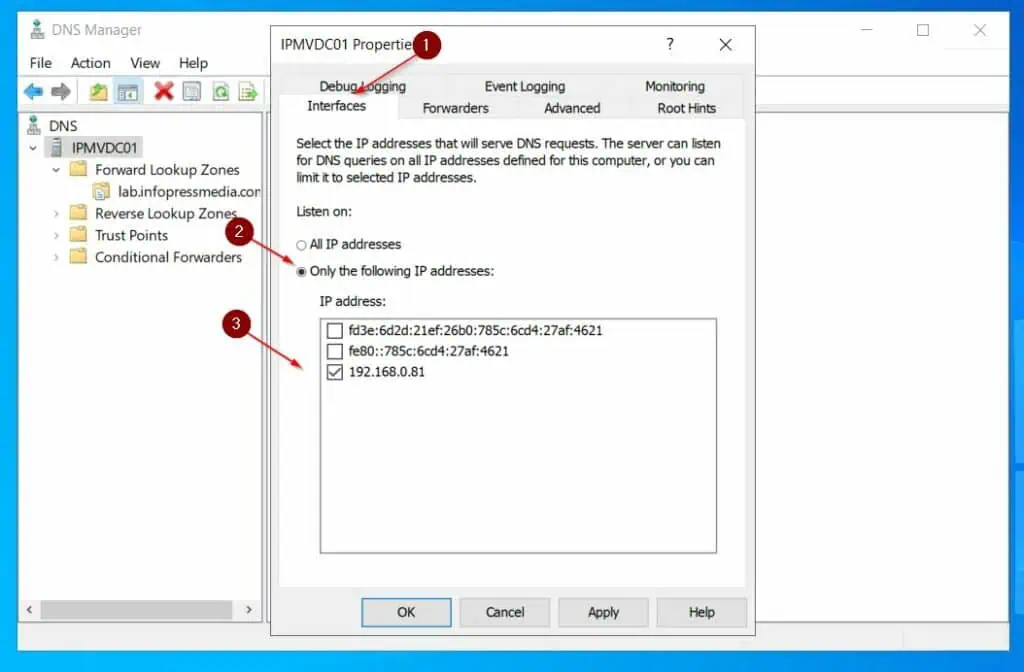
Step 3.4: Configure DNS Interfaces
Click the Interfaces tab, and choose Only the following IP address. After that, check the IPv4 address and uncheck the IPv6 addresses.
To save all the changes you have made, click OK (bottom left of the Properties sheet).

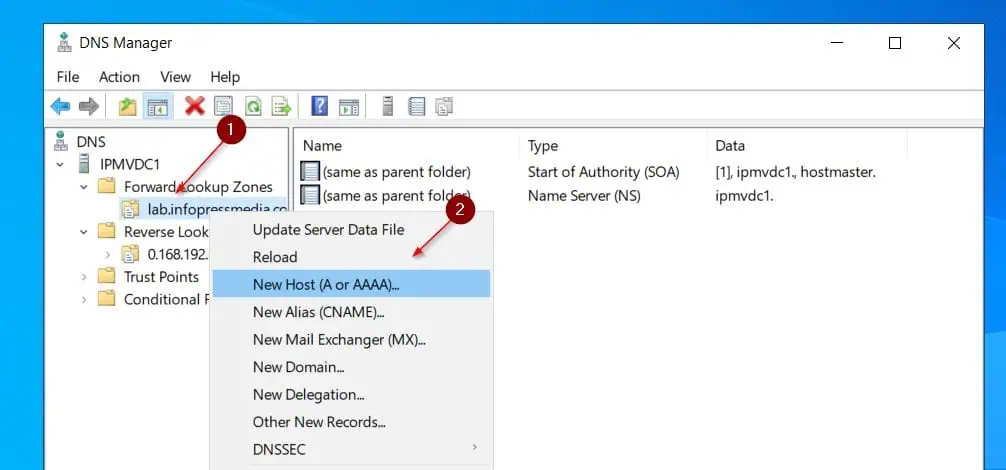
Step 3.5: Create the Server’s Host A Record
- To create a Host A record, right-click the Forward Lookup zone in DNS Manager, and choose Host (A or AAA) Record.

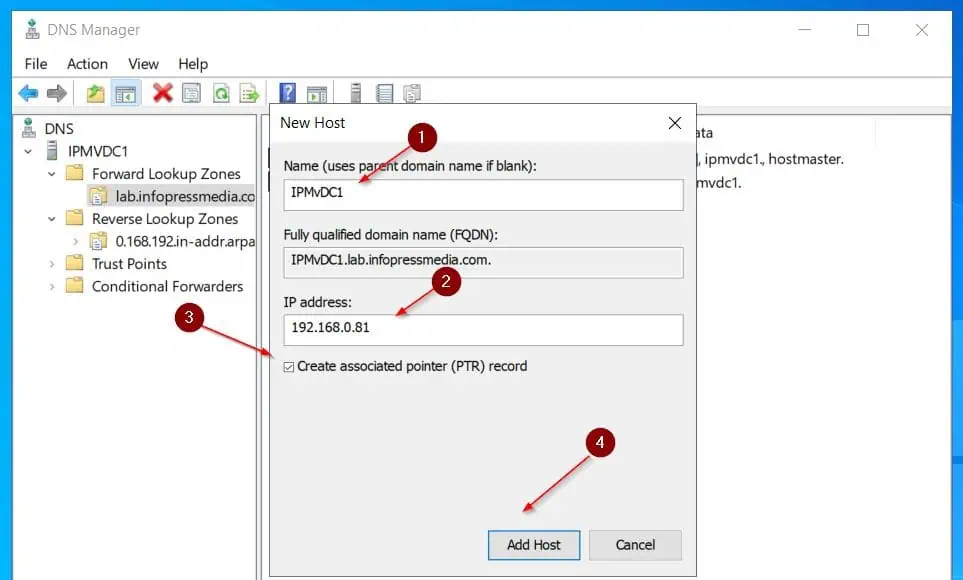
- Then, enter the name and IP address of the new server – ensure that the Create associate pointer (PTA) record checkbox is checked – then, click Add Host.

