Home & Garden
Annie Novak’s Best Tips for Beginners on How to Start Birdwatching
[ad_1]
Q: What do you love most about bird watching?
A: Birdwatching focuses my attention on the present moment, both where I am geographically and in time. I deeply appreciate the pause and wonder it adds to any given day. Birds are also tremendously charismatic, both across species and as individuals. I love their good company.
Q: What advice can you give for someone who wants to get started?
A: Birds are everywhere, so the best first step is to head outside (or look out a window) and start to notice them. I was astonished at how much I hadn’t seen just because I wasn’t conscientiously looking. When I started to take birding seriously, I also found serious birders to go out with. Their guidance helped me find better landscapes, test out various binoculars, and identify birds new to me. Many nature centers and conservation organizations offer bird walks, and I’m always pleasantly surprised at how collegial and welcoming those groups can be. The Feminist Bird Club and Birdabilty make birding even more accessible. Apps like EBird, Merlin Bird ID, and Sibley Birds are all fantastic for becoming familiar with the locations, sounds, and visuals of where and how to see birds.
Q: What can I do at home to lure birds?
A: I encourage you to move beyond the birdfeeder: birds need places to shelter, nest and play, too. If you have your own outdoor space, you can recultivate bird habitat. Before your home was there, a historic landscape of plants and insects supported the local and migratory bird populations. Do your research and find out what native plants best support birds near you.
If you are bringing more birds to your yard, you must make your windows bird-safe, too, or you’ll hurt the very birds you’re trying to help. The American Bird Conservancy provides easy resources to do this appropriately: Glass Collisions: Preventing Bird Window Strikes.
Q: Are there specific plants to grow? For example: if you plant it, they will come?
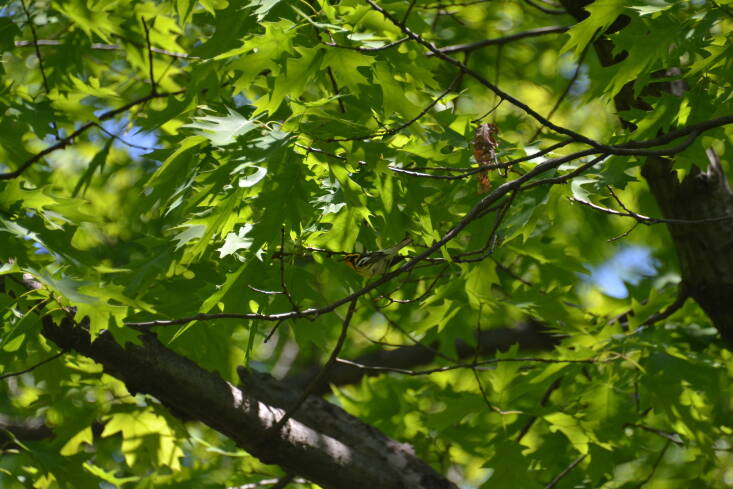

A: Across much of North America, oak trees are a fantastic place to start because of the hundreds of insects they attract—but fruiting trees and shrubs like hollies, junipers, raspberries and blackberries can all help too. The types of plants you choose depend on where you (and your birds!) live, but universally your best first step is to look up native plants to your region and make that your starting place. Pay attention to how they are planted, too—some birds like skulking in big clumps of shrubbery and others prefer open spaces. I learn my best landscaping lessons from taking photos of naturally occurring “birdy” spaces, and mirroring the design in my own yard. [To read more about Annie’s thoughts on native plants and birds, go here.]
Q: What can I do as an individual to protect birds?
Bird populations have plummeted across the Americas, including our most well-known birds, like the American Robin. This is due in no small part to large scale threats like habitat loss, but other contributors include easily addressable issues on the individual scale. The American Bird Conservancy does a fantastic job balancing civic actions like advocating on behalf of birds to your congressperson, and helping you find personal solutions, like deciding to keep your cat indoors. You can learn more about their work and how to participate at abcbirds.org.
See also:
You need to login or register to view and manage your bookmarks.
[ad_2]