In part 6 of my hands-on guide for migrating VMware to Hyper-V/SCVMM, you will perform further VMM configurations.
Regarding migrating VMware VMs to Hyper-V, the tasks in this part of the guide are not compulsory. However, they’re necessary to prepare your VMM/Hyper-V environment for deploying and managing new VMs.
Task 1: Import ISO Images to SCVMM Library
In this task, I will show you how to import an ISO image to the VMM library share.
- Select the library server share you want to upload the ISO image. Then, on the top menu, click Import Physical Resource.

- When the Import Library Resource menu opens, click Add Resource, navigate to the location of the ISO file, select it, and click Open.
If the ISO file is located on a network share, navigate to the share via \ServerNameSharename


- To specify where to save the ISO image resource on the Library server share, click Browse. Then, on the Select Destination Folder pop-up, expand the Library share and select ISO Images.
If the VMM library or its folders are not expanded, double-clicking expands a resource.




- Finally, review the ISO image file you’re importing, check the folder you selected to store it and if all looks good, click Import. VMM will open the import job where you can monitor the progress and review any errors.
I have structured this hands-on guide to ensure that – if you followed all the steps – all required permissions would have been set before this task. If the necessary permissions are not set, importing a resource may throw access denied errors.




Once the ISO image file has been imported, you can attach it to VMs.
The VMM Library share subfolders will not show up in VMM until you import content into them.
Task 2: Create a Network Site for the VM Network
In part 8 of this guide, we will create and configure network sites. However, to assign a VLAN ID to the VM template (Task 5 later in this guide), we need to create a network site for the VM network (the management Hyper-V switch).
Follow the steps below to create the network site:
- From the Fabric menu, select the Logical Networks node under Networking. After that, right-click the Logical Network and choose Properties.


- On the virtual network’s Properties sheet, select the Network Site tab, then click Add and choose Network Site.


The network site name is auto-created. If you compare the auto-created network name with column 2 of Table 7.1, it is the same. VMM creates the Network name by appending “_0” to the end of the switch’s name.
- Assign the Network Site to the Hyper-V Host Group by checking it. Then, click the Insert button to associate VLANs and IP subnets to the Network Site.


When you click the Insert button, two columns will be inserted – VLAN and IP Subnet.
- To assign the Network site to a VLAN, click the VLAN column and enter the VLAN ID. Similarly, to define the site’s IP Subnet, click the IP Subnet column and enter the value.
If you use a VLAN ID, you MUST specify it for the network site. Otherwise, when you create a hardware profile and VM (later in this guide), you will not be able to specify a VLAN ID. I added the VLAN ID of 10 for demonstration purposes. Since I do not use VLANs in my lab, I will delete it later.


Task 3: Create a VMM Hardware Profile
VMM offers profiles that allow you to preconfigure settings to deploy different workloads. See my screenshots below for the various profiles you can create in VMM.
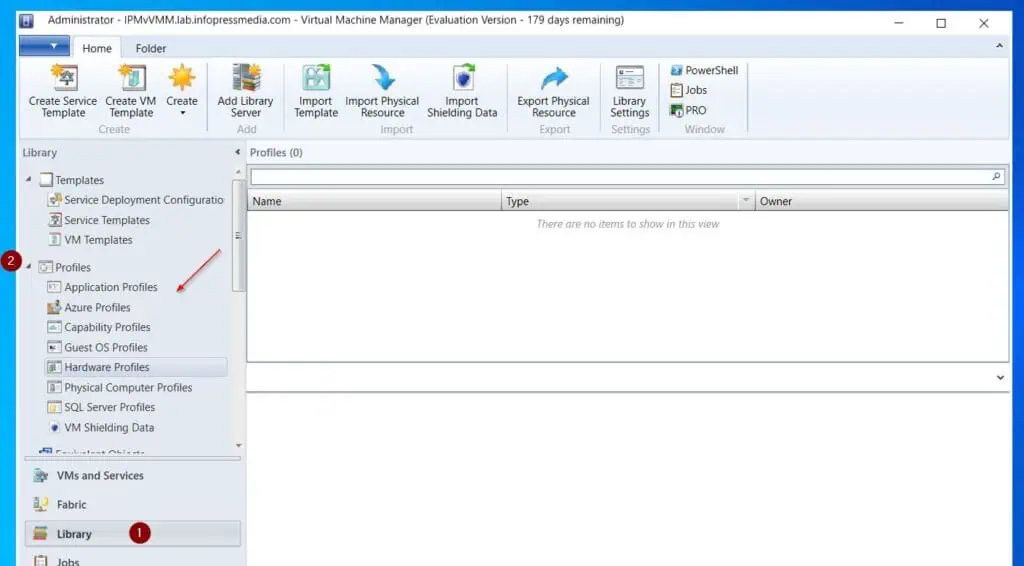

- To create a Hardware profile, select the Library menu, expand Profiles, then right-click Hardware Profiles and click Create Hardware Profile.


- Then, on the General tab, name the hardware profile, give it an optional description, and select the Hyper-V VM Generation the profile supports.
When you finish with the General tab, click the Hardware Profile tab.


In the Hardware profile settings tab, configure the baseline settings for the VMs to be created with this profile. My main focus in this section is the processor compatibility mode for VMs.
- To configure processor compatibility for the hardware profile, click the Processor tab and check the Allow migration to a virtual machine host with a different processor version checkbox.
Enabling processor compatibility mode in your hardware profile ensures that all new VMs you create using this profile have this feature enabled. If Processor compatibility mode is not enabled in a VM, Live Migration from a host with a higher processor model to one with a lower version will not be possible.