Step 3.6: Configure the Server’s DNS Address
To set the server to use its IP address, open PowerShell as administrator and run this command.
Get-NetAdapter | Set-DnsClientServerAddress -ServerAddresses 192.168.0.81
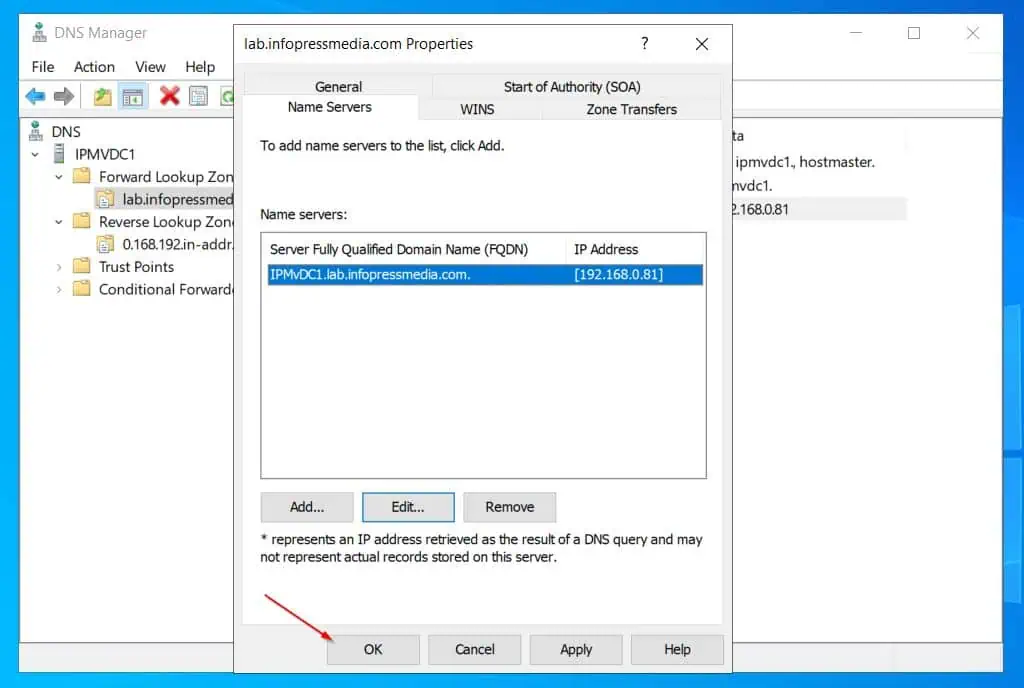
Step 3.7: Configure Name Servers
- Right-click the forward lookup zone and select Properties.
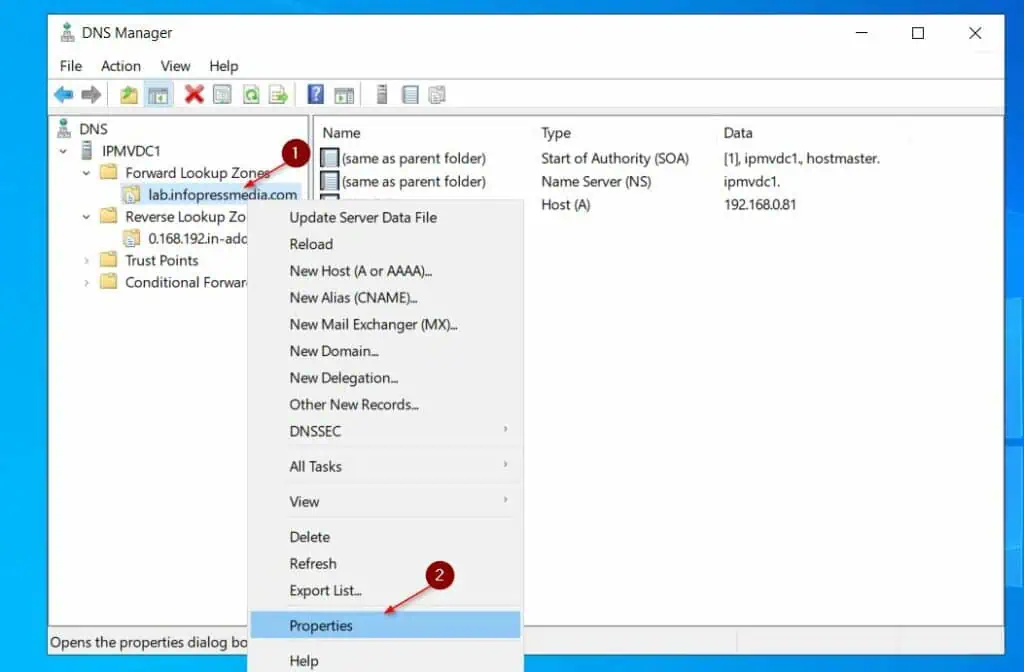

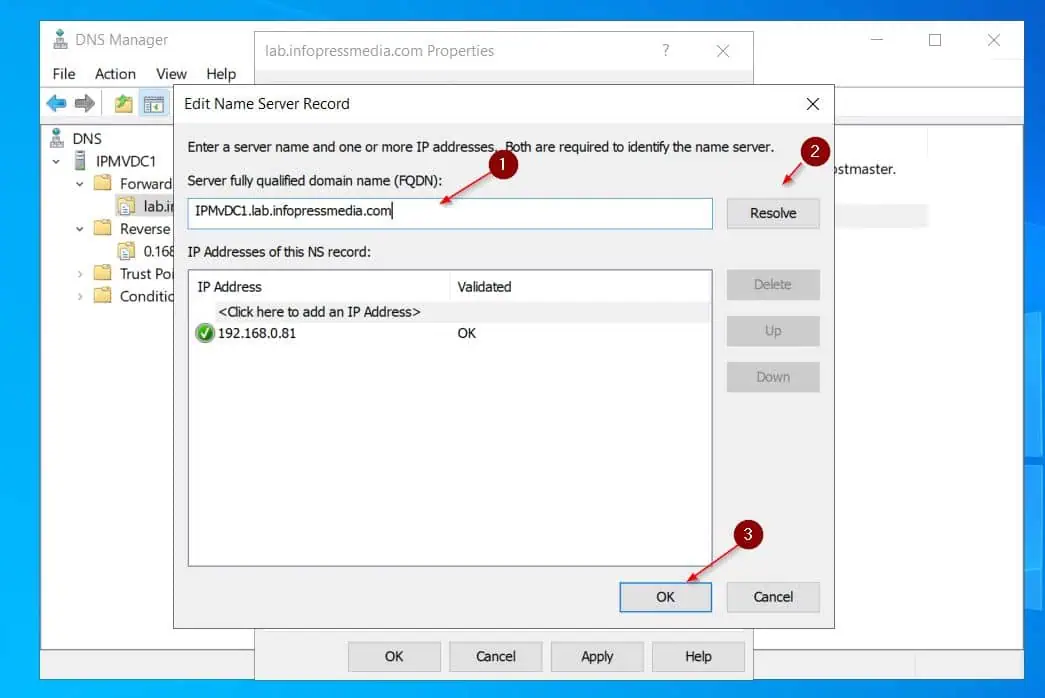
- Click the Name servers tab, the server should be selected, and click Edit. Then, enter the FQDN of the server and click Resolve – the IP address of the server should display – click OK.
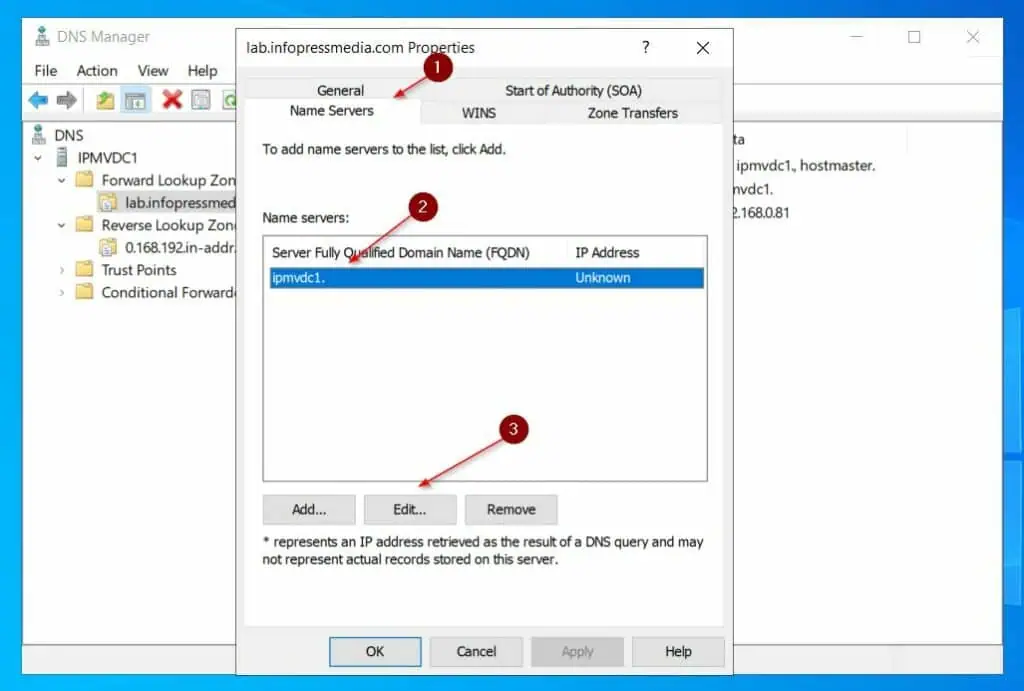


- Click the Start of Authority (SOA) tab, then use the Browse button to select the server’s name.
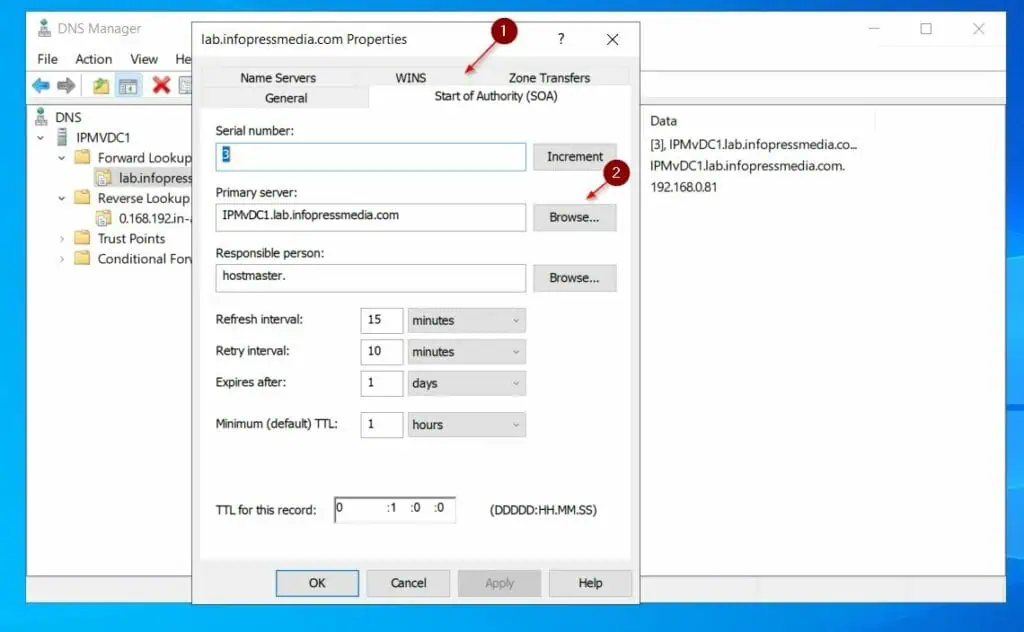

- Finally, click OK to save the changes and close the zone’s properties sheet. If prompted to confirm that you want to delete the original record, click Yes.

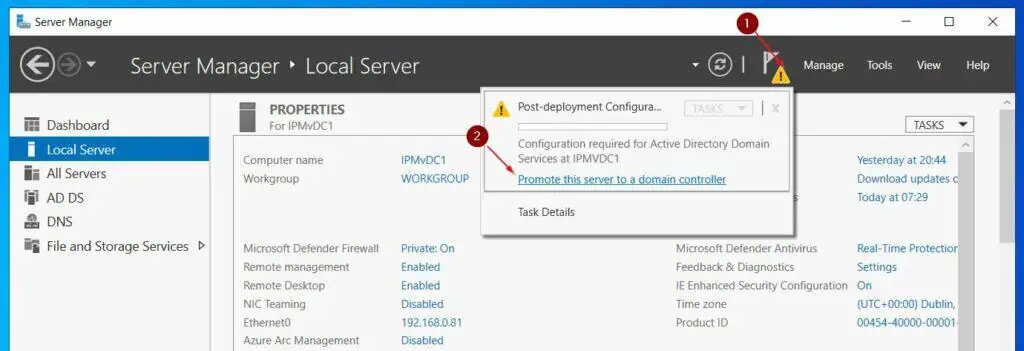
Step 4: Create an Active Directory Domain
- Open Server Manager, then, click the post-installation task icon and select Promote this server to a domain controller.