- Click the Availability submenu and check Make this virtual machine highly available.
If you do not enable this option, you cannot create VMs using the CSV volume. Also, when you try cloning a VM, it will throw the error message – “the host does not have access to sufficient storage of the requested storage classification.” – This is because the new VM creation wizard will not display the Cluster Shared Volume as it is a Highly Available resource.


- Click the Network adapter and choose Connected to a VM network. Then, use the Browse button to select the VM network (Mgt-vSwitch).


- You can also configure other settings of the hardware profile, such as the memory size and assigning an ISO image. When you finish, click OK to save your changes.
When you mount an ISO file from the library you created earlier, check the Share the files checkbox instead of copying it checkbox. If you do not check this option, every time you create a VM, the ISO file is copied to the VM’s folder.


Task 4: Copy VHD Files to the Cluster Library
When you installed SCVMM, a local library was created. In the process, VMM creates 2 blank VHD and 2 VHDX files. In this task, you will import those virtual disks to the Clustered VMM Library.
The local VHD files are located in “C:ProgramDataVirtual Machine Manager Library FilesVHDs.” Copy all files in this location to “lab-vmm-libVMMLibraryVHDs.”
After copying the files, refresh the clustered library share in the VMM console.


Task 5: Create a VMM VM Template
In this task, you will clone an existing Windows VM, and then perform some tasks to prepare it for use as a VM template.
Task 5.1: Prepare a Template VM
In this task, you will create a new VM for your template, install OS, Windows Update, and apps, and then shut it down. Follow the steps below to prepare a new template VM.
- Click the VM and Services node, right-click the cluster, and choose Create Virtual Machine.


- Then, on the first page of the wizard, choose the Create the new virtual machine with a blank virtual hard disk option.


- Give the new VM a name, enter a descripotion and select the VM generation.


- Select the hardware profile you created earlier. You can edit it if you wish to.
If you did not attach an ISO file to the hardware profile, remember to do it now.


- Click on the virtual hard disk and confirm that the type is Dynamic. This is the recommended configuration as it does not take up all the assigned disk space.
Change the disk size from 40 to 60 GB.


- On the next page, the Hyper-V host group should be selected. If not, choose it.


- Then, on the Select Host page, VMM will perform a review of each host and score them. When you choose a host by left-clicking it, VMM displays information about the host, including the current VMs deployed on the host.


- The CSV should be the default path since we already set in in the Hyper-V Settings earlier in this guide. If you have more than one Cluster Shared Volume, use the Browse button to change the VM path to another volume.


- Use the menu my arrow is pointing at in this screenshot to select the VM Network. Additionally, if you use VLAN ID, use the VLAN column to select the VLAN for the VM Network.


- Finally, configure the VM’s automatic actions. Then, on the final page, review the settings, and click Create to deploy the new VM.




The job creating the VM will be displayed.


After creating the VM, install the Operating system, install Windows Update, all apps you want to have in the template, and set time zone, then shut the VM down.
Task 5.2: Convert the VM to a Template
- Right-click the new VM, point to Clone and choose Create VM Template. Then, on the warning pop-up, click Yes.




- On the Identity page, give the template a name and description, then, click Next.


- On the Configure Hardware page, click next to continue. Then, on the Configure Operating System page, choose None – customization not required.


- On the Select Library Server page, choose the Cluster File Server Library Server.
VMM rated the Cluster file server library higher because it is a clustered resource.


- Use the Browse button to choose the VM Templates folder in the Library. Finally, click Create to start converting the VM to a template.




Monitor the progress on the job window. When the template is created, it will be available in the VM Templates folder of the VMM library – see the second screenshot below.


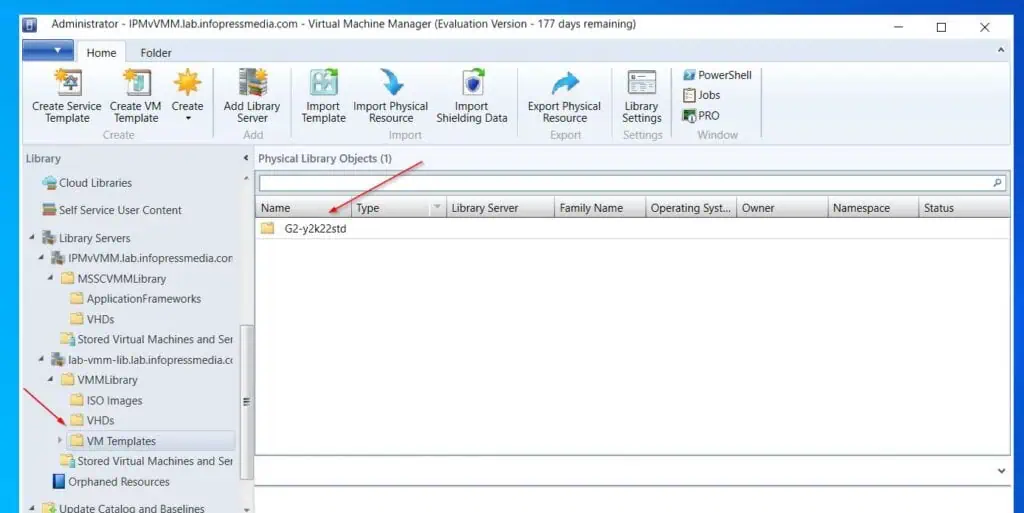

You have completed the essential SCVMM post-installation configurations. In part 7 of this guide, you will plan the networking for your SCVMM.
Victor Ashiedu
Source link