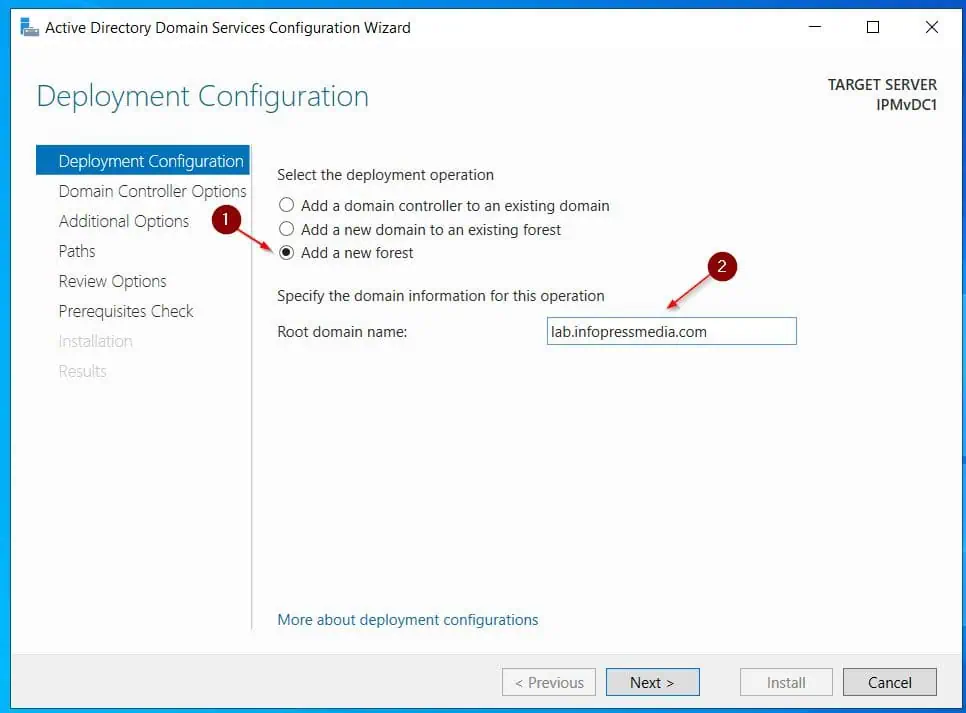
- Then, first page of the wizard, select the Add a new forest option and enter the Forest root domain – the domain name you want to configure. After that, click Next to load the next page.

- Enter the password of the domain’s administrator account.
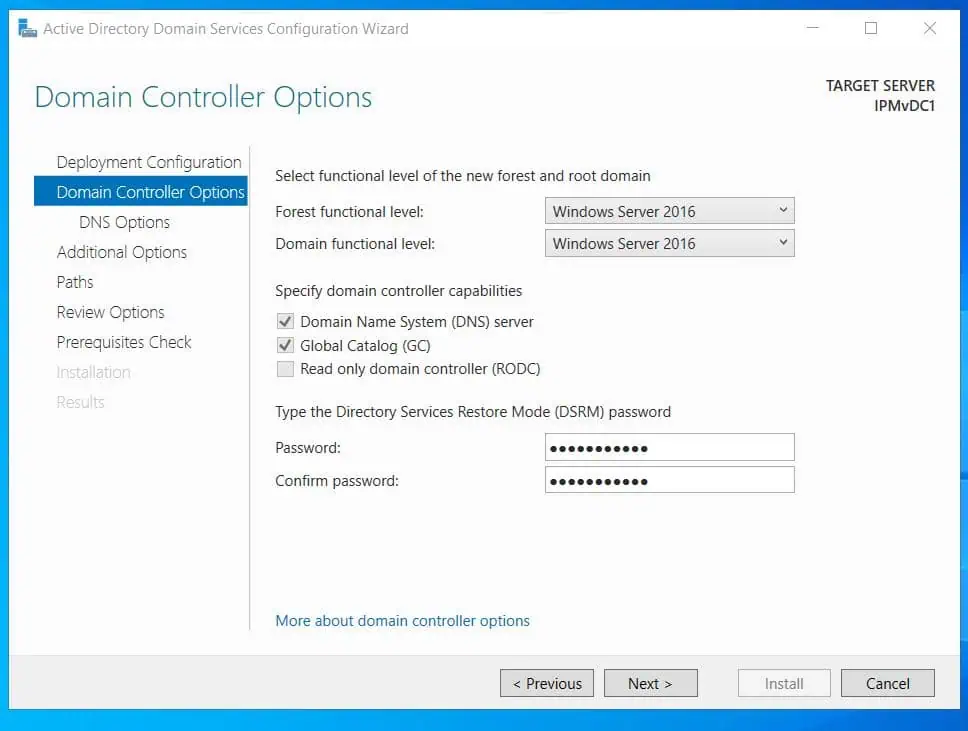

- On the DNS Options page, ignore the zone delegation warning and click Next. On the Additional Options page, the NetBIOS name will be selected automatically.


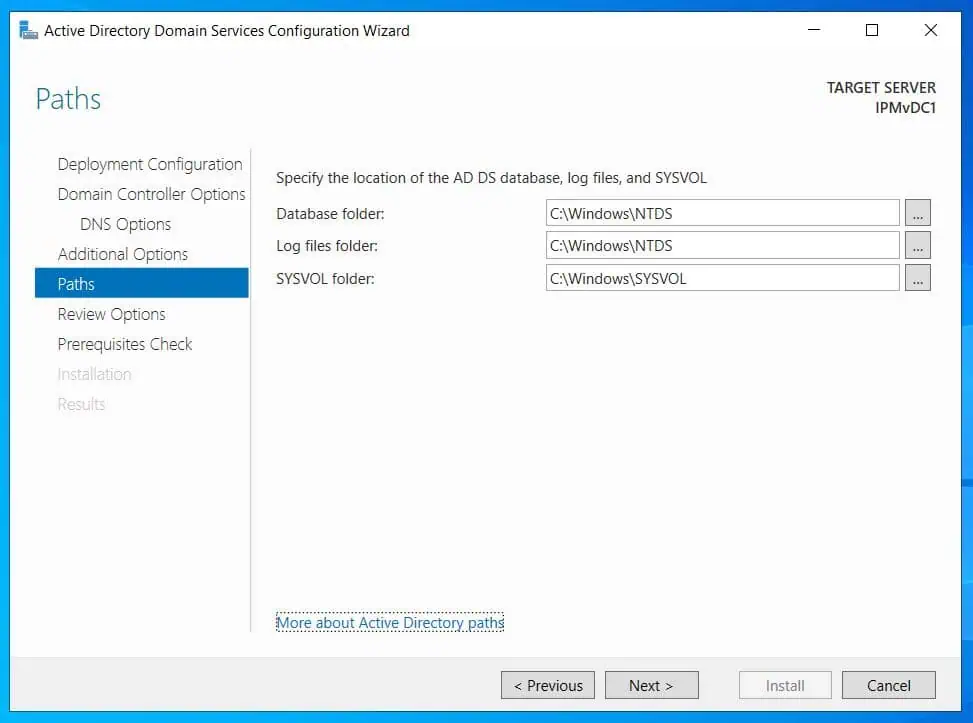
- Accept the default paths for the Database, Log files, and SYSVOL folders.

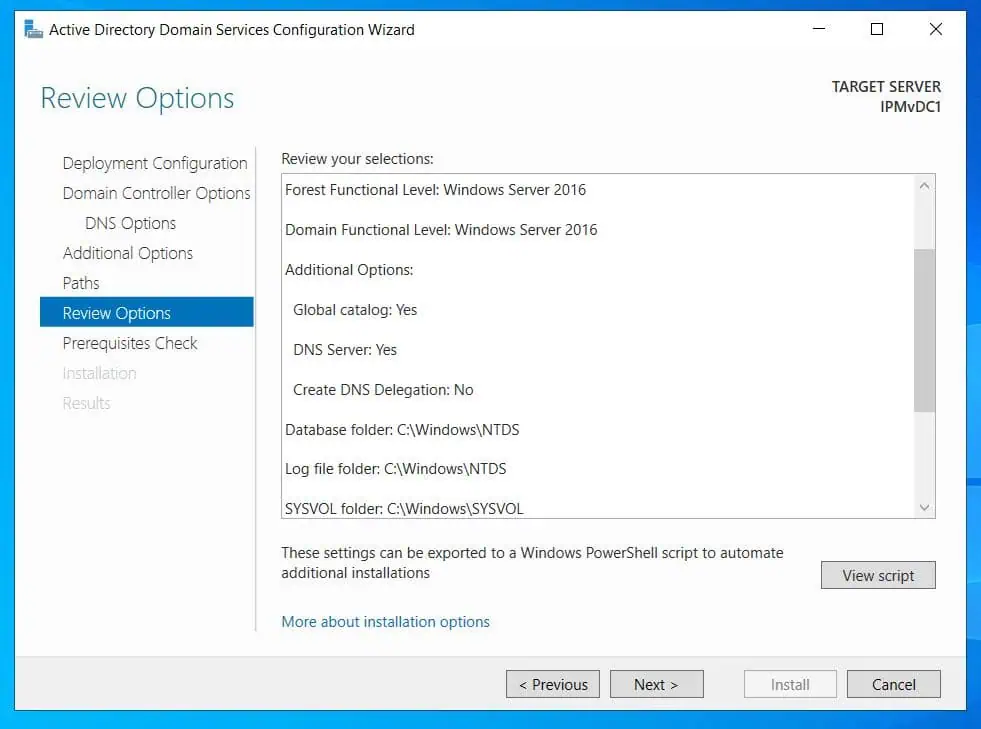
- Review your selections and click Next – the wizard will run pre-promotion checks. If all prerequisite checks pass, click Install and wait for the server to be promoted to a DC.

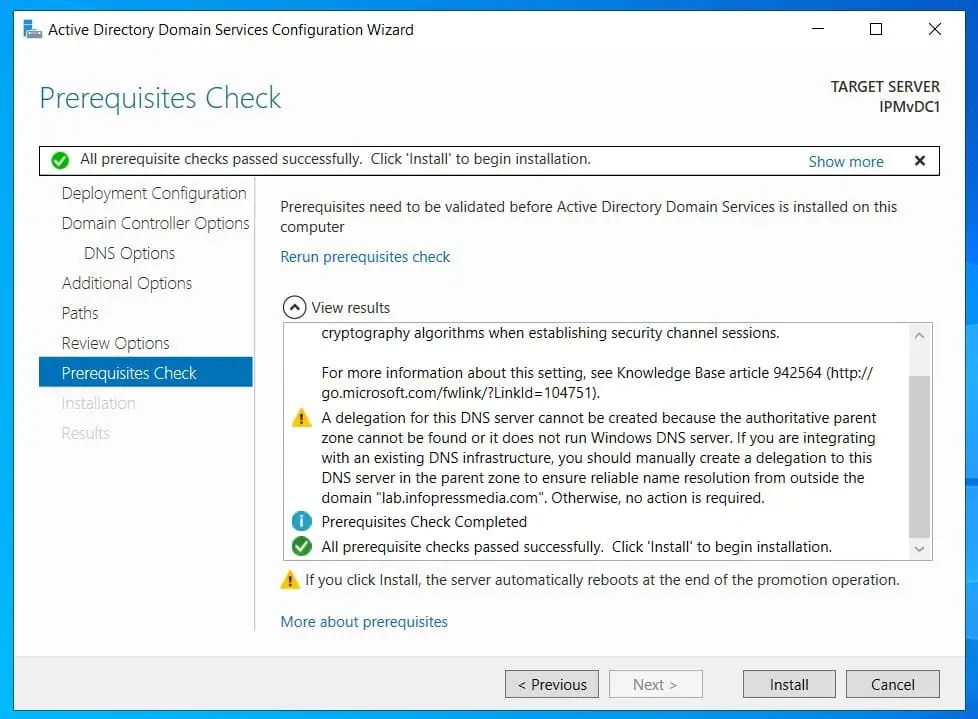

Step 5: Reconfigure the DNS Zone
After deploying Ad, you must reconfigure the DNS zone type to an Active Directory-integrated zone, and perform some other configurations.
Follow the steps below to complete these tasks.
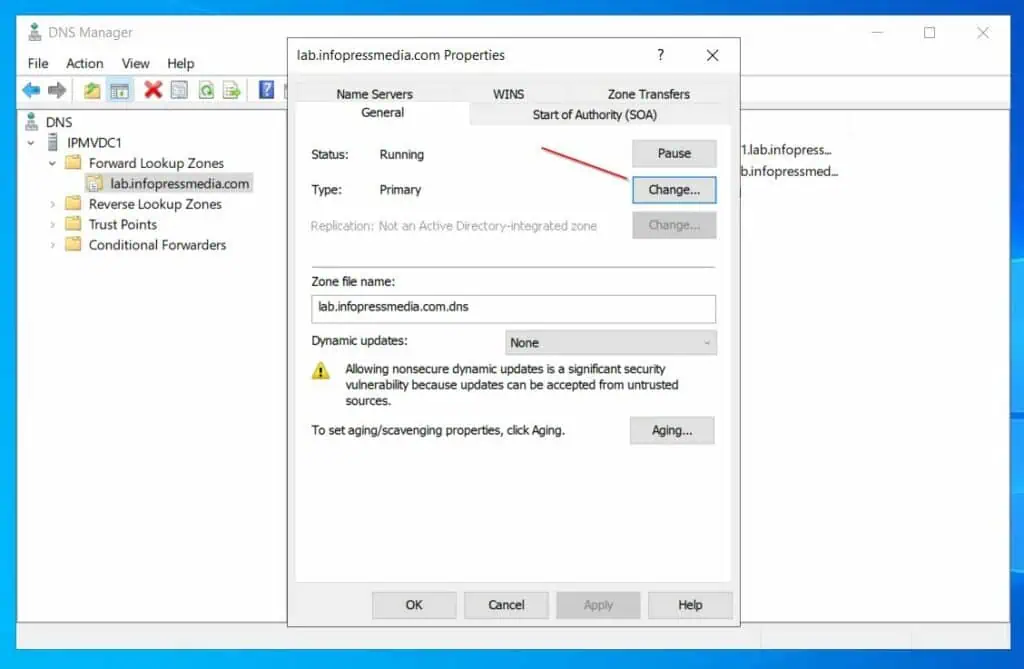
- Open the DNS manager, then right-click the forward lookup zone you created earlier and select Properties.
- On the General tab, click the Change button, next to the zone Type.

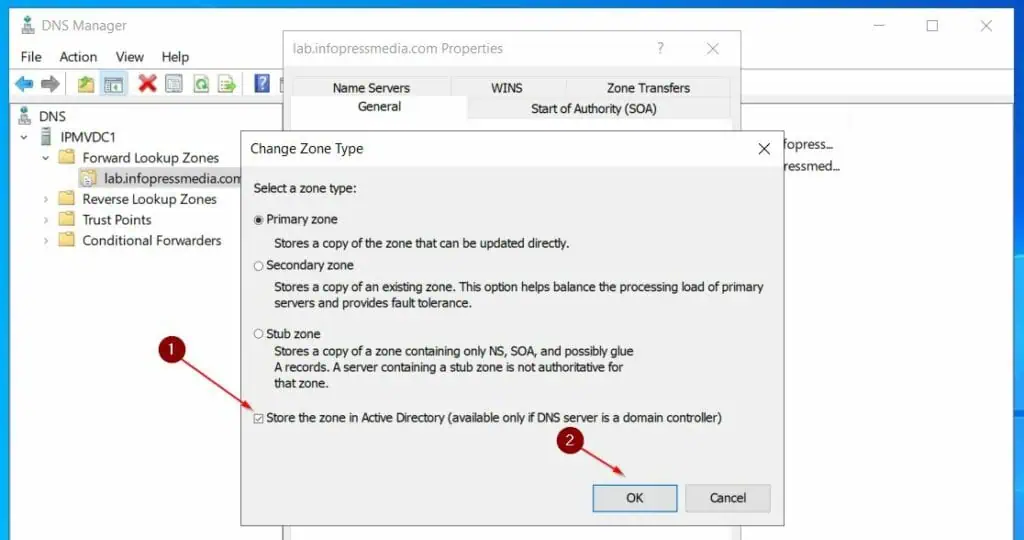
- Then, on the Zone Type pop-up, check the “Store the zone in Active Directory” checkbox and click OK. Click Yes to confirm the action.

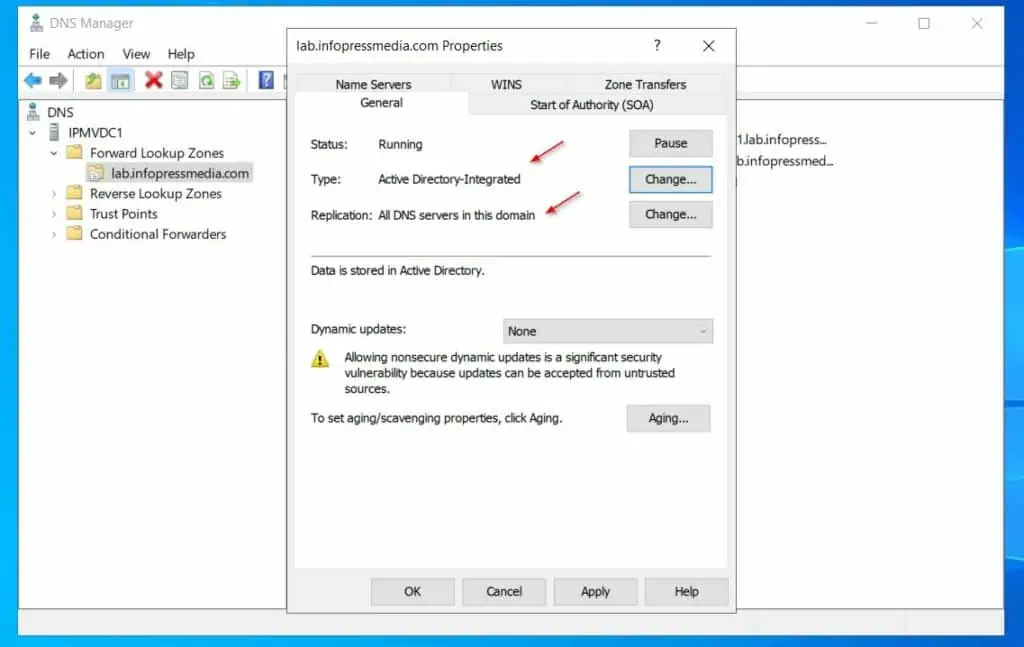
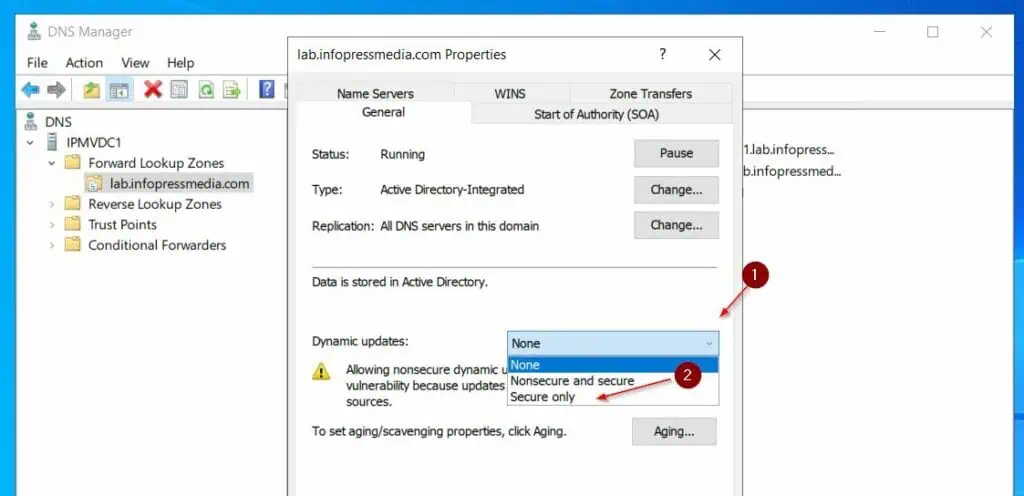
The zone type will now become Active Directory-integrated and Replication will be set to All DNS servers in the domain.

The final step is to configure the zone to allow only Secure Dynamic updates. To change the settings, click the Dynamic updates drop-down and choose Secure only.
Finally, to save your changes and close the zone’s properties sheet, click OK.

Repeat the steps in this section for the Reverse Lookup zone.
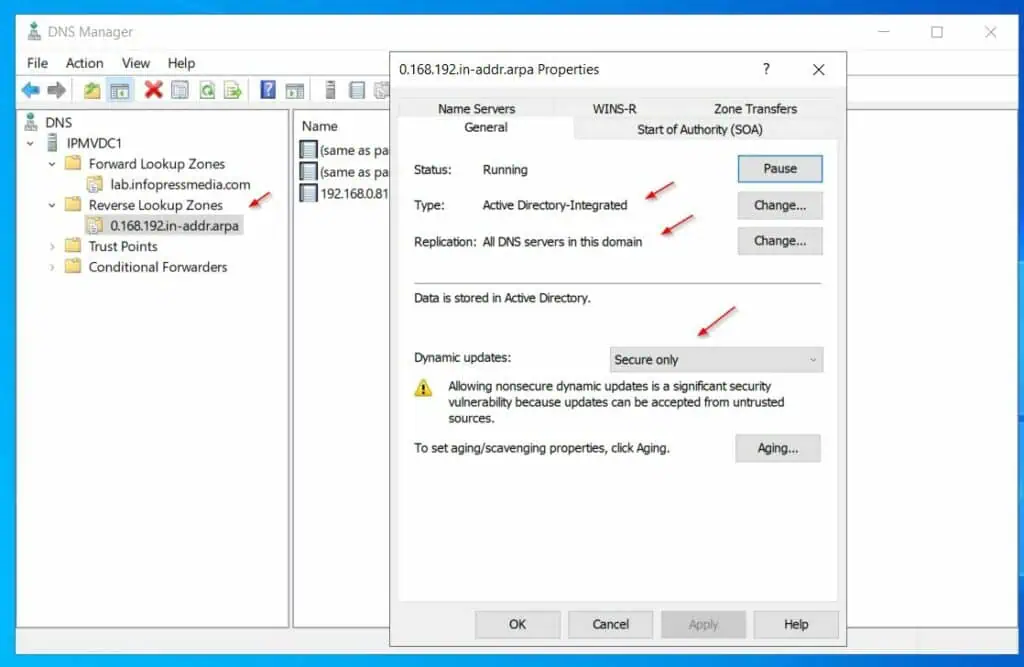

The steps in this section changed the DNS zone type from Primary to Active Directory-integrated. Secondly, the zone is set to replicate to all DNS servers in the domain – which is the default and recommended configuration for AD-integrated zones.
Finally, we set up the zone to allow only Secure Dynamic updates. This allows domain-joined computers to update their IP addresses in the DNS zone – it is the recommended setting for Active Directory-integrated DNS zones.
Step 6: Add the Domain to the DNS Zone
For computers on the network to be able to join the domain, you must add it as a record on the DNS zone. To do this:
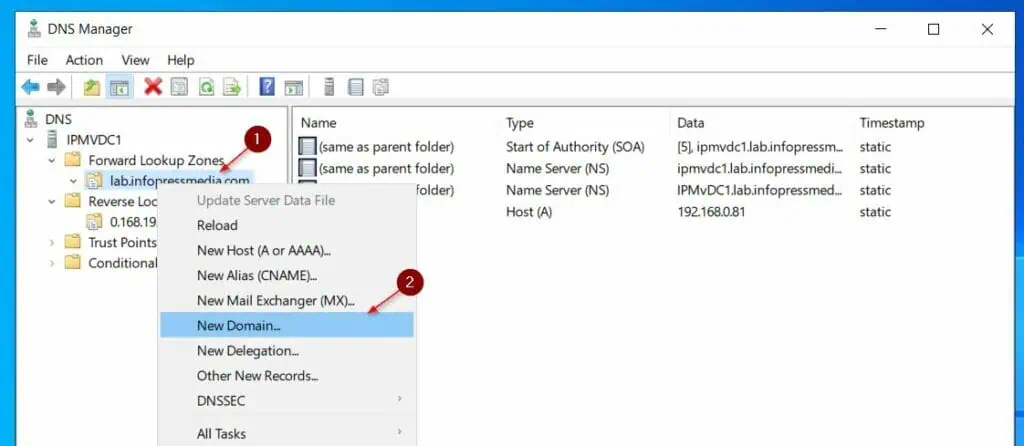
- Right-click the zone and choose New Domain.

- Then, enter the FQDN of the domain and click OK.
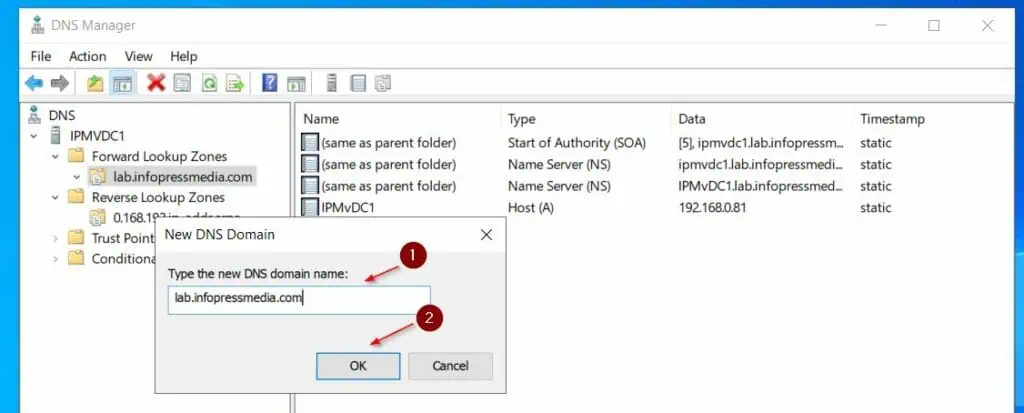

After adding the Domain to the DNS zone, when you refresh the zone, additional records like – _msdcs, _sites, _tcp, etc – would have been added.
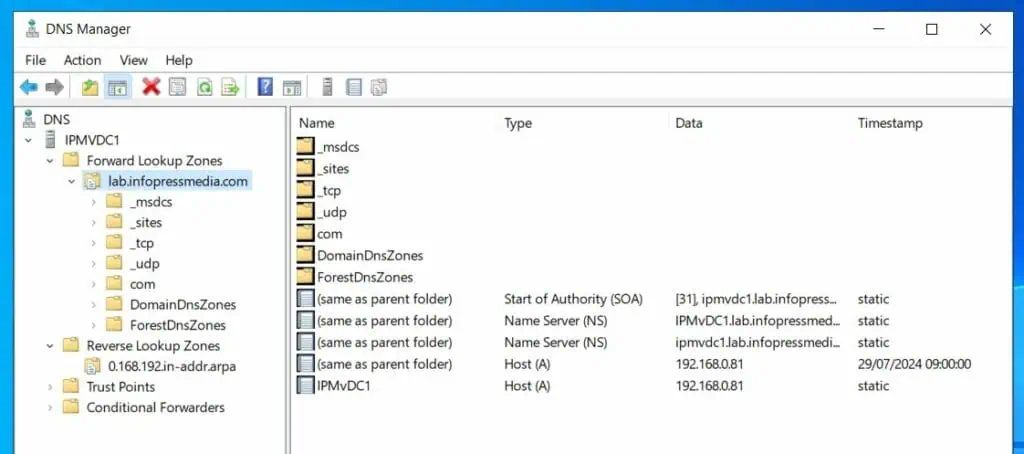

Step 7: Join Computers to the Domain
Before joining a computer to your new domain, you must change the DNS server to the DC’s IP address.
To join a computer to the domain:
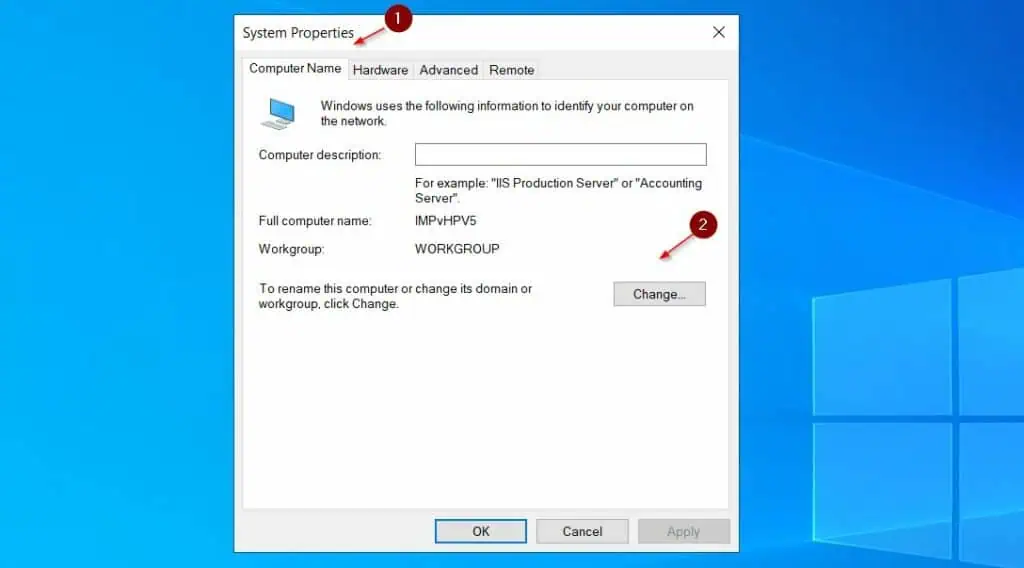
- Search advanced system settings and open it from the search results
- Then, click the Computer Name tab and then, the Change button.

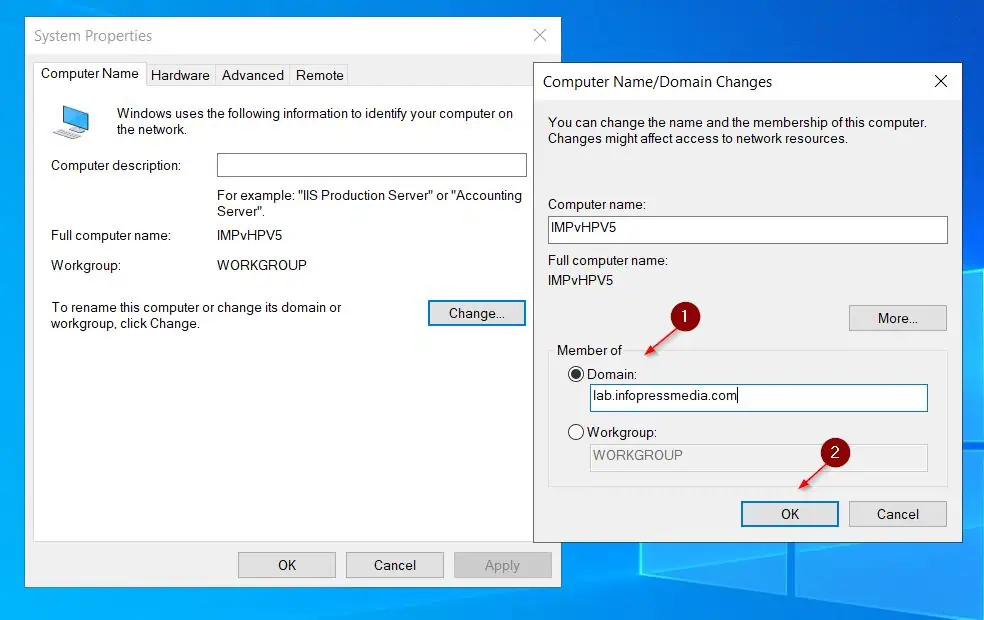
- Then, choose the Domain option, enter the FQDN of the domain, and click OK.

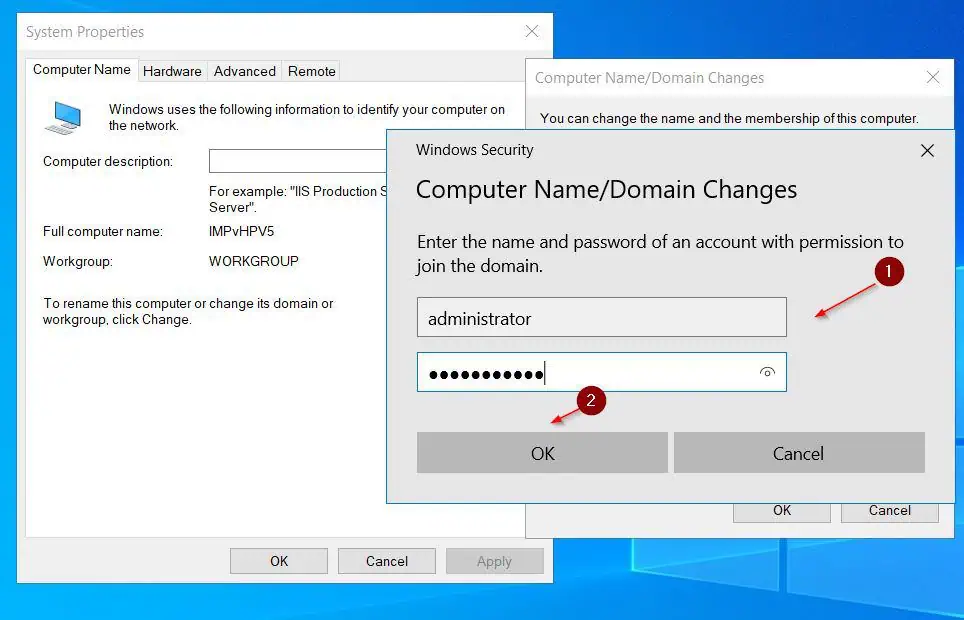
- Finally, enter the username and password for an account with the permission to add computers to the domain and click OK.
After a few seconds, you should receive a “welcome to

Conclusion
Setting up a new Active Directory domain is pretty simple. However, it requires going through specific steps which includes proper DNS configuration.
In this guide, I explained the steps you need to deploy the first Domain Controller in an AD Forest, thereby creating a new Active Directory Domain.
I’m confident that you found this guicde helpful but I will still want to hear from you. Let me know your thoughts by responding to the “Was this page helpful?” feedback request below.
[ad_2]
Victor Ashiedu
Source link
